|
Gemini 1
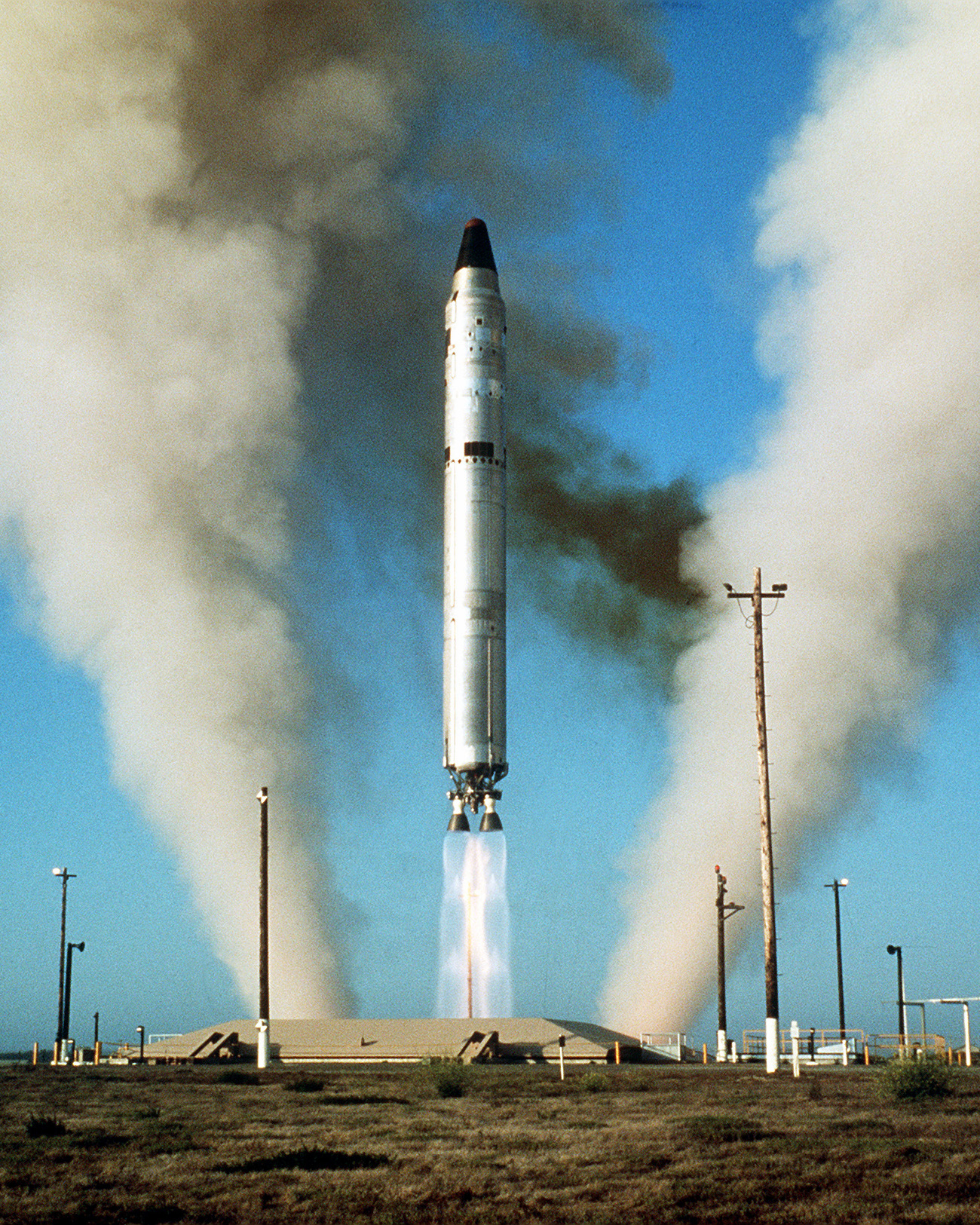
Gemini 1 was the first mission in NASA's Gemini program. An uncrewed test flight of the Gemini spacecraft, its main objectives were to test the structural integrity of the new spacecraft and modified Titan II launch vehicle. It was also the first test of the new tracking and communication systems for the Gemini program and provided training for the ground support crews for the first crewed missions. Originally scheduled for launch in December 1963, difficulties in the development of both the spacecraft and its booster caused four months of delay. Gemini 1 was launched from Launch Complex 19 at Cape Kennedy (now Canaveral), Florida on April 8, 1964. The spacecraft stayed attached to the second stage of the rocket. The mission lasted for three orbits while test data were taken, but the spacecraft stayed in space for almost 64 orbits until its orbit decayed due to atmospheric drag. The spacecraft was not intended to be recovered, and holes were drilled through its heat shield to en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Complex 19
Launch Complex 19 (LC-19) is a deactivated launch site on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida used by NASA to launch all of the Gemini crewed spaceflights. It was also used by uncrewed Titan I and Titan II missiles. LC-19 was in use from 1959 to 1966, during which time it saw 27 launches, 10 of which were crewed. The first flight from LC-19 was on August 14, 1959 and ended in a pad explosion, extensively damaging the facility, which took a few months to repair. The first successful launch from LC-19 was also a Titan I, on February 2, 1960. After being converted for the Titan II ICBM program in 1962, LC-19 was later designated for the Gemini flights. After the program concluded in December 1966, LC-19 was closed down. The Gemini white room from the top of the booster erector has been partially restored and is on display at the Air Force Space and Missile Museum located at Complex 26. Gallery Image:Complex19.jpg, Diagram of Complex 19. Image:Complex19block.jpg, Diagram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 19
Launch Complex 19 (LC-19) is a deactivated launch site on Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida used by NASA to launch all of the Gemini crewed spaceflights. It was also used by uncrewed Titan I and Titan II missiles. LC-19 was in use from 1959 to 1966, during which time it saw 27 launches, 10 of which were crewed. The first flight from LC-19 was on August 14, 1959 and ended in a pad explosion, extensively damaging the facility, which took a few months to repair. The first successful launch from LC-19 was also a Titan I, on February 2, 1960. After being converted for the Titan II ICBM program in 1962, LC-19 was later designated for the Gemini flights. After the program concluded in December 1966, LC-19 was closed down. The Gemini white room from the top of the booster erector has been partially restored and is on display at the Air Force Space and Missile Museum located at Complex 26. Gallery Image:Complex19.jpg, Diagram of Complex 19. Image:Complex19block.jpg, Diagra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-20
The Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar ("Dynamic Soarer") was a United States Air Force (USAF) program to develop a spaceplane that could be used for a variety of military missions, including aerial reconnaissance, bombing, space rescue, satellite maintenance, and as a space interceptor to sabotage enemy satellites. The program ran from October 24, 1957, to December 10, 1963, cost US$660 million ($ in current dollars), and was cancelled just after spacecraft construction had begun. Other spacecraft under development at the time, such as Mercury or Vostok, were space capsules with ballistic re-entry profiles that ended in a landing under a parachute. Dyna-Soar was more like an aircraft. It could travel to distant targets at the speed of an intercontinental ballistic missile, was designed to glide to Earth like an aircraft under control of a pilot, and could land at an airfield. Dyna-Soar could also reach Earth orbit, like conventional, manned space capsules. These characteristics made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern subregion of a single continent called America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a British Overseas Territory), Bouvet Island ( dependency of Norway), Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manned Space Flight Network
The Manned Space Flight Network (abbreviated MSFN, pronounced "''misfin''") was a set of tracking stations built to support the American Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Skylab space programs. There were two other NASA space communication networks at the time, the Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network (STADAN) for tracking satellites in low Earth orbit, and the Deep Space Network (DSN) for tracking more distant uncrewed missions. After the end of Skylab, the MSFN and STADAN were merged to form the Spaceflight Tracking and Data Network (STDN). STDN was in turn replaced by the satellite-based Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) during the Space Shuttle program, being used . Orbital versus deep space tracking Tracking vehicles in low Earth orbits (LEO) is quite different from tracking deep space missions. Deep space missions are visible for long periods of time from a large portion of the Earth's surface, and so require few stations (the DSN uses only three, ). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
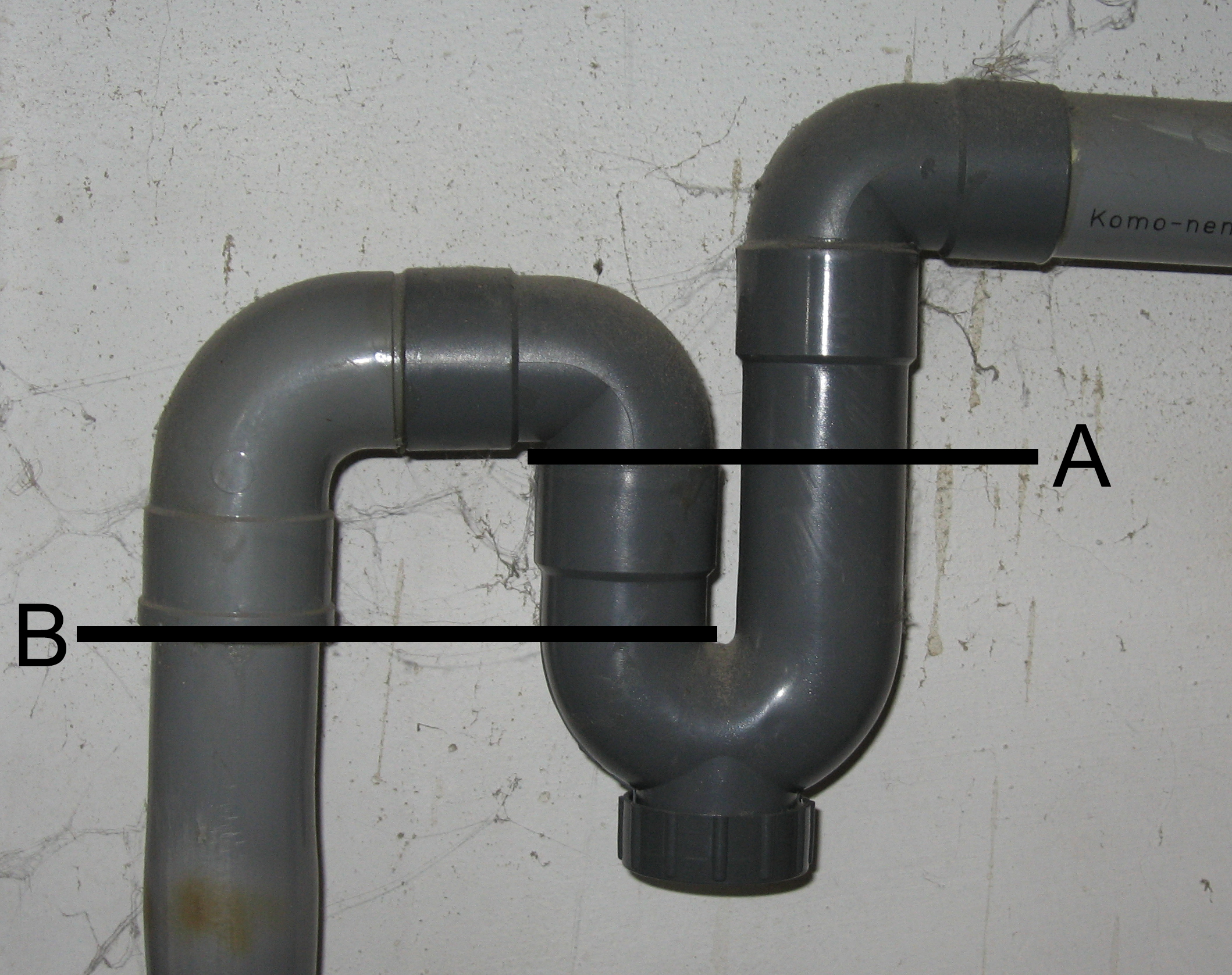
Standpipe (plumbing)
In plumbing, a trap is a U-shaped portion of pipe designed to trap liquid or gas to prevent unwanted flow; most notably sewer gases from entering buildings while allowing waste materials to pass through. In oil refineries, traps are used to prevent hydrocarbons and other dangerous gases and chemical fumes from escaping through drains. In heating systems, the same feature is used to prevent thermo-siphoning which would allow heat to escape to locations where it is not wanted. Similarly, some pressure gauges are connected to systems using U bends to maintain a local gas while the system uses liquid. For decorative effect, they can be disguised as complete loops of pipe, creating more than one U for added efficacy. General description In domestic applications, traps are typically U, S, Q, or J-shaped pipe located below or within a plumbing fixture. An S-shaped trap is also known as an S-bend. It was invented by Alexander Cumming in 1775 but became known as the U-bend following t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn I
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to low Earth orbit payloads.Terminology has changed since the 1960s; back then, 20,000 pounds was considered "heavy lift". The rocket's first stage was built as a cluster of propellant tanks engineered from older rocket tank designs, leading critics to jokingly refer to it as "Cluster's Last Stand". Its development was taken over from the Advanced Research Projects Agency in 1958 by the newly formed civilian NASA. Its design proved sound and flexible. It was successful in initiating the development of liquid hydrogen-fueled rocket propulsion, launching the Pegasus satellites, and flight verification of the Apollo command and service module launch phase aerodynamics. Ten Saturn I rockets were flown before it was replaced by the heavy lift derivative Saturn IB, which used a larger, higher total impulse second stage and an improved guidance and control system. It also led the way to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pogo Oscillation
Pogo oscillation is a self-excited vibration in liquid-propellant rocket engines caused by combustion instability. The unstable combustion results in variations of engine thrust, causing variations of acceleration on the vehicle's flexible structure, which in turn cause variations in propellant pressure and flow rate, closing the self-excitation cycle. The name is a metaphor comparing the longitudinal vibration to the bouncing of a pogo stick. Pogo oscillation places stress on the frame of the vehicle, which in severe cases can be dangerous. Origin In general, pogo oscillation occurs when a surge in engine pressure increases back pressure against the fuel coming into the engine, reducing engine pressure, causing more fuel to come in and increasing engine pressure again. Flexing of fuel pipes can also induce fluctuations in fuel pressure. If the cycle happens to match a resonance frequency of the rocket then dangerous oscillations can occur through positive feedback, which can, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGM-25C Titan II
The Titan II was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the Glenn L. Martin Company from the earlier Titan I missile. Titan II was originally designed and used as an ICBM, but was later adapted as a medium-lift space launch vehicle (these adaptations were designated Titan II GLV and Titan 23G) to carry payloads to Earth orbit for the United States Air Force (USAF), National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). Those payloads included the USAF Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP), NOAA weather satellites, and NASA's Gemini crewed space capsules. The modified Titan II SLVs (Space Launch Vehicles) were launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, up until 2003. Titan II missile The Titan II ICBM was the successor to the Titan I, with double the payload. Unlike the Titan I, it used hydrazine-based hypergolic propellant which was storable and reliably ignited. This red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablative Heat Shield
Atmospheric entry is the movement of an object from outer space into and through the gases of an atmosphere of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite. There are two main types of atmospheric entry: ''uncontrolled entry'', such as the entry of astronomical objects, space debris, or bolides; and ''controlled entry'' (or ''reentry'') of a spacecraft capable of being navigated or following a predetermined course. Technologies and procedures allowing the controlled atmospheric ''entry, descent, and landing'' of spacecraft are collectively termed as ''EDL''. Objects entering an atmosphere experience atmospheric drag, which puts mechanical stress on the object, and aerodynamic heating—caused mostly by compression of the air in front of the object, but also by drag. These forces can cause loss of mass (ablation) or even complete disintegration of smaller objects, and objects with lower compressive strength can explode. Crewed space vehicles must be slowed to subsonic speeds be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |