|
Georgios Konstantinos Vouris
Georgios Konstantinos Vouris ( el, Γεώργιος Κωνσταντίνου Βούρης; (1802 - 1860) aka Georg Konstantin Bouris was a Greek astronomer, physicist, mathematician, author, and professor. He was a pioneer in 19th-century Greek astronomy. Vouris lobbied tirelessly to create an astronomical observatory in Athens. He was the first director of the National Observatory of Athens. It was completed in 1846. Greece reconnected with its Astronomical roots. It was the first time since antiquity that a country named Greece played a significant role in Astronomy. He was the first author to publish a university textbook in the field of mathematics since the inception of the new country. He was born in Vienna to Greek parents. He studied astronomy and mathematics with some of the most important scientists of the time namely Andreas von Ettingshausen and Joseph Johann von Littrow. He did significant research in the fields of astrophysics, astronomy, geodesy, meteorology, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonia (region)
Macedonia () is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: larger parts in Greece, North Macedonia North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Socialist Feder ..., and Bulgaria, and smaller parts in Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately and has a population of 4.76 million. Its oldest known settlements date back approximately to 7,000 BC. From the middle of the 4th century BC, the Kingdom of Macedon became the dominant power on the Balkan Peninsula; since then Macedonia has had a diverse history. Etymology Both proper nouns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. It is referred to as one of the solar system's two ice giant planets (the other one being Uranus). Being composed primarily of gases and liquids, it has no well-defined "solid surface". The planet orbits the Sun once every 164.8 julian year (astronomy), years at an average distance of . It is named after the Neptune (mythology), Roman god of the sea and has the astronomical symbol , representing Neptune's trident. Neptune is not visible to the unaided eye and is the only planet in the Solar System found by mathematical prediction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirius
Sirius is the list of brightest stars, brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Ancient Greek language, Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinisation of names, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CMa or α CMa. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, Sirius is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. Sirius is a binary star consisting of a main-sequence star of spectral type A-type main-sequence star, A0 or A1, termed Sirius A, and a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type DA2, termed Sirius B. The distance between the two varies between 8.2 and 31.5 astronomical units as they orbit every 50 years. Sirius appears bright because of its intrinsic luminosity and its proximity to the Solar System. At a distance of , the Sirius system is one of Earth's List of nearest stars, nearest neighbours. Sirius is gradually moving closer to the Solar S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomische Nachrichten
''Astronomische Nachrichten'' (''Astronomical Notes''), one of the first international journals in the field of astronomy, was established in 1821 by the German astronomer Heinrich Christian Schumacher. It claims to be the oldest astronomical journal in the world that is still being published. The publication today specializes in articles on solar physics, extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, geophysics, and instrumentation for these fields. All articles are subject to peer review. Early history The journal was founded in 1821 by Heinrich Christian Schumacher,''Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific'', page 60, v.7 (1895) under the patronage of Christian VIII of Denmark, and quickly became the world's leading professional publication for the field of astronomy. Schumacher edited the journal at the Altona Observatory, then under the administration of Denmark, later part of Prussia, and today part of the German city of Hamburg. Schumacher edited the first 31 issue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meton Of Athens
Meton of Athens ( el, Μέτων ὁ Ἀθηναῖος; ''gen''.: Μέτωνος) was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, geometer, and engineer who lived in Athens in the 5th century BC. He is best known for calculations involving the eponymous 19-year Metonic cycle, which he introduced in 432 BC into the lunisolar Attic calendar. Euphronios says that Colonus was Meton's deme. Work The Metonic calendar incorporates knowledge that 19 solar years and 235 lunar months are very nearly of the same duration. Consequently, a given day of a lunar month will often occur on the same day of the solar year as it did 19 years previously. Meton's observations were made in collaboration with Euctemon, about whom nothing else is known. The Greek astronomer Callippus expanded on the work of Meton, proposing what is now called the Callippic cycle. A Callippic cycle runs for 76 years, or four Metonic cycles. Callippus refined the lunisolar calendar, deducting one day from the fourth Metonic cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Times
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events, and a fundamental quantity of measuring systems. Time or times may also refer to: Temporal measurement * Time in physics, defined by its measurement * Time standard, civil time specification * Horology, study of the measurement of time * Chronometry, science of the measurement of time * Metre (music), the grouping of basic temporal units, called beats, into regular measures ** Time signature, notational convention for the metre Businesses * Time (bicycle company), a French bicycle manufacturer * Time Inc., an American publisher of periodicals * Time Computer Systems, a British brand of Granville Technology Group * TIME Hotels Management, a UAE hotel management company Mathematics and its typography * Times, the operation used for multiplication in mathematics * Times symbol × Computing * Time (metadata), a representation term * time (Unix), a shell command on Unix and Unix-like operating systems * TIME (command), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
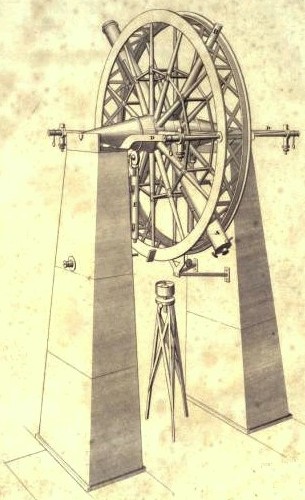
Meridian Circle
The meridian circle is an instrument for timing of the passage of stars across the local meridian, an event known as a culmination, while at the same time measuring their angular distance from the nadir. These are special purpose telescopes mounted so as to allow pointing only in the meridian, the great circle through the north point of the horizon, the north celestial pole, the zenith, the south point of the horizon, the south celestial pole, and the nadir. Meridian telescopes rely on the rotation of the sky to bring objects into their field of view and are mounted on a fixed, horizontal, east–west axis. The similar transit instrument, transit circle, or transit telescope is likewise mounted on a horizontal axis, but the axis need not be fixed in the east–west direction. For instance, a surveyor's theodolite can function as a transit instrument if its telescope is capable of a full revolution about the horizontal axis. Meridian circles are often called by these names, altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Plössl
Simon Plössl (September 19, 1794, Vienna – January 29, 1868, Vienna) was an Austrian optical instrument maker. Initially trained at the Voigtländer company, he set up his own workshop in 1823. His major achievement at the time was the improvement of the achromatic microscope objective. Today he is best known for the eponymous Plössl telescope eyepiece, which follows his 1860 design and has been used extensively by amateur astronomers Amateur astronomy is a hobby where participants enjoy observing or imaging celestial objects in the sky using the unaided eye, binoculars, or telescopes. Even though scientific research may not be their primary goal, some amateur astronomer ... since the 1980s. External links Instruments by Simon Georg Plössl A short biography and some instruments from the Hellenic Archives of Scientific Instruments Optical engineers People from Wieden 1794 births 1868 deaths Austrian scientific instrument makers {{Austria-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refracting Telescope
A refracting telescope (also called a refractor) is a type of optical telescope that uses a lens (optics), lens as its objective (optics), objective to form an image (also referred to a dioptrics, dioptric telescope). The refracting telescope design was originally used in spyglasses and astronomy, astronomical telescopes but is also used for long-focus lens, long-focus camera lenses. Although large refracting telescopes were very popular in the second half of the 19th century, for most research purposes, the refracting telescope has been superseded by the reflecting telescope, which allows larger apertures. A refractor's magnification is calculated by dividing the focal length of the objective lens by that of the eyepiece. Refracting telescopes typically have a lens at the front, then a optical train, long tube, then an eyepiece or instrumentation at the rear, where the telescope view comes to focus. Originally, telescopes had an objective of one element, but a century later, tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophil Hansen
Baron Theophil Edvard von Hansen (; original Danish name: Theophilus Hansen ; 13 July 1813 – 17 February 1891) was a Danish architect who later became an Austrian citizen. He became particularly well known for his buildings and structures in Athens and Vienna, and is considered an outstanding representative of Neoclassicism and Historicism. Biography Hansen was born in Copenhagen. After training with Prussian architect Karl Friedrich Schinkel and some years studying in Vienna, he moved to Athens in 1837, where he studied architecture and design, with a concentration and interest in Byzantine architecture. During his stay in Athens, Hansen designed his first building, the National Observatory of Athens and two of the three contiguous buildings forming the so-called "Athenian Trilogy": the Academy of Athens and the National Library of Greece, the third building of the trilogy being the National and Capodistrian University of Athens, which was designed by his brother Hans Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Schaubert
Gustav Eduard Schaubert ( el, Εδουάρδος Σάουμπερτ, translit=Edouárdos Sáoumpert) 27 July 1804, Breslau, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia – 30 March 1860, Breslau) was a Prussian architect, who made a major contribution to the re-planning of Athens after the Greek War of Independence. Life Urban planner Schaubert studied in Breslau and at the Bauakademie in Berlin, where he was a pupil of Karl Friedrich Schinkel and studied alongside Stamatios Kleanthis. Schaubert and Kleanthis were among the pioneers of nineteenth century urban redevelopment in Greece. After studying in Berlin they began their architectural careers in Athens under Ioannis Kapodistrias, producing a highly detailed topographical plan of Athens' ancient ruins, Byzantine churches and the buildings of the old city in 1831. This plan became the foundation of the building of a modern capital for the new Kingdom of Greece, expanding it in a triangle to the north of the Acropolis of Athens, Acropolis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |