|
Gauliga Ostmark
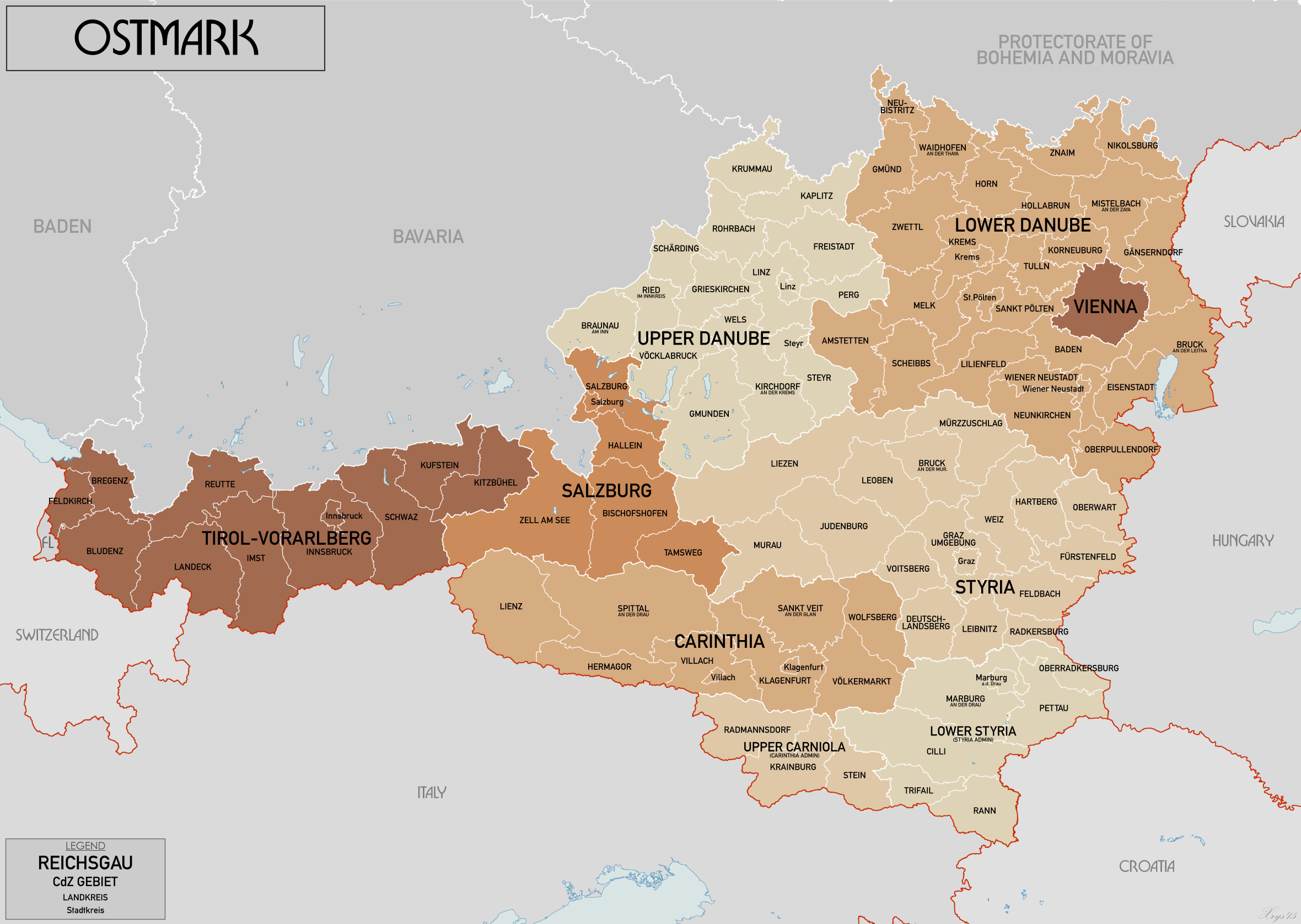
The Gauliga Ostmark, renamed Gauliga Donau-Alpenland in 1941, was the highest football league in Austria after its annexation by Germany in 1938. Shortly after the occupation, the Nazis reorganised the administrative regions in Austria, and the seven ''Gaue'' ''Carinthia'', ''Niederdonau'', ''Oberdonau'', ''Salzburg'', ''Styria'', ''Vienna'' and ''Tyrol-Vorarlberg'' replaced the country of Austria. From 1941, the northernmost region of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, ''Drava Banovina'', became part of the ''Gaue'' ''Carinthia'' and ''Styria''. Overview The ''Gauliga Ostmark'' was introduced by the Nazi Sports Office in 1938, after Austria's annexation, to replace the previously existing national league (German:''Nationalliga'') in the occupied country. The former country of Austria was renamed ''Ostmark'' (English:''Eastern March'') and became part of Germany until 1945. The renaming of Austria to ''Ostmark'' was carried out to eradicate all recognition of the country's former independ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1938–39 Gauliga
The 1938–39 Gauliga was the sixth season of the Gauliga, the first tier of the football league system in Germany from 1933 to 1945. It was the last completed season before the Second World War. The league operated in eighteen regional divisions, of which the Gauliga Sudetenland was played in a knock-out format of regional champions, with the league containing 175 clubs all up, five less than the previous season. The league champions entered the 1939 German football championship, won by FC Schalke 04 who defeated Admira Wien 9–0 in the final. It was Schalke's fourth national championship, with the club winning six championships all up during the Gauliga era. Four clubs remained unbeaten during the league season, those being FC Schalke 04, Hindenburg Allenstein, VfR Mannheim and SV Dessau 05. At the other end of the table one club finished the season without a win, SV Algermissen. Hamburger SV scored the most goals of any Gauliga club with 87 while ESV Wacker Wiener Neusta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is to score more goals than the opposition by moving the ball beyond the goal line into a rectangular framed goal defended by the opposing side. Traditionally, the game has been played over two 45 minute halves, for a total match time of 90 minutes. With an estimated 250 million players active in over 200 countries, it is considered the world's most popular sport. The game of association football is played in accordance with the Laws of the Game, a set of rules that has been in effect since 1863 with the International Football Association Board (IFAB) maintaining them since 1886. The game is played with a football that is in circumference. The two teams compete to get the ball into the other team's goal (between the posts and under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Football Champions
The German football champions are the annual winners of the highest association football competition in Germany. The history of the German football championship is complex and reflects the turbulent history of the country through the course of the 20th century. Brought to the country by English expatriates, the sport had taken root in the cities of Berlin, Hamburg, Stuttgart, and Leipzig in the 1890s, leading to the growth of city, regional, and academic leagues, each with their own championships. Following the establishment of the German Football Association (Deutscher Fußball Bund) in 1900, the first recognized national championship final was hosted by Hamburg club Altona 93 in 1903 in which VfB Leipzig defeated DFC Prag 7–2.Grüne, Hardy (2003) 100 Jahre Deutsche Meisterschaft. Die Geschicte des Fußballs in Deutschland. Before the formation of the Bundesliga in 1963, the championship format was based on a knockout competition, contested between the winners of each of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostmark (Austria)
Ostmark (, "Eastern March") was the name used by Nazi propaganda from 1938 to 1942 to replace that of the formerly independent Federal State of Austria after the ''Anschluss'' with Nazi Germany. From the ''Anschluss'' until 1939, the official name used was Land Österreich ("State of Austria"). History Once Austrian-born Adolf Hitler completed the union between his birth country and Germany ''(Anschluss)'', the Nazi government had the incorporated territory renamed. The name ''Austria'' (''Österreich'' in German, meaning "Eastern Realm") was at first replaced by "Ostmark", referring to the 10th century '' Marcha orientalis''. The change was meant to refer to Austria as the new "eastern march" of the Reich. In August 1938, the ''Donau-Zeitung'' proudly referred to Passau as "the cradle of the new ''Ostmark''". Subdivision According to the ''Ostmarkgesetz'' with effect from 1 May 1939 the former States of Austria were reorganized into seven ''Reichsgaue'', each under the rule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Sports Office
The National Socialist League of the Reich for Physical Exercise (german: Nationalsozialistischer Reichsbund für Leibesübungen, abbreviated NSRL) was the umbrella organization for sports and physical education in Nazi Germany. The NSRL was known as the German League of the Reich for Physical Exercise (german: Deutscher Reichsbund für Leibesübungen, abbreviated DRL) until 1938. The organization was expanded to Austria after that country's annexation by Nazi Germany. The NSRL was led by the ''Reichssportführer'', who after 1934 simultaneously presided over the German National Olympic Committee. The NSRL's leaders were Hans von Tschammer und Osten (1933–1943), Arno Breitmeyer (1943–1944) and Karl Ritter von Halt (1944–1945). History Preliminary organizations: Effects of the Nazi takeover The 1916 Summer Olympics had been awarded to Berlin, but were canceled because of the duration of World War I. The ''Deutscher Reichsausschuss für Olympische Spiele'' (DRA or DRAfOS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauliga
A Gauliga () was the highest level of play in German football from 1933 to 1945. The leagues were introduced in 1933, after the Nazi takeover of power by the National Socialist League of the Reich for Physical Exercise. Name The German word ''Gauliga'' is composed of Gau, approximately meaning county or region, and ''Liga'', or league. The plural is ''Gauligen''. While the name Gauliga is not in use in German football any more, mainly because it is attached to the Nazi past, some sports in Germany still have Gauligen, like gymnastics and faustball. Overview The Gauligen were formed in 1933 to replace the previously existing Bezirksligas in Weimar Germany. The Nazis initially introduced 16 regional Gauligen, some of them subdivided into groups. The introduction of the Gauligen was part of the ''Gleichschaltung'' process, whereby the Nazis completely revamped the domestic administration. The Gauligen were largely formed along the new Gaue, designed to replace the old German s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drava Banovina
The Drava Banovina or Drava Banate ( Slovene and Serbo-Croatian: ''Dravska banovina''), was a province ( banovina) of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of most of present-day Slovenia and was named for the Drava River. The capital city of the Drava Banovina was Ljubljana. Borders According to the 1931 Constitution of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Also in 1931, the Municipality of Štrigova (now in Croatia) was separated from the Čakovec District and the rest of Međimurje and was included in the Ljutomer District in the Drava Banovina. Administration The Drava Banovina was administratively subdivided into 29 counties (called ''srez''): Aftermath In 1941 the World War II Axis powers occupied the Drava Banovina, and it was divided largely between Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy, while Hungary annexed Prekmurje and the Independent State of Croatia annexed some smaller border areas. Following World War II the region was reconstituted, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Yugoslavia
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Jugoslavija, Краљевина Југославија; sl, Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast Europe, Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941. From 1918 to 1929, it was officially called the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Kraljevina Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca, Краљевина Срба, Хрвата и Словенаца; sl, Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev), but the term "Yugoslavia" (literally "Land of South Slavs") was its colloquial name due to its origins."Kraljevina Jugoslavija! Novi naziv naše države. No, mi smo itak med seboj vedno dejali Jugoslavija, četudi je bilo na vseh uradnih listih Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev. In tudi drugi narodi, kakor Nemci in Francozi, so pisali že prej v svojih listih mnogo o Jugoslaviji. 3. oktobra, ko je kralj Aleksander podpisal "Zakon o nazivu in razdelitvi kraljevine n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrol-Vorarlberg
The Reichsgau Tyrol-Vorarlberg (German: ''Reichsgau Tirol-Vorarlberg'') was an List of Gaue of Nazi Germany, administrative division of Nazi Germany consisting of Vorarlberg and North Tyrol (both in Austria). It existed from 1938 to 1945. It did not include East Tyrol (Lienz), which was instead part of Reichsgau Kärnten, Reichsgau Carinthia. After the Armistice with Italy, Italian Armistice with the Allies the Italian provinces of Province of Belluno, Belluno, South Tyrol and Trentino were placed under direct German control as the Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills (''Operationszone Alpenvorland'', OZAV), which was ''de facto'' annexed and administered as part of Tyrol-Vorarlberg. History The Nazi Gau (plural Gaue) system was originally established in a Nazi Party, party conference on 22 May 1926, in order to improve administration of the party structure. From 1933 onwards, after the Nazi seizure of power, the ''Gaue'' increasingly replaced the German states as administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gau (administrative Division)
''Gau'' (German , nl, gouw , fy, gea or ''goa'' ) is a Germanic term for a region within a country, often a former or current province. It was used in the Middle Ages, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an English shire. The administrative use of the term was revived as a subdivision during the period of Nazi Germany in 1933–1945. It still appears today in regional names, such as the Rheingau or Allgäu. Middle Ages Etymology The Germanic word is reflected in Gothic ''gawi'' (neuter; genitive ''gaujis'') and early Old High German ''gewi, gowi'' (neuter) and in some compound names ''-gawi'' as in Gothic (e.g. ''Durgawi'' "Canton of Thurgau", ''Alpagawi'' "Allgäu"), later ''gâi, gôi'', and after loss of the stem suffix ''gaw, gao'', and with motion to the feminine as ''gawa'' besides ''gowo'' (from ''gowio''). Old Saxon shows further truncation to ''gâ, gô''. As an equivalent of Latin ''pagus'', a ''gau'' is analogous with a ''pays'' of the Kingdom of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism (german: Hitlerfaschismus). The later related term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. It incorporates a dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and the use of eugenics into its creed. Its extreme nationalism originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist '' Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationalism since the late 19th century, and it was strongly influenced by the paramilitary groups that emerged af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |