|
Gaurishankar Conservation Area
Gaurishankar Conservation Area is a protected area in the Himalayas of Nepal that was established in January 2010, covering in the Ramechhap, Dolakha and Sindhupalchok districts and encompassing 22 Village Development Committees. It is contiguous with Tibet in the north.NTNC (2010)Gaurishankar Conservation Area Project National Trust for Nature Conservation, Nepal. The protected area connects the Langtang and Sagarmatha National Parks. The Government of Nepal handed over the management of Gaurishankar Conservation Area to National Trust for Nature Conservation (NTNC) for 20 years in 2010. Following the models of Annapurna and Manaslu Conservation Areas, NTNC has been managing the area through its Gaurishankar Conservation Area Project. It is a part of the Sacred Himalayan Landscape The headquarters is in Charikot. History In April 2006, the Dolakha Chamber of Commerce and Industries has requested the Government of Nepal and the Nepal Tourism Board to declare the Rolwaling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinus Wallichiana
''Pinus wallichiana'' is a coniferous evergreen tree native to the Himalaya, Karakoram and Hindu Kush mountains, from eastern Afghanistan east across northern Pakistan and north west India to Yunnan in southwest China. It grows in mountain valleys at altitudes of 1800–4300 m (rarely as low as 1200 m), reaching in height. It favours a temperate climate with dry winters and wet summers. In Pashto, it is known as ''Nishtar''. This tree is often known as Bhutan pine, (not to be confused with the recently described Bhutan white pine, '' Pinus bhutanica'', a closely related species). Other names include blue pine, Himalayan pine and Himalayan white pine. Description The leaves ("needles") are in fascicles (bundles) of five and are 12–18 cm long. They are noted for being flexible along their length, and often droop gracefully. The cones are long and slender, 16–32 cm, yellow-buff when mature, with thin scales; the seeds are 5–6 mm long with a 20– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalinchowk (3780 M) (3306554742)
Kalinchowk is a Rural municipality located within the Dolakha district of the Bagmati province of Nepal. The municipality spans of area, with a total population of 22,954 according to a 2011 Nepal census. On March 10, 2017, the Government of Nepal restructured the local level bodies into 753 new local level structures. The previous Kalinchowk, Babare, Lamidanda, Lapilang, Sunakhani, and Sundrawati VDCs were merged to form Kalinchowk Rural Municipality. Kalinchowk is divided into 9 wards, with Sunakhani declared the administrative center of the rural municipality. Kalinchowk is a hill station and a tourist hotspot. It is located at 3842 meters of altitude and about 150km northeast from national capital Kathmandu. The place is best known for trekking and skiing. During the December, January and February (mainly Paush and Magh in Nepali months) snowfalls in Kalinchowk. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Kalinchowk Rural Municipality had a population of 22,95 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalinchowk Bhagwati Shrine
Kalinchok Bhagwati Temple ( ne, कालिञ्चोक भगवती मन्दिर) is a Hindu shrine located in the eastern hilly region of Nepal, Kalinchowk Rural Municipality in Dolkha District. It is situated in Kalinchok Village (ward no. 1 of Kalinchok RM) at the altitude of from sea level. It is a part of Gaurishankar Conservation Area from where two rivers Sun Koshi and Tamakoshi rivers are sourced. Kalinchowk is one of the most visited local destinations in the winter. It is known for the trek to the shrine. It used to be the only way to the temple, but in 2018 a cable car Cable car most commonly refers to the following cable transportation systems: * Aerial lift, such as aerial tramways and gondola lifts, in which the vehicle is suspended in the air from a cable ** Aerial tramway ** Chairlift ** Gondola lift ** ... has been added to help with the growing number of visitors. Tourism Kalinchowk is a destination for adventurous sports such as skii ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Muntjac
The Indian muntjac or the common muntjac (''Muntiacus muntjak''), also called the southern red muntjac and barking deer, is a deer species native to South and Southeast Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. In popular local language, it is known as ''Kaakad'' or ''Kakad'' (काकड़) This muntjac has soft, short, brownish or grayish hair, sometimes with creamy markings. It is among the smallest deer species. It is an omnivore and eats grass, fruit, shoots, seeds, bird eggs, and small animals, and occasionally scavenges on carrion. Its calls sound like barking, often when frightened by a predator, hence the common name "barking deer". Males have canines, short antlers that usually branch just once near the base, and a large postorbital scent gland used to mark territories. Name The species was formerly classified as '. Characteristics The Indian muntjac has a short but very soft, thick, dense coat that is more dense in cooler regions. Its face is dar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayan Serow
The Himalayan serow (''Capricornis sumatraensis thar''), also known as the thar ( , ), is a subspecies of the mainland serow native to the Himalayas. It was previously considered its own species, as ''Capricornis thar''. It is the official state animal of the Indian state of Mizoram. Taxonomy In 1831, Brian Houghton Hodgson first described a goat-like animal with short annulated horns occurring in montane regions between the Sutlej and Teesta Rivers under the name "Bubaline Antelope". As "Bubaline" was preoccupied, he gave it the scientific name ''Antelope thar'' a few months later. When William Ogilby described the genus '' Capricornis'' in 1838, he determined the Himalayan serow as type species of this genus. Description The Himalayan serow is mostly blackish, with flanks, hindquarters, and upper legs that are a rusty red; its lower legs are whitish. Distribution and habitat The Himalayan serow inhabits hilly forests above an elevation of , but descends to in winter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayan Goral
The Himalayan goral (''Naemorhedus goral'') or the gray goral, is a bovid species native to the Himalayas. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List because the population is thought to be declining significantly due to habitat loss and hunting for meat. Characteristics The Himalayan goral is in length and weighs . It has a gray or gray-brown coat with tan legs, lighter patches on its throat, and a single dark stripe along its spine. Males have short manes on their necks. Both males and females have backward-curving horns which can grow up to in length. In addition to certain peculiarities in the form of the skull, gorals are chiefly distinguished from the closely related serows in that they do not possess preorbital glands below their eyes, nor corresponding depressions in their skulls. Distribution and habitat The Himalayan goral occurs in the Himalayas from Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, southern Tibet, and the states of Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh in Ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masked Palm Civet
The masked palm civet (''Paguma larvata''), also called the gem-faced civet, is a palm civet species native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. It has been listed as least concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 as it occurs in many protected areas, is tolerant to some degree of habitat modification, and widely distributed with presumed large populations that are unlikely to be declining. The genus ''Paguma'' was first named and described by John Edward Gray in 1831. All described forms are regarded as a single species. In 2003, masked palm civets at a wildlife market in China were found to have been infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Characteristics The masked palm civet's fur is grayish to ochraceous, black on the head, shoulders and neck, and blackish brown on the tail and feet. It has a white blaze on the forehead; white marks above and below the eyes extend to the ears, forming a half-collar. In morphology the masked palm cive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assam Macaque
The Assam macaque (''Macaca assamensis'') or Assamese macaque is a macaque of the Old World monkey family native to South and Southeast Asia. Since 2008, it has been listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List, as it is experiencing significant declines due to poaching, habitat degradation, and fragmentation. Characteristics The Assam macaque has a yellowish-grey to dark brown pelage. The facial skin is dark brownish to purplish. The head has a dark fringe of hair on the cheeks directed backwards to the ears. The hair on the crown is parted in the middle. The shoulders, head and arms tend to be paler than the hindquarters, which are greyish. The tail is well-haired and short. Head-to-body-length measures , and the tail is long. Adult weight is . Distribution and habitat The ''Macaca assamensis'' "Nepal population" is endemic to Nepal and likely in some way distinct from the two recognized subspecies, which occupy adjacent areas to the southeast and east of the ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
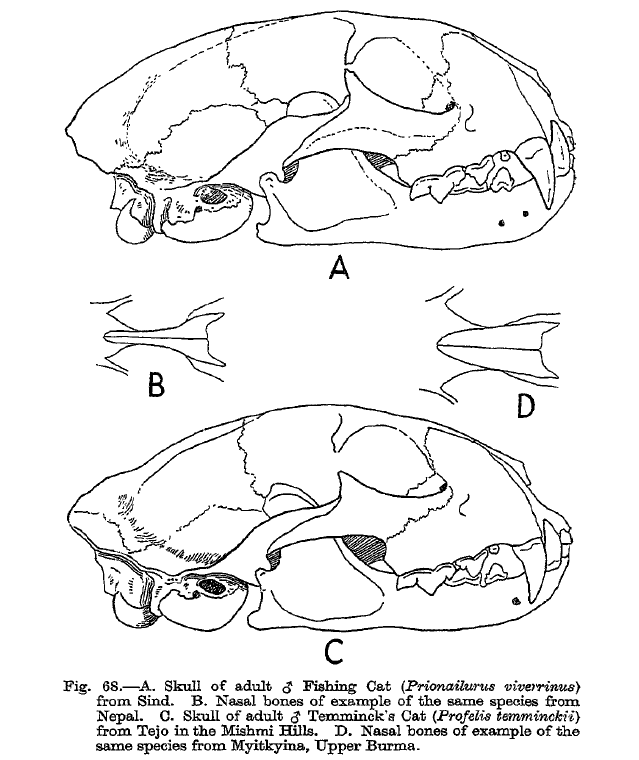
Asian Golden Cat
The Asian golden cat (''Catopuma temminckii'') is a medium-sized wild cat native to the northeastern Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and China. It has been listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List since 2008, and is threatened by poaching and habitat destruction, since Southeast Asian forests are undergoing the world's fastest regional deforestation. The Asian golden cat's scientific name honours Coenraad Jacob Temminck. It is also called Temminck's cat and Asiatic golden cat. Taxonomy ''Felis temmincki'' was the scientific name used in 1827 by Nicholas Aylward Vigors and Thomas Horsfield who described a reddish brown cat skin from Sumatra. ''Felis moormensis'' proposed by Brian Houghton Hodgson in 1831 was a young male cat caught alive by Moormi hunters in Nepal. ''Felis tristis'' proposed by Alphonse Milne-Edwards in 1872 was a spotted Asian golden cat from China. It was subordinated to the genus ''Catopuma'' proposed by Nikolai Severtzov in 1853. Two subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Panda
The red panda (''Ailurus fulgens''), also known as the lesser panda, is a small mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It has dense reddish-brown fur with a black belly and legs, white-lined ears, a mostly white muzzle and a ringed tail. Its head-to-body length is with a tail, and it weighs between . It is well adapted to climbing due to its flexible joints and curved semi-retractile claws. The red panda was first formally described in 1825. The two currently recognised subspecies, the Himalayan and the Chinese red panda, genetically diverged about 250,000 years ago. The red panda's place on the evolutionary tree has been debated, but modern genetic evidence places it in close affinity with raccoons, weasels, and skunks. It is not closely related to the giant panda, which is a bear, though both possess elongated wrist bones or "false thumbs" used for grasping bamboo. The evolutionary lineage of the red panda ( Ailuridae) stretches back around , a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayan Thar
The Himalayan tahr (''Hemitragus jemlahicus'') is a large even-toed ungulate native to the Himalayas in southern Tibet, northern India, western Bhutan and Nepal. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List, as the population is declining due to hunting and habitat loss. A recent phylogenetic analysis indicates that the genus ''Hemitragus'' is monospecific, and that the Himalayan tahr is a wild goat. The Himalayan tahr has been introduced to Argentina, New Zealand, South Africa and the United States. Taxonomy Tahr belong to the subfamily Caprinae in the order Artiodactyla. Their closest relatives in the subfamily Caprinae are sheep and goats. A subspecies, the Eastern Himalayan tahr or shapi, was described in 1944. This classification is not considered valid anymore, and no subspecies are currently recognized. Etymology The word "tahr," first used in English writings in 1835, is derived from the animal's local name in the Western Himalayas, which has otherw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_male_head_Nagarjun.jpg)