|
Gerald Gardner
Gerald Brosseau Gardner (13 June 1884 – 12 February 1964), also known by the craft name Scire, was an English Wiccan, as well as an author and an amateur anthropologist and archaeologist. He was instrumental in bringing the Contemporary Pagan religion of Wicca to public attention, writing some of its definitive religious texts and founding the tradition of Gardnerian Wicca. Born into an upper-middle-class family in Blundellsands, Lancashire, Gardner spent much of his childhood abroad in Madeira. In 1900, he moved to colonial Ceylon, and then in 1911 to Malaya, where he worked as a civil servant, independently developing an interest in the native peoples and writing papers and a book about their magical practices. After his retirement in 1936, he travelled to Cyprus, penning the novel ''A Goddess Arrives'' before returning to England. Settling down near the New Forest, he joined an occult group, the Rosicrucian Order Crotona Fellowship, through which he said he had enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blundellsands, Lancashire
Blundellsands is an area of Crosby in the ceremonial county of Merseyside, England and in the historic county of Lancashire. It is part of the Metropolitan Borough of Sefton, and a Sefton council electoral ward. At the 2001 Census the population was recorded as 11,514. This area was not measured in the 2011 Census. For current figures see Blundellsands (Ward). Description Blundellsands is an area north to the city of Liverpool and to the west of Crosby with Hightown and Little Crosby to the north, Great Crosby and Thornton to the east and Brighton-le-Sands and Waterloo to the south. The area is served by Blundellsands & Crosby and Hall Road railway stations. Its shoreline, the northern part of Crosby Beach, includes parts of the popular exhibit, ''Another Place'', designed by the sculptor Antony Gormley. Several of the Gormley statues are accessible from the Burbo Bank car park. The area is generally considered to be very affluent with many local celebrities, footballer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Forest Coven
The New Forest coven were an alleged group of witches who met around the area of the New Forest in southern England during the early 20th century. According to his own claims, in September 1939, a British occultist named Gerald Gardner was initiated into the coven and subsequently used its beliefs and practices as a basis from which he formed the tradition of Gardnerian Wicca. Gardner described some of his experiences with the coven in his published books ''Witchcraft Today'' (1954) and ''The Meaning of Witchcraft'' (1959) although on the whole revealed little about it, saying he was respecting the privacy of its members. Meanwhile, another occultist, Louis Wilkinson, corroborated Gardner's claims by revealing in an interview with the writer Francis X. King that he too had encountered the coven and expanded on some of the information that Gardner had provided about them. According to Gardner, the faith which they followed was the continuation of the Witch-Cult, a pre-Christian r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecil Williamson
Cecil Williamson (18 September 1909 – 9 December 1999) was a British screenwriter, editor and film director and influential English Neopagan Warlock. He was the founder of both the Witchcraft Research Center which was a part of MI6's war against Nazi Germany, and the Museum of Witchcraft. He was a friend of both Gerald Gardner, who was the founder of Wicca, and also of the notorious occultist Aleister Crowley. Biography Early life Williamson was born in Paignton, Devon.''The Museum of Witchcraft'', page 2 His father was a senior officer in the Royal Navy and was posted abroad. He first encountered witchcraft in 1916, when, on a visit to North Bovey, also in Devon, to visit his uncle, a local vicar, he saw a woman being publicly beaten and accused of being a witch. Williamson tried to defend the woman, and in doing so befriended her. In 1921, whilst at the boarding school Malvern College, Williamson was bullied, but got help from a woman who lived on the school grounds, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor Bone
Eleanor "Ray" Bone (15 December 1911 – 21 September 2001) who also went under the craft name Artemis, was an influential figure in the neopagan religion of Wicca. She claimed to have been initiated in 1941 by a couple of hereditary witches in Cumbria. She later met and became friends with Gerald Gardner, and was initiated into Wicca, becoming the High Priestess in one of his covens. She was a friend of several important figures in Wicca during the modern Witchcraft revival, including " Dafo", Jack Bracelin, Patricia Crowther, Doreen Valiente and Idries Shah. Bone was a close confidant of Gardner's initiator Dafo, and she reported that the New Forest coven was a hereditary coven that followed the old ways of the Hampshire region, and that they traced their origins to the time of the death of King William Rufus in the Norman era.Eleanor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patricia Crowther (Wiccan)
Patricia Crowther (born 14 October 1927) who also goes by the craft name Thelema, is a British occultist considered influential in the early promotion of the Wiccan religion and she is the mother of the witch or wiccan runes. Early life Crowther was born in Sheffield in 1927, then as Patricia Dawson. She was initiated into Witchcraft by fellow well-known Wiccan Gerald Gardner in 1960. (This is incorrect as in fact her handfasting to Arnold was in 1960. This was not the date of her initiation Career Along with like Doreen Valiente Doreen Edith Dominy Valiente (4 January 1922 – 1 September 1999) was an English Wiccan who was responsible for writing much of the early religious liturgy within the tradition of Gardnerian Wicca. An author and poet, she also published five ..., Lois Bourne, and Eleanor Bone, Crowther is considered to be one of the "early mothers" of modern Wicca. Patricia and her then-husband, Arnold Crowther (1909–1974), founded the Sheffield Coven in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lois Bourne
Lois is a common English name from the New Testament. Paul the Apostle mentions Lois, the pious grandmother of Saint Timothy in the Second Epistle to Timothy (commending her for her faith in 2 Timothy 1:5). The name was first used by English Christians after the Protestant Reformation, and it was popular, particularly in North America, during the first half of the 20th century. Notable women * Lois Bryan Adams (1817-1870), American writer, journalist, newspaper editor * Lois McMaster Bujold, author * Lois Capps, congresswoman * Lois Chiles, actress * Lois Collier, actress * Lois Ehlert, writer * Lois Hole, lieutenant governor of Alberta (2000–2005) * Lois Johnson (1942–2014), American country music singer * Lois Kolkhorst, American politician * Lois M. Leveen, author * Lois Lilienstein, singer * Lois Long, writer for The New Yorker * Lois Lowry, author * Lois Maffeo (''Lois''), musician * Lois Maxwell, actress * Lois McCallin, athlete * Lois McConnell, lead singer of Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doreen Valiente
Doreen Edith Dominy Valiente (4 January 1922 – 1 September 1999) was an English Wiccan who was responsible for writing much of the early religious liturgy within the tradition of Gardnerian Wicca. An author and poet, she also published five books dealing with Wicca and related esoteric subjects. Born to a middle-class family in Surrey, Valiente began practising magic while a teenager. Working as a translator at Bletchley Park during the Second World War, she also married twice in this period. Developing her interest in occultism after the war, she began practising ceremonial magic with a friend while living in Bournemouth. Learning of Wicca, in 1953 she was initiated into the Gardnerian tradition by its founder, Gerald Gardner. Soon becoming the High Priestess of Gardner's Bricket Wood coven, she helped him to produce or adapt many important scriptural texts for Wicca, such as ''The Witches Rune'' and the '' Charge of the Goddess'', which were incorporated into the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bricket Wood Coven
The Bricket Wood coven, or Hertfordshire coven Page 289 is a coven of Gardnerian witches founded in the 1940s by Gerald Gardner. It is notable for being the first coven in the Gardnerian line, though having its supposed origins in the pre-Gardnerian New Forest coven. The coven formed after Gardner bought the Fiveacres Country Club, a naturist club in the village of Bricket Wood, Hertfordshire, southern England, and met within the club's grounds. It played a significant part in the history of the neopagan religion of Wicca. Many important and influential figures in Wicca were once members of the coven, including Dafo, Doreen Valiente, Jack Bracelin, Fred Lamond, Dayonis and Lois Bourne. The coven is still active today, though it maintains secrecy and its history was only known up until the 1970s. Chapter 11 and 12 There have been misleading and fraudulent online claims by people claiming to be running (and thus admitting new members to) the Bricket Wood coven. Concern among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Meaning Of Witchcraft
''The Meaning of Witchcraft'' is a non-fiction book written by Gerald Gardner. Gardner, known to many in the modern sense as the "Father of Wicca", based the book around his experiences with the religion of Wicca and the New Forest Coven. It was first published in 1959, only after the British Parliament repealed the Witchcraft Act of 1735, and proved to be Gardner's final book. The Wicca religion as expounded by Gardner was focused on a goddess, identified with the night sky and with wild nature, and a horned god who represented the fertilizing powers of the natural world. It was organized into covens, through which members were initiated through three ascending degrees of competence and authority and which were governed by a high priestess, supported by a high priest. More historical context to the pagan practice of Wicca can be found in the book Wicca: History, Belief, and Community in Modern Pagan Witchcraft That book discusses Wiccan life, covering how and why people convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witchcraft Today
''Witchcraft Today'' is a non-fiction book written by Gerald Gardner. Published in 1954, ''Witchcraft Today'' recounts Gardner's thoughts on the history and the practices of the witch-cult, and his claim to have met practising witches in 1930s England. It also deals with his theory that the Knights Templar had practised the religion, and that the belief in faeries in ancient, mediaeval and early modern Europe is due to a secretive pygmy race that lived alongside other communities. ''Witchcraft Today'' is one of the foundational texts for the religion of Wicca, along with Gardner's second book on the subject, 1959's '' The Meaning of Witchcraft''. Gerald Gardner in the foreword to Witchcraft Today: Whilst by the time of writing, Gardner had been initiated into the religion, and had formed his own coven, he did not state this in the book, instead he "posed as a disinterested anthropologist". page 206 The introduction to the book was written by Margaret Murray, who had widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
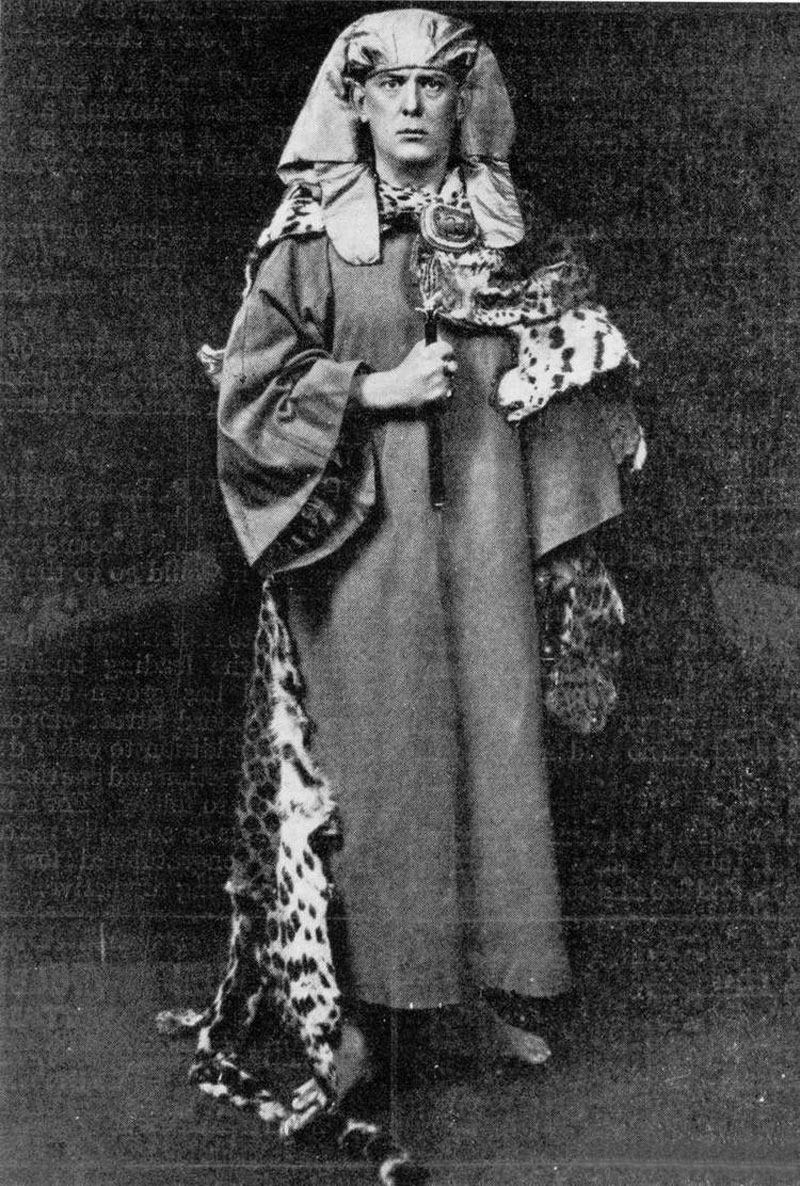
Aleister Crowley
Aleister Crowley (; born Edward Alexander Crowley; 12 October 1875 – 1 December 1947) was an English occultist, ceremonial magician, poet, painter, novelist, and mountaineer. He founded the religion of Thelema, identifying himself as the prophet entrusted with guiding humanity into the Æon of Horus in the early 20th century. A prolific writer, he published widely over the course of his life. Born to a wealthy family in Royal Leamington Spa, Warwickshire, Crowley rejected his parents' fundamentalist Christian Plymouth Brethren faith to pursue an interest in Western esotericism. He was educated at Trinity College at the University of Cambridge, where he focused his attentions on mountaineering and poetry, resulting in several publications. Some biographers allege that here he was recruited into a British intelligence agency, further suggesting that he remained a spy throughout his life. In 1898, he joined the esoteric Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, where he was train ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceremonial Magic
Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of Magic (supernatural), magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an extension of ritual magic, and in most cases synonymous with it. Popularized by the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, it draws on such schools of philosophical and occult thought as Hermetic Qabalah, Enochian magic, Thelema, and the magic of various grimoires. Ceremonial magic is part of Hermeticism and Western esotericism. The synonym magick is a archaic spelling of 'magic' used during the Renaissance, which was revived by Aleister Crowley to show and differentiate the occult from magic (illusion), performance magic. He defined it as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", including "mundane" acts of will as well as ritual magic. Crowley wrote that "it is theoretically possible to cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |