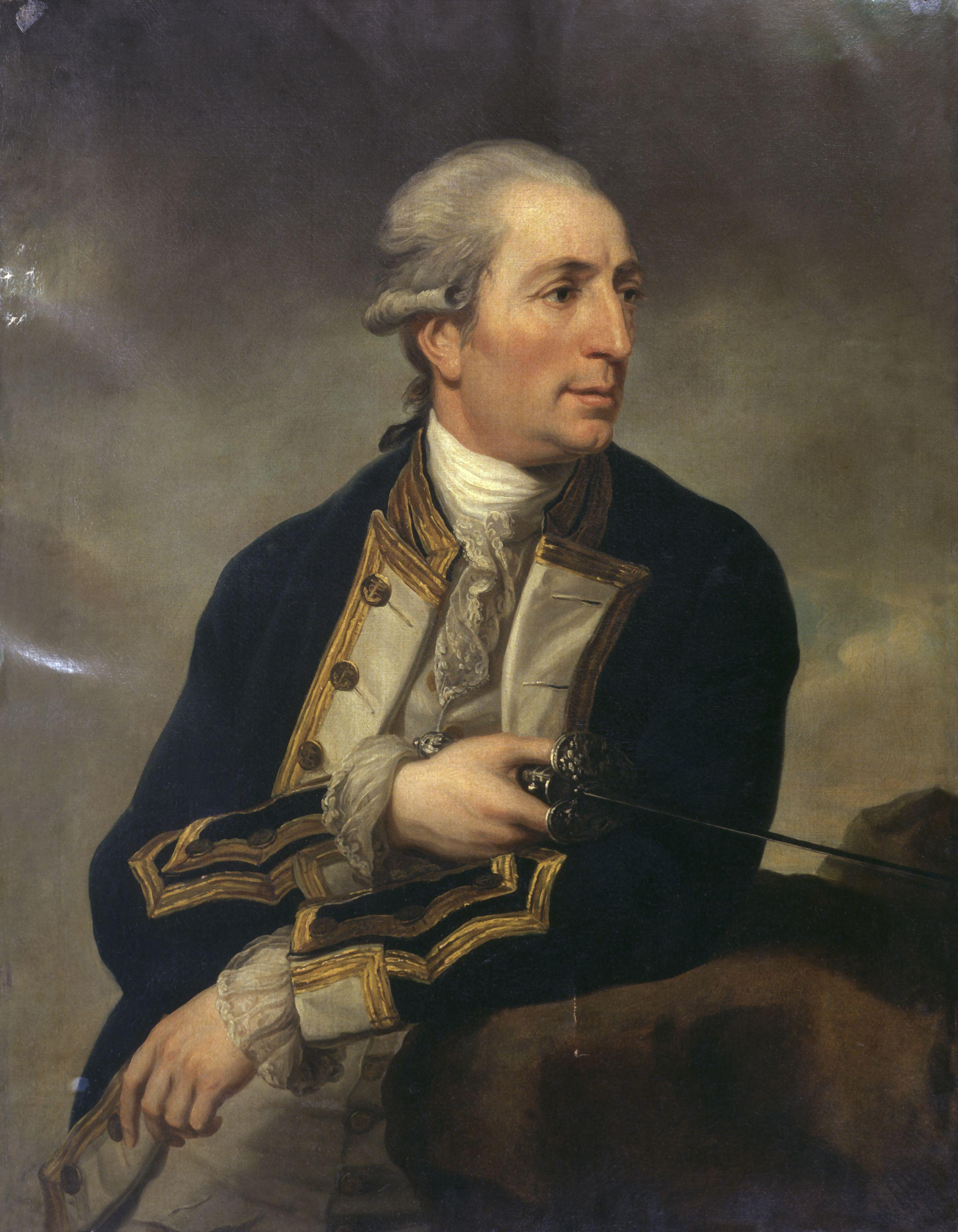
|
George Cumberland
George Cumberland (27 November 1754 – 8 August 1848) was an English art collector, writer and poet. He was a lifelong friend and supporter of William Blake, and like him was an experimental printmaker. He was also an amateur watercolourist, and one of the earliest members of the Bristol School of artists. He made use of his wide circle of connections to help its other members, in particular assisting and influencing Edward Bird and Francis Danby. Early life Cumberland, whose father was also called George, was born in London in 1754. From 1769–85 he was an insurance clerk with the Royal Exchange Assurance Corporation. In 1772 he also attended the Royal Academy Schools and exhibited at the Academy in 1782 and 1783, but failed to be elected an Associate in 1784. He formed a low opinion of the Academy and attacked it in various essays. Along with John Flaxman and Thomas Stothard, Cumberland joined the social circle of William Blake within a year of Blake becoming a stude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. What he called his " prophetic works" were said by 20th-century critic Northrop Frye to form "what is in proportion to its merits the least read body of poetry in the English language". His visual artistry led 21st-century critic Jonathan Jones to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced". In 2002, Blake was placed at number 38 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. While he lived in London his entire life, except for three years spent in Felpham, he produced a diverse and symbolically rich collection of works, which embraced the imagination as "the body of God" or "human existence itself". Although Blake was considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, he is held in high regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intaglio Printing
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface. Normally, copper or in recent times zinc sheets, called plates, are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching, engraving, drypoint, aquatint or mezzotint, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates. After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular prints until the mid 19th century. Process In intaglio printing, the lines to be printed are cut into a metal (e.g. copper) plate by means either of a cutting tool called a burin, held in the hand – in which case the process is called ''engraving''; or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism was born in Rome largely thanks to the writings of Johann Joachim Winckelmann, at the time of the rediscovery of Pompeii and Herculaneum, but its popularity spread all over Europe as a generation of European art students finished their Grand Tour and returned from Italy to their home countries with newly rediscovered Greco-Roman ideals. The main Neoclassical movement coincided with the 18th-century Age of Enlightenment, and continued into the early 19th century, laterally competing with Romanticism. In architecture, the style continued throughout the 19th, 20th and up to the 21st century. European Neoclassicism in the visual arts began c. 1760 in opposition to the then-dominant Rococo style. Rococo architecture emphasizes grace, ornamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egham
Egham ( ) is a university town in the Borough of Runnymede in Surrey, England, approximately west of central London. First settled in the Bronze Age, the town was under the control of Chertsey Abbey for much of the Middle Ages. In 1215, Magna Carta was sealed by King John at Runnymede, to the north of Egham, having been chosen for its proximity to the King’s residence at Windsor. Under the Dissolution of the Monasteries in the early 16th Century, the major, formerly ecclesiastical, manorial freehold interests in the town and various market revenues passed to the Crown. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Egham became a stop on coaching routes between London and many places to the west. The importance of this shrank from the building of the Western and South Western Railways but was for many decades offset by the stark growth in the population of London and the country at large. Egham station was opened in 1856 on the line from Waterloo to Reading and services are ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southampton
Southampton () is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire, South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Portsmouth and the towns of Havant, Waterlooville, Eastleigh, Fareham and Gosport. A major port, and close to the New Forest, it lies at the northernmost point of Southampton Water, at the confluence of the River Test and River Itchen, Hampshire, Itchen, with the River Hamble joining to the south. Southampton is classified as a Medium-Port City . Southampton was the departure point for the and home to 500 of the people who perished on board. The Supermarine Spitfire, Spitfire was built in the city and Southampton has a strong association with the ''Mayflower'', being the departure point before the vessel was forced to return to Plymouth. In the past century, the city was one of Europe's mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Woods Of Hafod-JohnWarwickSmith 1795
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giulio Bonasone
Giulio Bonasone (c. 1498 – after 1574) (or ''Giulio de Antonio Buonasone'' or ''Julio Bonoso'') was an Italian painter and engraver born in Bologna. He possibly studied painting under Lorenzo Sabbatini, and painted a ''Purgatory'' for the church of San Stefano, but all his paintings have been lost. He is better known as an engraver and is believed to have trained with Marcantonio Raimondi. He worked mainly in Mantua, Rome and Venice and with great success, producing etchings and engravings after the old masters and his own designs. He signed his plates ''B., I.B., Julio Bonaso, Julio Bonasone, Juli Bonasonis, Julio Bolognese Bonahso''. He has been regarded an engraver with extraordinary skills in reproducing, as he could accurately convey the sources' compositions, colours, and essence. Moreover, he expressed his understanding about the controversies about religion and culture in his time through his prints. He is considered among the most important and productive engrav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcantonio Raimondi
Marcantonio Raimondi, often called simply Marcantonio (c. 1470/82 – c. 1534), was an Italian engraver, known for being the first important printmaker whose body of work consists largely of prints copying paintings. He is therefore a key figure in the rise of the reproductive print. He also systematized a technique of engraving that became dominant in Italy and elsewhere. His collaboration with Raphael greatly helped his career, and he continued to exploit Raphael's works after the painter's death in 1520, playing a large part in spreading High Renaissance styles across Europe. Much of the biographical information we have comes from his life, the only one of a printmaker, in Vasari's '' Lives of the Artists''. He is attributed with around 300 engravings. After years of great success, his career ran into trouble in the mid-1520s; he was imprisoned for a time in Rome over his role in the series of erotic prints '' I Modi'', and then, according to Vasari, lost all his money in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino, better known as Raphael (; or ; March 28 or April 6, 1483April 6, 1520), was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form, ease of composition, and visual achievement of the Neoplatonic ideal of human grandeur. Together with Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo, he forms the traditional trinity of great masters of that period. His father was court painter to the ruler of the small but highly cultured city of Urbino. He died when Raphael was eleven, and Raphael seems to have played a role in managing the family workshop from this point. He trained in the workshop of Perugino, and was described as a fully trained "master" by 1500. He worked in or for several cities in north Italy until in 1508 he moved to Rome at the invitation of the pope, to work on the Vatican Palace. He was given a series of important commissions there and elsewhere in the city, and began to work as an architect. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Woodforde
Samuel Woodforde (29 March 1763 – 27 July 1817) was a British painter. Life Woodforde was born at Castle Cary, Somerset. He was the second son of Heighes Woodforde, an accountant of Ansford, and his wife Anne. He was a lineal descendant of the painter Samuel Woodford, and nephew of the diarist, James Woodforde. He was supported by the banker Henry Hoare of Stourhead, Wiltshire and his family. On 8 March 1782, he became a student at the Royal Academy Schools and started exhibiting pictures in 1784.Dodgson and Fiske, "Samuel Woodforde". He contributed no less than 133 pictures to the Royal Academy and 39 at the British Institution. Richard Hoare granted Woodforde £100 a year, which allowed him to travel to Italy in 1786. He spent most of his time in Rome, studying the works of Raphael, Michelangelo, and Paolo Veronese. He also visited Venice and Florence before returning to London in 1791. Between 1792 and 1815, "he exhibited constantly, showing portraits, scenes of Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Grignion The Younger
Charles Grignion the Younger (1754–1804) was a British history and portrait painter and engraver. Biography Grignion was born in London London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow .... His uncle was the prolific engraver Charles Grignion the Elder. He died in Livorno after a short illness and was buried there in the Old English Cemetery References External links * 18th-century British painters British male painters 1754 births 1804 deaths Painters from London 18th-century English people 18th-century engravers {{UK-painter-18thC-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Fagan
Robert Fagan ( – 26 August 1816) was a painter, diplomat and archaeologist. Born in London, he spent most of his career in Rome and Sicily. Career The son of Cork immigrants, Fagan was born ca. 1761 in London. He arrived in Rome in 1781. Like other artists in Rome he became involved in dealing in antiquities, and, with the financial backing of some British patrons, carried out several archeological digs. In 1792 he excavated at Vigna San Sebastiano on Via Appia, financed by Corbet Corbet (whose portrait he painted that year). In 1793 the visiting British Prince Augustus Frederick secured permission from the Pope for Fagan to export antiquities. As an archaeologist he was involved in the excavations near Laurentum, which resulted in the discovery of the Venus, now at the Capitoline. As an artist, he made a career out of painting portraits, often for traveling British families. He was married twice, first to Anna Marie Ferri and then to Maria Ludovica Flajani a young Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)





