|
Generative Cell
Generative may refer to: * Generative art, art that has been created using an autonomous system that is frequently, but not necessarily, implemented using a computer * Generative design, form finding process that can mimic nature’s evolutionary approach to design * Generative music, music that is ever-different and changing, and that is created by a system Mathematics and science * Generative anthropology, a field of study based on the theory that history of human culture is a genetic or "generative" development stemming from the development of language * Generative model, a model for randomly generating observable data in probability and statistics * Generative artificial intelligence, a type of machine learning system that uses generative models * Generative programming, a type of computer programming in which some mechanism generates a computer program to allow human programmers write code at a higher abstraction level * Generative sciences, an interdisciplinary and multidisci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Art
Generative art is post-conceptual art that has been created (in whole or in part) with the use of an autonomous system. An ''autonomous system'' in this context is generally one that is non-human and can independently determine features of an artwork that would otherwise require decisions made directly by the artist. In some cases the human creator may claim that the Generative systems, generative system represents their own artistic idea, and in others that the system takes on the role of the creator. "Generative art" often refers to algorithmic art (algorithmically determined Computer-generated artwork, computer generated artwork) and synthetic media (general term for any algorithmically generated media), but artists can also make generative art using systems of chemistry, biology, mechanics and robotics, smart materials, manual randomization, mathematics, data mapping, symmetry, and Tessellation, tiling. Generative algorithms, algorithms programmed to produce artistic work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
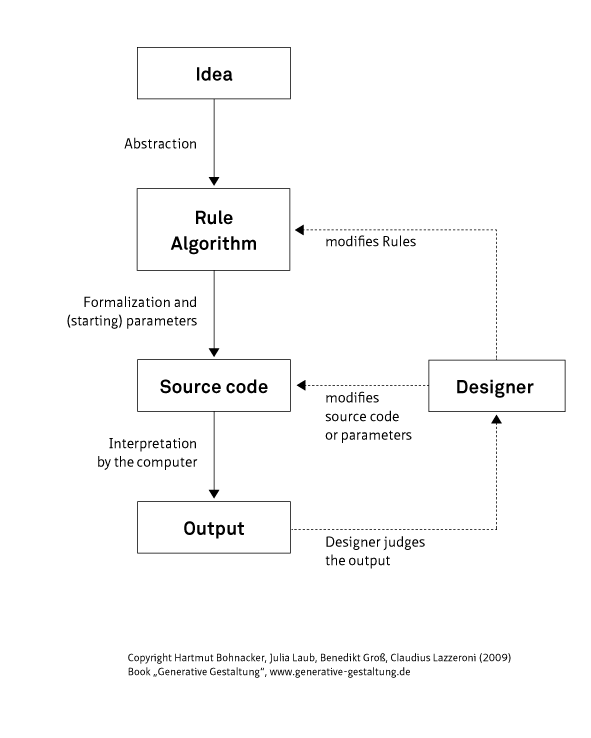
Generative Design
Generative design is an iterative design process that uses software to generate outputs that fulfill a set of constraints iteratively adjusted by a designer. Whether a human, test program, or artificial intelligence, the designer algorithmically or manually refines the feasible region of the program's inputs and outputs with each iteration to fulfill evolving design requirements. By employing computing power to evaluate more design permutations than a human alone is capable of, the process is capable of producing an optimal design that mimics nature's evolutionary approach to design through genetic variation and selection. The output can be images, sounds, architectural models, animation, and much more. It is, therefore, a fast method of exploring design possibilities that is used in various design fields such as art, architecture, communication design, and product design. Generative design has become more important, largely due to new programming environments o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Music
Generative music is a term popularized by Brian Eno to describe music that is ever-different and changing, and that is created by a system. Historical background In 1995 whilst working with SSEYO's Koan_(program), Koan software (built by Tim Cole and Pete Cole who later evolved it to Noatikl then Wotja), Brian Eno used the term "generative music" to describe any music that is ever-different and changing, created by a system. The term has since gone on to be used to refer to a wide range of music, from entirely random music mixes created by multiple simultaneous CD playback, through to live rule-based computer composition. Koan was SSEYO's first real-time music generation system, developed for the Windows platform. Work on Koan was started in 1990, and the software was first released to the public in 1994. In 1995 Brian Eno started working with SSEYO's Koan Pro software, work which led to the 1996 publication of his title 'Generative Music 1 with SSEYO Koan Software'. Eno's ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Anthropology
Generative anthropology is a field of study based on the hypothesis that the origin of human language happened in a singular event. The discipline of Generative Anthropology centers upon this original event which Eric Gans calls The Originary Scene. This scene is a kind of origin story that hypothesizes the specific event where language originated. The Originary Scene is powerful because any human ability: our ability to do science, to be ironic, to love, to think, to dominate, etc can be carefully explained first by reference to this scene of origin. Because The Originary Scene was the origin of all things human; Generative Anthropology attempts to understand all cultural phenomena in the simplest terms possible: all things human can be traced back to this hypothetical single origin point. Origin Generative anthropology originated with Professor Eric Gans of UCLA who developed his ideas in a series of books and articles beginning with ''The Origin of Language: A Formal Theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Model
In statistical classification, two main approaches are called the generative approach and the discriminative approach. These compute classifiers by different approaches, differing in the degree of statistical modelling. Terminology is inconsistent, but three major types can be distinguished: # A generative model is a statistical model of the joint probability distribution P(X, Y) on a given observable variable ''X'' and target variable ''Y'';: "Generative classifiers learn a model of the joint probability, p(x, y), of the inputs ''x'' and the label ''y'', and make their predictions by using Bayes rules to calculate p(y\mid x), and then picking the most likely label ''y''. A generative model can be used to "generate" random instances ( outcomes) of an observation ''x''. # A discriminative model is a model of the conditional probability P(Y\mid X = x) of the target ''Y'', given an observation ''x''. It can be used to "discriminate" the value of the target variable ''Y'', given an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Artificial Intelligence
Generative artificial intelligence (Generative AI, GenAI, or GAI) is a subfield of artificial intelligence that uses generative models to produce text, images, videos, or other forms of data. These models Machine learning, learn the underlying patterns and structures of their training data and use them to produce new data based on the input, which often comes in the form of natural language Prompt (natural language), prompts. Generative AI tools have become more common since an "AI boom" in the 2020s. This boom was made possible by improvements in transformer (machine learning model), transformer-based deep learning, deep neural networks, particularly large language models (LLMs). Major tools include chatbots such as ChatGPT, Microsoft Copilot, Copilot, Gemini (chatbot), Gemini, Grok (chatbot), Grok, and DeepSeek (chatbot), DeepSeek; text-to-image models such as Stable Diffusion, Midjourney, and DALL-E; and text-to-video models such as Sora (text-to-video model), Sora and Veo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Programming
Generative may refer to: * Generative art, art that has been created using an autonomous system that is frequently, but not necessarily, implemented using a computer * Generative design, form finding process that can mimic nature’s evolutionary approach to design * Generative music, music that is ever-different and changing, and that is created by a system Mathematics and science * Generative anthropology, a field of study based on the theory that history of human culture is a genetic or "generative" development stemming from the development of language * Generative model, a model for randomly generating observable data in probability and statistics * Generative artificial intelligence, a type of machine learning system that uses generative models * Generative programming, a type of computer programming in which some mechanism generates a computer program to allow human programmers write code at a higher abstraction level * Generative sciences, an interdisciplinary and multidisci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Sciences
Generative science is an area of research that explores the natural world and its complex behaviours. It explores ways "to generate apparently unanticipated and infinite behaviour based on deterministic and finite rules and parameters reproducing or resembling the behavior of natural and social phenomena". By modelling such interactions, it can suggest that properties exist in the system that had not been noticed in the real world situation. An example field of study is how unintended consequences arise in social processes. Generative sciences often explore natural phenomena at several levels of organization.J. Schmidhuber. (1997A computer scientist's view of life, the universe, and everything Foundations of Computer Science: Potential – Theory – Cognition, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 201–208, Springer Self-organizing natural systems are a central subject, studied both theoretically and by simulation experiments. The study of complex systems in general has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Systems
Generative systems are technologies with the overall capacity to produce unprompted change driven by large, varied, and uncoordinated audiences. When generative systems provide a common platform, changes may occur at varying layers (physical, network, application, content) and provide a means through which different firms and individuals may cooperate indirectly and contribute to innovation. Depending on the rules, the patterns can be extremely varied and unpredictable. One of the better-known examples is Conway's Game of Life, a cellular automaton. Other examples include Boids and Wikipedia. More examples can be found in generative music, generative art, in video games such as Spore, and more recently generative generosity and platforms likgeneros.io Theory Jonathan Zittrain In 2006, Jonathan Zittrain published ''The Generative Internet'' in Volume 119 of the Harvard Law Review The ''Harvard Law Review'' is a law review published by an independent student group at Harva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Grammar
Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists (), tend to share certain working assumptions such as the competence–performance distinction and the notion that some domain-specific aspects of grammar are partly innate in humans. These assumptions are rejected in non-generative approaches such as usage-based models of language. Generative linguistics includes work in core areas such as syntax, semantics, phonology, psycholinguistics, and language acquisition, with additional extensions to topics including biolinguistics and music cognition. Generative grammar began in the late 1950s with the work of Noam Chomsky, having roots in earlier approaches such as structural linguistics. The earliest version of Chomsky's model was called Transformational grammar, with subsequent itera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Lexicon
Generative lexicon (GL) is a theory of linguistic semantics which focuses on the distributed nature of compositionality in natural language. The first major work outlining the framework is James Pustejovsky's 1991 article "The Generative Lexicon". Subsequent important developments are presented in Pustejovsky and Boguraev (1993), Bouillon (1997), and Busa (1996). The first unified treatment of GL was given in Pustejovsky (1995). Unlike purely verb-based approaches to compositionality, generative lexicon attempts to spread the semantic load across all constituents of the utterance. Central to the philosophical perspective of GL are two major lines of inquiry: (1) How is it that we are able to deploy a finite number of words in our language in an unbounded number of contexts? (2) Is lexical information and the representations used in composing meanings separable from our commonsense knowledge? Motivation GL was initially developed as a theoretical framework for encoding selectiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Metrics
Generative metrics is the collective term for three distinct theories of verse structure (focusing on the English iambic pentameter) advanced between 1966 and 1977. Inspired largely by the example of Noam Chomsky's ''Syntactic Structures'' (1957) and Chomsky and Morris Halle's '' The Sound Pattern of English'' (1968), these theories aim principally at the formulation of explicit linguistic rules that will ''generate'' all possible well-formed instances of a given meter (e.g. iambic pentameter) and exclude any that are ''not'' well-formed. T.V.F. Brogan notes that of the three theories, " l three have undergone major revision, so that each exists in two versions, the revised version being preferable to the original in every case." Halle–Keyser The earliest (and most-discussed) theory of generative metrics is that put forth by Morris Halle and Samuel Jay Keyser — first in 1966 with respect to Chaucer's iambic pentameter, and in its full and revised form in 1971's ''English St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |