|
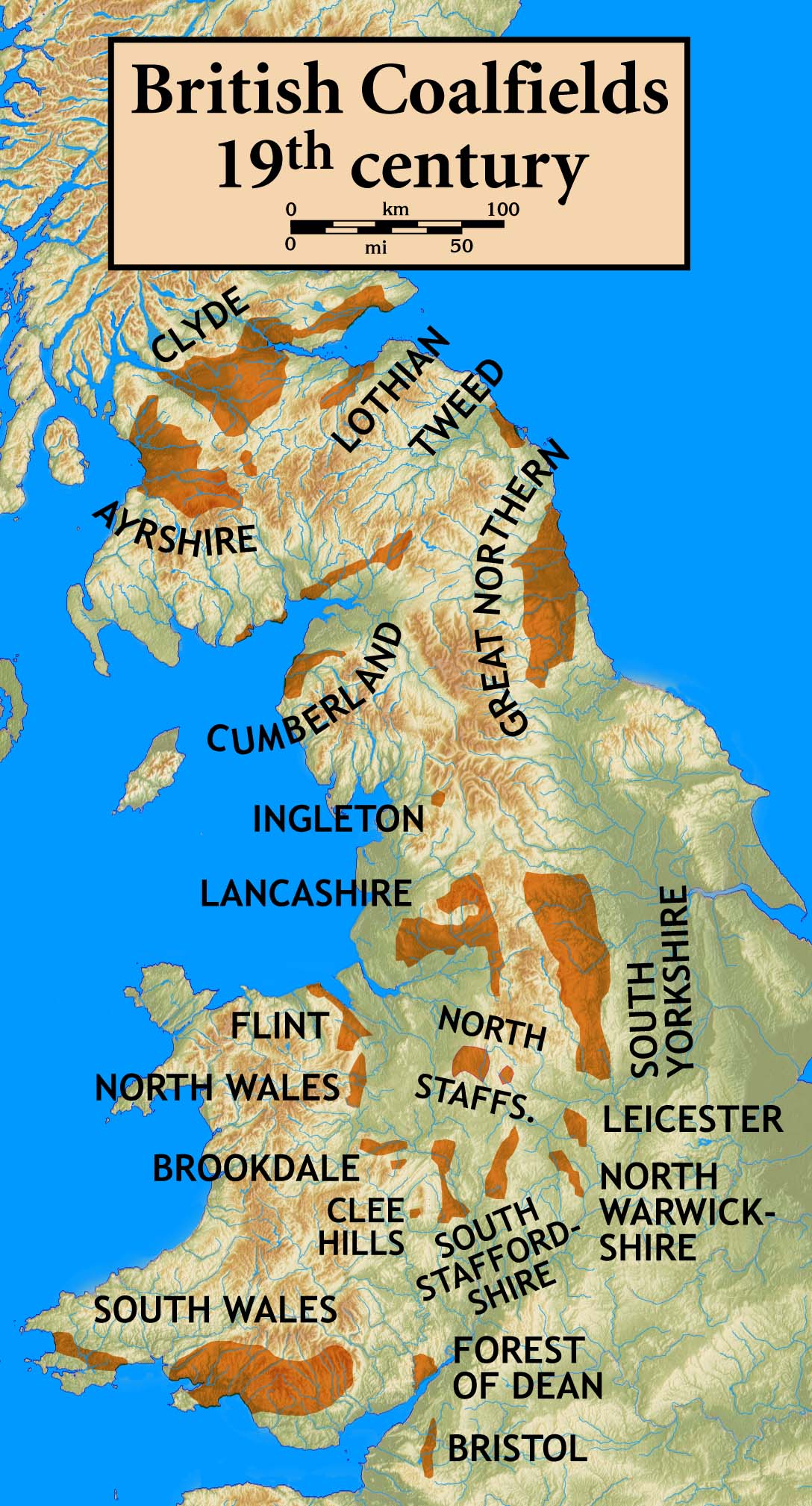
Geology Of Monmouthshire
: ''This article describes the geology of the Monmouthshire (historic), historic county of Monmouthshire. It includes the Monmouthshire, modern administrative county and the Principal areas of Wales, 'principal areas' of Torfaen, Newport, Wales, Newport and Blaenau Gwent together with those parts of Cardiff and Caerphilly (county borough), Caerphilly to the east of the Rhymney River.'' The geology of Monmouthshire in southeast Wales largely consists of a thick series of sedimentary rocks of different types originating in the Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, Triassic and Jurassic periods. The oldest rocks, of Silurian age, occur as a broad, northeast to southwest aligned anticline in the heart of the county. The central portion of this zone, between Usk and Pontypool, comprises the outcrop of the older shales, limestones and sandstones and, surrounded as it is by outcrops of younger rocks, is traditionally referred to as the Usk Inlier. These younger rocks are a mix of sandstones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monmouthshire (historic)
, Status= Historic countyCeremonial county (until 1974)Administrative county (1889–1974) , Start= 1535 , Origin= Laws in Wales Act 1535 , Motto= Faithful to both (Utrique Fidelis) , Image= Flag adopted in 2011 , Map= , HQ= Monmouth and Newport , Replace= Gwent, Mid Glamorgan, South Glamorgan , Arms= ''Coat of arms of Monmouthshire County Council'' , Government= Monmouthshire County Council (1889–1974)Newport County Borough Council (1891–1974)Cardiff County Borough Council (part) (1938–1974) , Code= MON , CodeName= Chapman code , PopulationFirst= 98,130Vision of Britain �1831 Census/ref> , PopulationFirstYear= 1831 , AreaFirst= , AreaFirstYear= 1831 , DensityFirst= 0.3/acre , DensityFirstYear= 1831 , PopulationSecond= 230 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontypool
Pontypool ( cy, Pont-y-pŵl ) is a town and the administrative centre of the county borough of Torfaen, within the historic boundaries of Monmouthshire in South Wales. It has a population of 28,970. Location It is situated on the Afon Lwyd river in the county borough of Torfaen. Located at the eastern edge of the South Wales coalfields, Pontypool grew around industries including iron and steel production, coal mining and the growth of the railways. A rather artistic manufacturing industry which also flourished here alongside heavy industry was Japanning, a type of lacquer ware. Pontypool itself consists of several smaller districts, these include Abersychan, Cwmffrwdoer, Pontnewynydd, Trevethin, Penygarn, Wainfelin, Tranch, Brynwern, Pontymoile, Blaendare, Cwmynyscoy, New Inn, Griffithstown and Sebastopol. History The name of the town in Welsh – ''Pont-y-pŵl'' – originates from a bridge ('pont') associated with a pool in the Afon Lwyd. The Welsh word ''pŵl'' is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llanwern
Llanwern is a community in the eastern part of the City of Newport, South East Wales. Llanwern is bounded by the M4 and Langstone to the north, Ringland, Lliswerry and the River Usk to the west, the River Severn to the south and the city boundary to the east. The population of the Llanwern community in 2011 was 333). which contains Llanwern village and the western half of the site of Llanwern steelworks. The area is governed by the Newport City Council. The community population dropped to 289 in 2011. The community also includes the area of Glan Llyn. Llanwern House Llanwern House was the home of Lord Rhondda of Llanwern, David Alfred Thomas, who was Minister of Food during the First World War. In 1887, a year before his election to Parliament, Thomas took the lease of the house, where he lived the life of a somewhat unconventional country squire, riding to hounds and breeding prize Hereford cattle. He bought the house in 1900 and acquired the neighbouring Pencoed estate sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Measures
In lithostratigraphy, the coal measures are the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. In the United Kingdom, the Coal Measures Group consists of the Upper Coal Measures Formation, the Middle Coal Measures Formation and the Lower Coal Measures Formation. The group records the deposition of fluvio-deltaic sediments which consists mainly of clastic rocks (claystones, shales, siltstones, sandstones, conglomerates) interstratified with the beds of coal. In most places, the coal measures are underlain by coarser clastic sequences known as Millstone Grit, of Namurian age. The top of the coal measures may be marked by an unconformity, the overlying rocks being Permian or later in age. In some parts of Britain, however, the coal measures grade up into mainly coal-barren red beds of late Westphalian and possibly Stephanian age. Within the Pennine Basin these barren measures are now referred to as the Warwickshire Group, from the district where they achieve their thickest d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its electricity. Some iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marros Group
The Marros Group is the name given to a suite of rocks of Namurian age laid down during the Carboniferous Period in South Wales. These rocks were formerly known as the Millstone Grit Series but are now distinguished from the similar but geographically separate rock sequences of the Pennines and Peak District of northern England and northeast Wales by this new name. Stratigraphy The Group comprises a thick unit of coarse sandstone known as the Twrch Sandstone (formerly the ‘Basal Grit’) which is overlain by the Bishopston Mudstone and the Telpyn Point Sandstone. The mudstones of these latter two formations was formerly known as the ‘Middle Shales’, a name reflecting the position of this sequence sandwiched between the Basal Grit below and the Farewell Rock, the lowermost sandstone of the South Wales Coal Measures, above. The mudstone itself contains a few bands of sandstone such as the ‘Twelve Foot Sandstone’ and locally the ‘Cumbriense Sandstone’. Likewise the Twrc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous Limestone
Carboniferous Limestone is a collective term for the succession of limestones occurring widely throughout Great Britain and Ireland that were deposited during the Dinantian Epoch of the Carboniferous Period. These rocks formed between 363 and 325 million years ago. Within England and Wales, the entire limestone succession, which includes subordinate mudstones and some thin sandstones, is known as the Carboniferous Limestone Supergroup. Depositional basins Within Great Britain the suite of rocks known traditionally as the Carboniferous Limestone Series was deposited as marine sediments in three distinct ‘provinces’ separated by contemporary landmasses. One of these landmasses was the Wales-London-Brabant Massif, an east–west aligned belt of land stretching through central Wales and the English Midlands to East Anglia and on into Belgium. The limestones deposited to its south form a distinct South Wales-Mendip province which extends from Pembrokeshire in the west through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (geology)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also extends northwards into Greenland and Svalbard. These areas were a part of the ancient continent of Euramerica, Euramerica/Laurussia. In Britain it is a lithostratigraphy, lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) to which Stratigraphy, stratigraphers accord Geological unit#Lithostratigraphic units, supergroup status and which is of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, ORS is often used in literature on the subject. The term was coined to distinguish the sequence from the younger New Red Sandstone which also occurs widely throughout Britain. Sedimentology The Old Red Sandstone describes a suite of sedimentary rocks deposited in a variety of environments during the Devonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology.'' New York, New York, W. H. Freeman, 2nd ed, 529 pp. The term ''mudstone'' is also used to describe carbonate rocks (limestone or dolomite) that are composed predominantly of carbonate mud. However, in most contexts, the term refers to siliciclastic mudstone, composed mostly of silicate minerals. The NASA Curiosity rover has found deposits of mudstone on Mars that contain organic substances such as propane, benzene and toluene. Definition There is not a single definition of mudstone that has gained general acceptance,Boggs 2006, p.143 though there is wide agreement that mudstones are fine-grained sedimentary rocks, composed mostly of silicate grains with a grain size less than . Individual grains this size are too small to be disting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usk Inlier
The Usk Inlier is a domed outcrop of rock strata of Silurian age in Monmouthshire in south-eastern Wales. It is located in the countryside between the towns of Caerleon and Pontypool and the village of Raglan. The longer axis of the dome or ' pericline', often referred to as the Usk Anticline, is aligned north–south. The inlier is largely surrounded by a sequence of Old Red Sandstone rocks of Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ... age, though both these and the Silurian rocks are largely obscured by superficial deposits.British Geological Survey 1:50,000 scale geological map sheets 232, 233, 249 & 250 (England & Wales series) References Anticlines Landforms of Monmouthshire Geology of Wales Rock formations of Wales {{Wales-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |