|
General William J. Fox Airfield
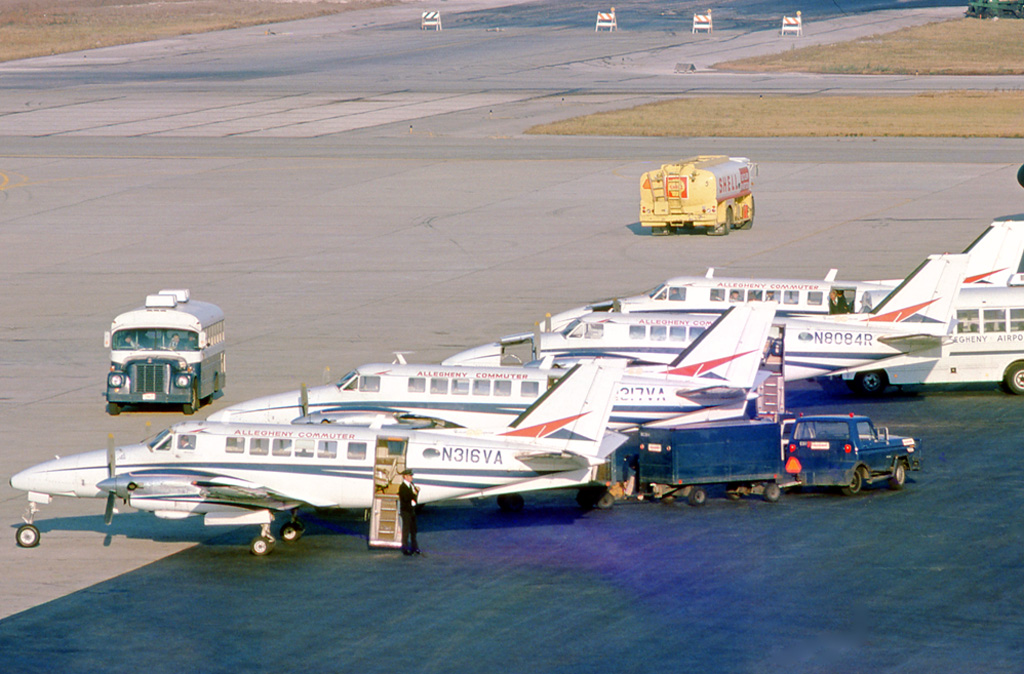
General William J. Fox Airfield is a county-owned, public airport in Los Angeles County, California, five miles northwest of Lancaster, California, United States. Locally known as Fox Field, the airport serves the Antelope Valley. The airport is named after William J. Fox, "a Marine war hero, a movie stunt man, the first Los Angeles County engineer and, for 20 years after his retirement, a cowboy." The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015 categorized it as a ''general aviation'' facility. The airport has limited scheduled cargo operations. The U.S. Forest Service has a fixed wing airtanker and helicopter base on the airfield which becomes one of the main hubs in the region for aerial firefighting suppression efforts during fire season. Historical airline service Fox Field had scheduled passenger air service as early as the late 1950s operated by Southwest Airways with Douglas DC-3 aircraft primarily to the Los Angeles International Airport (LAX). Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Los Angeles
Los Angeles County, officially the County of Los Angeles, and sometimes abbreviated as L.A. County, is the most populous county in the United States and in the U.S. state of California, with 9,861,224 residents estimated as of 2022. It is the most populous non–state-level government entity in the United States. Its population is greater than that of 40 individual U.S. states. At and with 88 incorporated cities and many unincorporated areas, it is home to more than one-quarter of California residents and is one of the most ethnically diverse counties in the United States. Its county seat, Los Angeles, is also California's most populous city and the second-most populous city in the United States, with about 3.9 million residents. In recent times, statewide droughts in California have placed great strain on the County’s (and the City of Los Angeles's) water security. History Los Angeles County is one of the original counties of California, created at the time of sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin 4-0-4
The Martin 4-0-4 was an American pressurized passenger airliner built by the Glenn L. Martin Company. In addition to airline use initially in the United States, it was used by the United States Coast Guard and United States Navy as the RM-1G (later as the VC-3A). Design and development When production of the earlier Martin 2-0-2 was stopped due to problems with wing structural failure the company decided to re-wing an improved version (which had already flown as the Martin 3-0-3). The new aircraft was the Martin 4-0-4. It had structural changes to the wings, pressurization and was lengthened slightly to take 40 passengers. Like the earlier 2-0-2, the 4-0-4 was a cantilever monoplane with a standard tail unit (cantilever tailplane and single vertical stabilizer). It had an airstair in the lower tail section for passenger boarding and disembarkation, retractable tricycle landing gear and was powered by two Pratt & Whitney R-2800-CB16 radial piston engines. Operational history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vertical datum). The term ''elevation'' is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while ''altitude'' or ''geopotential height'' is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and '' depth'' is used for points below the surface. Elevation is not to be confused with the distance from the center of the Earth. Due to the equatorial bulge, the summits of Mount Everest and Chimborazo have, respectively, the largest elevation and the largest geocentric distance. Aviation In aviation the term elevation or aerodrome elevation is defined by the ICAO as the highest point of the landing area. It is often measured in feet and can be found in approach charts of the aerodrome. It is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about and one hectare contains about . In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the ''are'' was defined as 100 square metres, or one square decametre, and the hectare ("hecto-" + "are") was thus 100 ''ares'' or km2 (10,000 square metres). When the metric system was further rationalised in 1960, resulting in the International System of Units (), the ''are'' was not included as a recognised unit. The hectare, however, remains as a non-SI unit accepted for use with the SI and whose use is "expected to continue indefinitely". Though the dekare/decare daa (1,000 m2) and are (100 m2) are not officially "accepted for use", they are still used in some contexts. Description The hectare (), although not a unit of SI, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imperial, Nebraska * Imperial, Pennsylvania * Imperial, Texa ... and United States customary units#Units of area, US customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the International yard and pound, international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".National Institute of Standards and Technolog(n.d.) General Tables of Units of Measurement . Traditionally, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Hope Airport
Hollywood Burbank Airport, legally and formerly marketed as Bob Hope Airport after entertainer Bob Hope , is a public airport northwest of downtown Burbank, in Los Angeles County, California, United States.. Federal Aviation Administration. effective November 9, 2017 The airport serves Downtown Los Angeles and the northern Greater Los Angeles area, which include Glendale, Pasadena, and the San Fernando Valley. It is closer to many popular attractions including Griffith Park, Universal Studios Hollywood, Hollywood, and Downtown Los Angeles than Los Angeles International Airport (LAX), and is the only airport in the area with a direct rail connection to Downtown Los Angeles, with service from two stations: Burbank Airport–North and Burbank Airport–South. Nonstop flights mostly serve cities in the western United States, while JetBlue has daily flights to New York City. Originally the entire airport was within the Burbank city limits, but the north end of Runway 15/33 ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beechcraft 99
The Beechcraft Model 99 is a civilian aircraft produced by Beechcraft. It is also known as the Beech 99 Airliner and the Commuter 99. The 99 is a twin-engine, unpressurized, 15 to 17 passenger seat turboprop aircraft, derived from the earlier Beechcraft King Air and Queen Air. It uses the wings of the Queen Air, the engines and nacelles of the King Air, and sub-systems from both, with a specifically designed nose structure. Design and development Designed in the 1960s as a replacement for the Beechcraft Model 18, it first flew in July 1966. It received type certification on May 2, 1968, and 62 aircraft were delivered by the end of the year. In 1984, the Beechcraft 1900, a pressurized 19-passenger airplane, was introduced as the follow-on aircraft. Production ended in early 1987. Nearly half the Beech 99s in airline service are now operated as freighters by Ameriflight. Variants * : Twin-engined Commuter and cargo transport aircraft, 10,400 lb max takeoff weight, accomm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Sun Airlines
Mesa Airlines, Inc., is an American regional airline based in Phoenix, Arizona. It is an FAA Part 121–certificated air carrier operating under air carrier certificate number MASA036A issued on June 29, 1979. It is a subsidiary of Mesa Air Group and operates flights as American Eagle and United Express via respective code sharing agreements with American Airlines and United Airlines. It serves more than 180 markets in the Western Hemisphere. In a 1997 article from the ''Journal of Air Transportation'', Mesa's safety record was noted as having the fewest incidents among domestic regional airlines at that time. Mesa filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in January 2010, hoping to shed financial obligations for leases on airplanes it no longer needed and emerged from bankruptcy in March 2011. In November 2017, Mesa opened a new training center in Phoenix. The 23,000-square-foot facility features a full-size CRJ-200 cabin trainer aircraft, 14 classrooms, and has the capacity to train ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beechcraft C99
The Beechcraft Model 99 is a civilian aircraft produced by Beechcraft. It is also known as the Beech 99 Airliner and the Commuter 99. The 99 is a twin-engine, unpressurized, 15 to 17 passenger seat turboprop aircraft, derived from the earlier Beechcraft King Air and Queen Air. It uses the wings of the Queen Air, the engines and nacelles of the King Air, and sub-systems from both, with a specifically designed nose structure. Design and development Designed in the 1960s as a replacement for the Beechcraft Model 18, it first flew in July 1966. It received type certification on May 2, 1968, and 62 aircraft were delivered by the end of the year. In 1984, the Beechcraft 1900, a pressurized 19-passenger airplane, was introduced as the follow-on aircraft. Production ended in early 1987. Nearly half the Beech 99s in airline service are now operated as freighters by Ameriflight. Variants * : Twin-engined Commuter and cargo transport aircraft, 10,400 lb max takeoff weight, accomm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoth Yosemite Airport
Mammoth Yosemite Airport is a town-owned public airport seven miles east of Mammoth Lakes, in Mono County, California, United States. Also known as Mammoth Lakes Airport or Mammoth–June Lake Airport, it is mainly used for general aviation, but has scheduled passenger flights operated by one airline which primarily serves the airport on a seasonal basis during the winter ski season. Additional scheduled passenger service for the Mammoth area is seasonally available at the nearby Eastern Sierra Regional Airport located in Bishop, CA. The airport had 665 passenger boardings (enplanements) in calendar year 2008, 6,157 enplanements in 2009, and 19,814 in 2010. The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015 categorized it as a ''general aviation'' airport. However, the report for 2015-2019 upgraded this status to that of a primary/non-hub commercial airport. Facilities The airport covers 230 acres (93 ha) at an elevation of 7,135 feet (2,175 m). Its one runway, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes Airwest
Hughes Airwest was a regional airline in the western United States, backed by Howard Hughes' Summa Corporation. Its original name in 1968 was Air West and the air carrier was owned by Nick Bez. Hughes Airwest flew routes in the western U.S. and to several destinations in Mexico and Canada; its headquarters were on the grounds of San Francisco International Airport (SFO) in unincorporated San Mateo County, California. With distinctive all-yellow aircraft, the company slogan was ''Top Banana in the West''; Hughes Airwest was purchased by Republic Airlines on October 1, 1980. History On April 17, 1968, three "local service" airlines in the western U.S. merged to form Air West: * Pacific Air Lines, which previously operated as Southwest Airways when it was founded in 1941, was based in San Francisco, flew along the coast and California's Central Valley, linking cities from Medford, Oregon, to southern California. Pacific operated Boeing 727-100s and Fairch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter
The de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter is a Canadian STOL (Short Takeoff and Landing) utility aircraft developed by de Havilland Canada, which produced the aircraft from 1965 to 1988; Viking Air purchased the type certificate, then restarted production in 2008 before re-adopting the DHC name in 2022. The aircraft's fixed tricycle undercarriage, STOL capabilities, twin turboprop engines and high rate of Climb (aeronautics), climb have made it a successful commuter airliner, typically seating 18-20 passengers, as well as a cargo and medical evacuation aircraft. In addition, the Twin Otter has been popular with commercial skydiving operations, and is used by the United States Army Parachute Team and the United States Air Force's 98th Flying Training Squadron. Design and development Development of the aircraft began in 1964, with the first flight on May 20, 1965. A twin-engine replacement for the single-engine de Havilland Canada DHC-3 Otter, DHC-3 Otter retaining DHC's STOL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_JP7769673.jpg)



_(2).jpg)
.jpg)