|
Geophagy And Five Japanese Monkeys
Geophagia (), also known as geophagy (), is the intentional practice of eating earth or soil-like substances such as clay, chalk, or termite mounds. It is a behavioural adaptation that occurs in many non-human animals and has been documented in more than 100 primate species. Geophagy in non-human primates is primarily used for protection from parasites, minerals supplements and helps metabolize toxic compounds from leaves. Geophagy also occurs in humans and is most commonly reported among children and pregnant women. Human geophagia is a form of pica – the craving and purposive consumption of non-food items – and is classified as an eating disorder in the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) if not socially or culturally appropriate. Sometimes geophagy is a consequence of carrying a hookworm infection. Although its etiology remains unknown, geophagy has many potential adaptive health benefits as well as negative consequences. Animals Geophagia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascaris Infection In X-ray Image- Pica, The Practice Of Eating Soil (South Africa) (16424840111)
''Ascaris'' is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the "small intestinal roundworms", which is a type of parasitic worm. One species, ''Ascaris lumbricoides'', affects humans and causes the disease ascariasis. Another species, ''Ascaris suum'', typically infects pigs. ''Parascaris equorum'', the equine roundworm, is also commonly called an "ascarid". Their eggs are deposited in feces and soil. Plants with the eggs on them infect any organism that consumes them. ''A. lumbricoides'' is the largest intestinal roundworm and is the most common helminth infection of humans worldwide. Infestation can cause morbidity by compromising nutritional status, affecting cognitive processes, inducing tissue reactions such as granuloma to larval stages, and by causing intestinal obstruction, which can be fatal. Morphology * Adult: cylindrical shape, creamy white or pinkish in color * Male: average 15–30 cm (6–12 inches); more slender than the female * Female: average 20–35&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Lick
A mineral lick (also known as a salt lick) is a place where animals can go to lick essential mineral nutrients from a deposit of salts and other minerals. Mineral licks can be naturally occurring or artificial (such as blocks of salt that farmers place in pastures for livestock to lick). Natural licks are common, and they provide essential elements such as phosphorus and the biometals (sodium, calcium, iron, zinc, and trace elements) required in the springtime for bone, muscle and other growth in deer and other wildlife, such as moose, elephants, tapirs, cattle, woodchucks, domestic sheep, fox squirrels, mountain goats and porcupines. Such licks are especially important in ecosystems with poor general availability of nutrients. Harsh weather exposes salty mineral deposits that draw animals from miles away for a taste of needed nutrients. It is thought that certain fauna can detect calcium in salt licks. Overview Many animals regularly visit mineral licks to consume clay, suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimalarial
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young children and pregnant women. As of 2018, modern treatments, including for severe malaria, continued to depend on therapies deriving historically from quinine and artesunate, both parenteral (injectable) drugs, expanding from there into the many classes of available modern drugs. Incidence and distribution of the disease ("malaria burden") is expected to remain high, globally, for many years to come; moreover, known antimalarial drugs have repeatedly been observed to elicit resistance in the malaria parasite—including for combination therapies featuring artemisinin, a drug of last resort, where resistance has now been observed in Southeast Asia. As such, the needs for new antimalarial agents and new strategies of treatment (e.g., new combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichilia Rubescens
''Trichilia rubescens'' is a species of plant in the family Meliaceae Meliaceae, the mahogany family, is a flowering plant family of mostly trees and shrubs (and a few herbaceous plants, mangroves) in the order Sapindales. They are characterised by alternate, usually pinnate leaves without stipules, and by syncarp .... It is native from Nigeria to northwest Tanzania. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q15526211 rubescens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaolinite
Kaolinite ( ) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is an important industrial mineral. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina () octahedra. Rocks that are rich in kaolinite are known as kaolin () or china clay. Kaolin is occasionally referred to by the antiquated term lithomarge, from the Ancient Greek ''litho-'' and Latin ''marga'', meaning 'stone of marl'. Presently the name lithomarge can refer to a compacted, massive form of kaolin. The name ''kaolin'' is derived from Gaoling (), a Chinese village near Jingdezhen in southeastern China's Jiangxi Province. The name entered English in 1727 from the French version of the word: , following François Xavier d'Entrecolles's reports on the making of Jingdezhen porcelain. Kaolinite has a low shrink–swell capacity and a low cation-exchange capacity (1–15 meq/100 g). It is a soft, earthy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa: Due to the historical .... The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The southern part of the country includes a substantial portion of Lake Victoria, shared with Kenya and Tanzania. Uganda is in the African Great Lakes region. Uganda also lies within the Nile, Nile basin and has a varied but generally a modified equatorial climate. It has a population of around 49 million, of which 8.5 million live in the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kampala. Uganda is named after the Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a large portion of the south of the country, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibale National Park
Kibale Forest National Park is a national park in western Uganda, protecting moist evergreen rainforest. It is in size and ranges between and in elevation. Despite encompassing primarily moist evergreen forest, it contains a diverse array of landscapes.McGrew, William, ''et al''. ''Great Ape Societies''. Cambridge University Press, 1996. Print. Kibale is one of the last remaining expanses to contain both lowland and montane forests. In eastern Africa, it sustains the last significant expanse of pre-montane forest. The park was gazetted in 1932 and formally established in 1993 to protect a large area of forest previously managed as a logged forest reserve. The park forms a continuous forest with Queen Elizabeth National Park. This adjoining of the parks creates a wildlife corridor. It is an important ecotourism and safari destination, well-known for its population of habituated chimpanzees and twelve other species of primates. It is also the location of the Makerere University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
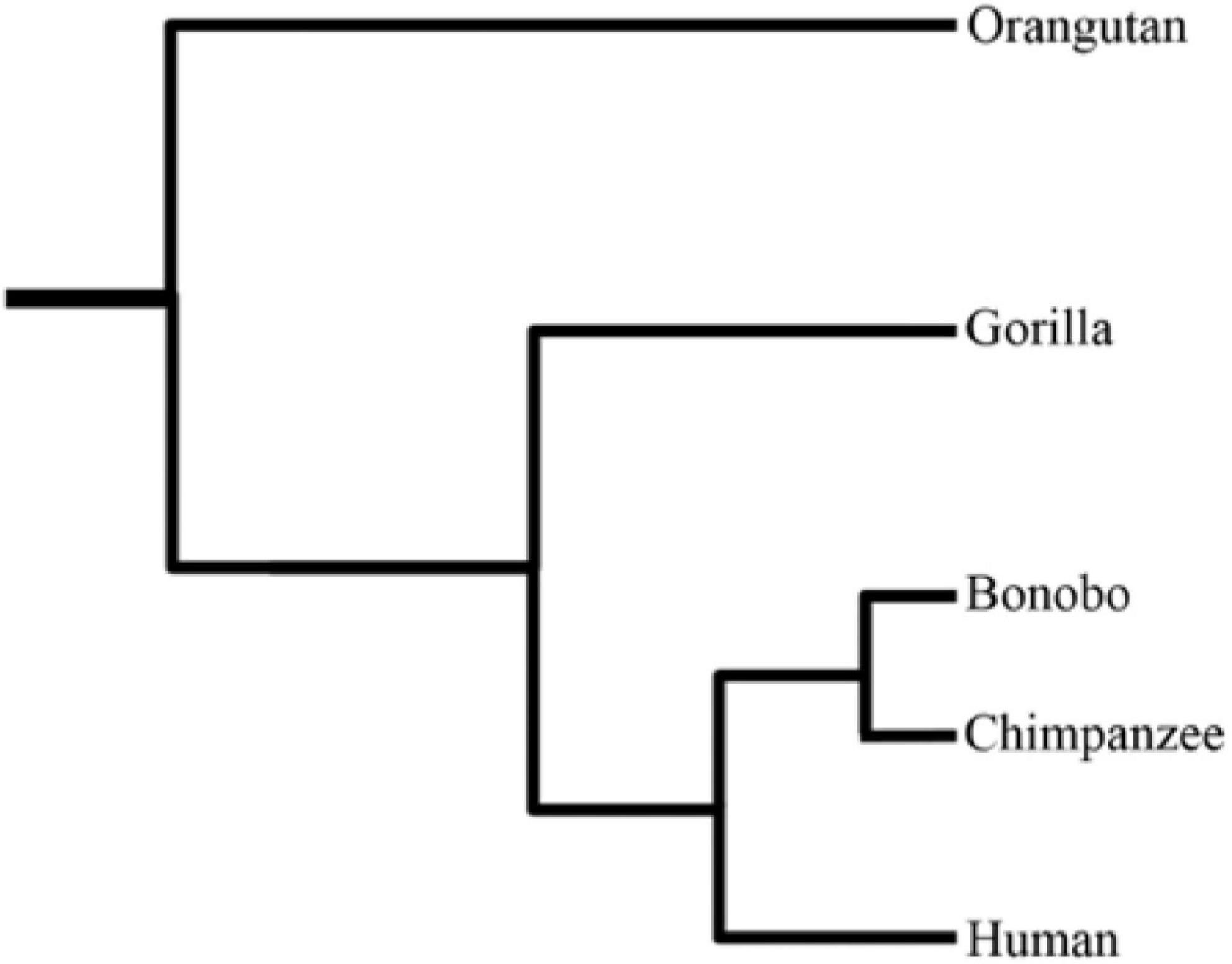
Common Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of Hominidae, great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the bonobo was more commonly known as the pygmy chimpanzee, this species was often called the common chimpanzee or the robust chimpanzee. The chimpanzee and the bonobo are the only species in the genus Pan (genus), ''Pan''. Evidence from fossils and DNA sequencing shows that ''Pan'' is a sister taxon to the Human evolution, human lineage and is humans' closest living relative. The chimpanzee is covered in coarse black hair, but has a bare face, fingers, toes, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. It is larger and more Robustness (morphology), robust than the bonobo, weighing for males and for females and standing . The chimpanzee lives in groups that range in size from 15 to 150 members, although individuals travel and forag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophagy And Five Japanese Monkeys
Geophagia (), also known as geophagy (), is the intentional practice of eating earth or soil-like substances such as clay, chalk, or termite mounds. It is a behavioural adaptation that occurs in many non-human animals and has been documented in more than 100 primate species. Geophagy in non-human primates is primarily used for protection from parasites, minerals supplements and helps metabolize toxic compounds from leaves. Geophagy also occurs in humans and is most commonly reported among children and pregnant women. Human geophagia is a form of pica – the craving and purposive consumption of non-food items – and is classified as an eating disorder in the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) if not socially or culturally appropriate. Sometimes geophagy is a consequence of carrying a hookworm infection. Although its etiology remains unknown, geophagy has many potential adaptive health benefits as well as negative consequences. Animals Geophagia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophagy And Two Japanese Monkeys
Geophagia (), also known as geophagy (), is the intentional practice of eating earth or soil-like substances such as clay, chalk, or termite mounds. It is a behavioural adaptation that occurs in many non-human animals and has been documented in more than 100 primate species. Geophagy in non-human primates is primarily used for protection from parasites, minerals supplements and helps metabolize toxic compounds from leaves. Geophagy also occurs in humans and is most commonly reported among children and pregnant women. Human geophagia is a form of pica – the craving and purposive consumption of non-food items – and is classified as an eating disorder in the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM) if not socially or culturally appropriate. Sometimes geophagy is a consequence of carrying a hookworm infection. Although its etiology remains unknown, geophagy has many potential adaptive health benefits as well as negative consequences. Animals Geophagia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parrots At A Clay Lick -Tambopata National Reserve, Peru-8d
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittacoidea ("true" parrots), the Cacatuoidea (cockatoos), and the Strigopoidea (New Zealand parrots). One-third of all parrot species are threatened by extinction, with higher aggregate extinction risk ( IUCN Red List Index) than any other comparable bird group. Parrots have a generally pantropical distribution with several species inhabiting temperate regions in the Southern Hemisphere, as well. The greatest diversity of parrots is in South America and Australasia. Characteristic features of parrots include a strong, curved bill, an upright stance, strong legs, and clawed zygodactyl feet. Many parrots are vividly coloured, and some are multi-coloured. Most parrots exhibit little or no sexual dimorphism in the visual spectrum. They form the mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(16424840111).jpg)