|
Gatelodge
A gatekeeper's lodge or gate lodge is a small, often decorative building, situated at the entrance to the estate of a mansion or country house. Originally intended as the office and accommodation for a gatekeeper who was employed by the landowner to control access to the property, they fell out of use in the early 20th century but surviving examples are often preserved and can sometimes be used as domestic housing. History Originating from the gatehouses of medieval monasteries and manorhouses, gatekeeper's lodges became fashionable in the Georgian era along with landscape gardens. Initially these lodges were functional wooden buildings, intended to retain livestock and deter intruders, but during the 18th century, they developed into a visual statement, designed to give an initial impression of the landowner's wealth and taste. British architect John Buonarotti Papworth, wrote that park gates and their associated lodges should be: Lodges were often designed to give a visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Lodge At Moy - Geograph
A gate or gateway is a point of entry to or from a space enclosed by walls. The word derived from old Norse "gat" meaning road or wikt:path, path; But other terms include ''yett and portal (architecture), port''. The concept originally referred to the gap or hole in the wall or fence, rather than a Barricade, barrier which closed it. Gates may prevent or control the entry or exit of individuals, or they may be merely decorative. The moving part or parts of a gateway may be considered "Door, doors", as they are fixed at one side whilst opening and closing like one. A gate may have a latch (hardware), latch that can be raised and lowered to both open a gate or prevent it from swinging. Locks are also used on gates to increase the security. Larger gates can be used for a whole building, such as a castle or fortified town. Actual doors can also be considered gates when they are used to block entry as prevalent within a gatehouse. Today, many gate doors are opened by an Electric ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cottage
A cottage, during Feudalism in England, England's feudal period, was the holding by a cottager (known as a Cotter (farmer), cotter or ''bordar'') of a small house with enough garden to feed a family and in return for the cottage, the cottager had to provide some form of service to the Lord of the manor, manorial lord.Daniel D. McGarry, ''Medieval history and civilization'' (1976) p 242 However, in time cottage just became the general term for a small house. In modern usage, a cottage is usually a modest, often cosy dwelling, typically in a rural or semi-rural location and not necessarily in England. The cottage orné, often quite large and grand residences built by the nobility, dates back to a movement of "rustic" stylised cottages of the late 18th and early 19th century during the Romantic movement. In British English the term now denotes a small dwelling of traditional build, although it can also be applied to modern construction designed to resemble traditional houses ("wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tudor Revival Architecture
Tudor Revival architecture (also known as mock Tudor in the UK) first manifested itself in domestic architecture in the United Kingdom in the latter half of the 19th century. Based on revival of aspects that were perceived as Tudor architecture, in reality it usually took the style of English vernacular architecture of the Middle Ages that had survived into the Tudor period. The style later became an influence elsewhere, especially the British colonies. For example, in New Zealand, the architect Francis Petre adapted the style for the local climate. In Singapore, then a British colony, architects such as R. A. J. Bidwell pioneered what became known as the Black and White House. The earliest examples of the style originate with the works of such eminent architects as Norman Shaw and George Devey, in what at the time was considered Neo-Tudor design. Tudorbethan is a subset of Tudor Revival architecture that eliminated some of the more complex aspects of Jacobethan in favour of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doorn
Doorn is a town in the municipality of Utrechtse Heuvelrug in the central Netherlands, in the province of Utrecht. History In a document from 885 to 896, the settlement is called "Thorhem", dwelling of Thor, the God of Thunder. Vikings quartered at Dorestad (now Wijk bij Duurstede) called the place Thorhem because, reputedly, the god of thunder was worshipped there. Indeed, archeological diggings in a moor on the estate of Hoog Moersbergen, north of Doorn, prove that there was a pagan sacrificial site. At the time, the settlement of Thorhem belonged to the homestead of Villa Thorhem. Around 1200, this homestead was in the possession of a provost of the Bishopric of Utrecht. He, or one of his successors, had a castle built in the 14th Century, now Huis Doorn, and a church called the Maartenskerk ("St. Martin's Church") around 1200. The church was extended in the 15th century. It fell into Protestant hands around 1585 and is still in use as a Protestant church. Another castle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia and the Spanish and Portuguese colonies in Latin America. About 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe. Baroque architects took the basic elements of Renaissance architecture, including domes and colonnades, and made them higher, grander, more decorated, and more dramatic. The interior effects were often achieved with the use of ''quadratura'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drenagh
Drenagh is a 19th-century house and gardens near Limavady, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. Drenagh has been the home of the McCausland family since 1729, and the present house was built in 1835. It was the first major work by Charles Lanyon, known for his work in Belfast. The gardens include features from the 18th century, as well as an extensive 19th-century Giardino all'italiana, Italian garden and elements added in the 1960s. The house is a Grade A listed building. History The Drenagh estate, then known as Fruithill, was purchased by William Conolly (1662-1729), a wealthy self-made man and speaker of the Parliament of Ireland, Irish Parliament. Conolly's daughter married Robert McCausland, who inherited Fruithill on his death. McCausland was the grandson of Baron Alexander McAuslane who had settled in the Strabane area in the 1540s, and he named his first son Conolly McCausland for his father-in-law. In the 1730s Robert McCausland built the first house at Fruithill, loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
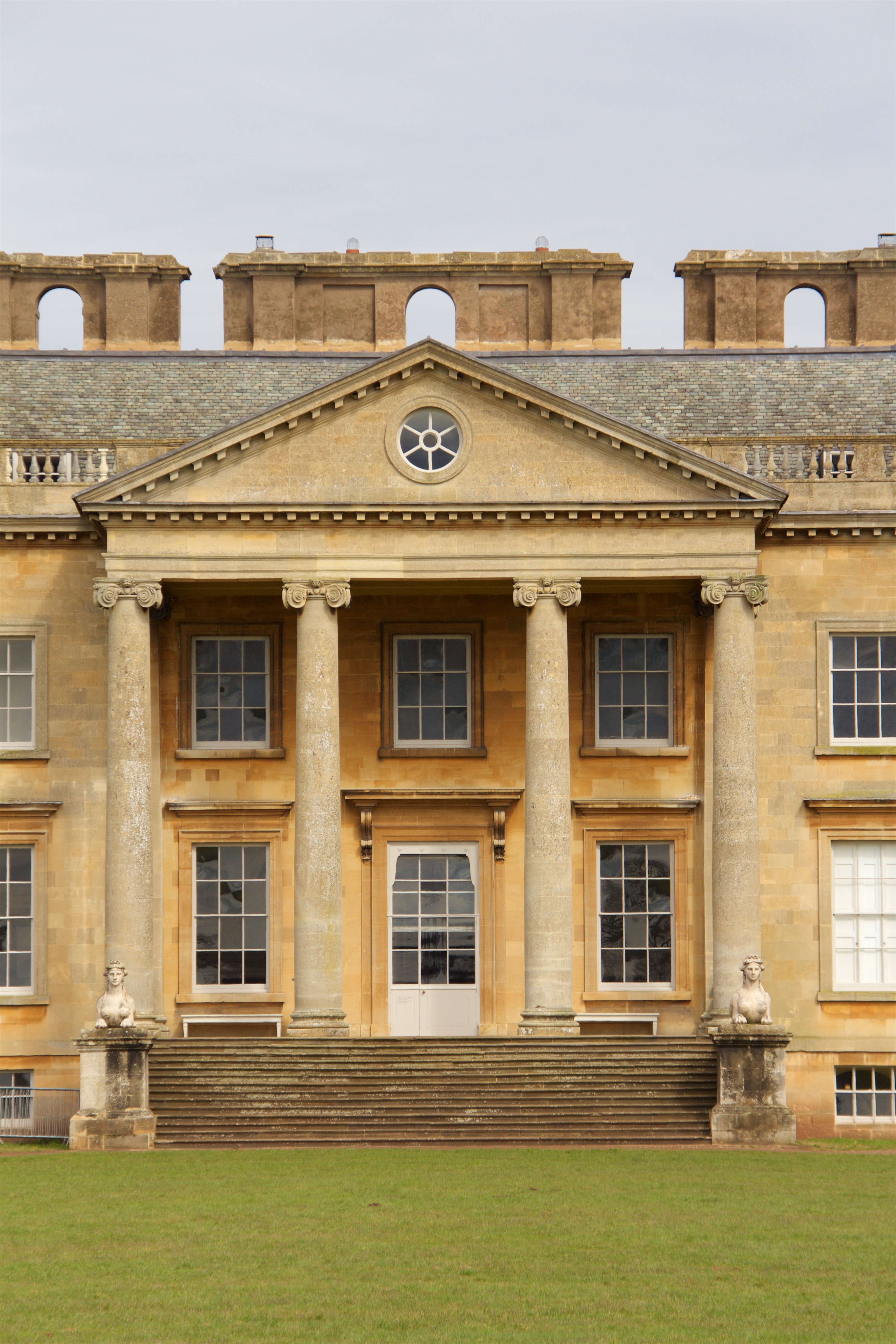
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
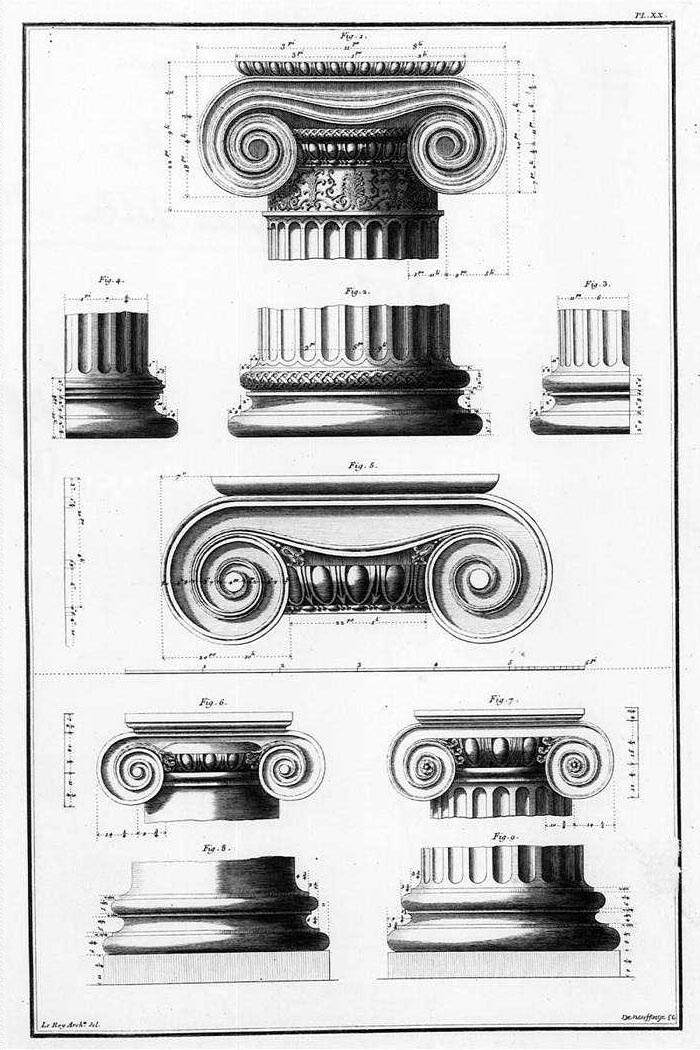
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric and the Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. The Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital, which have been the subject of much theoretical and practical discourse, based on a brief and obscure passage i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
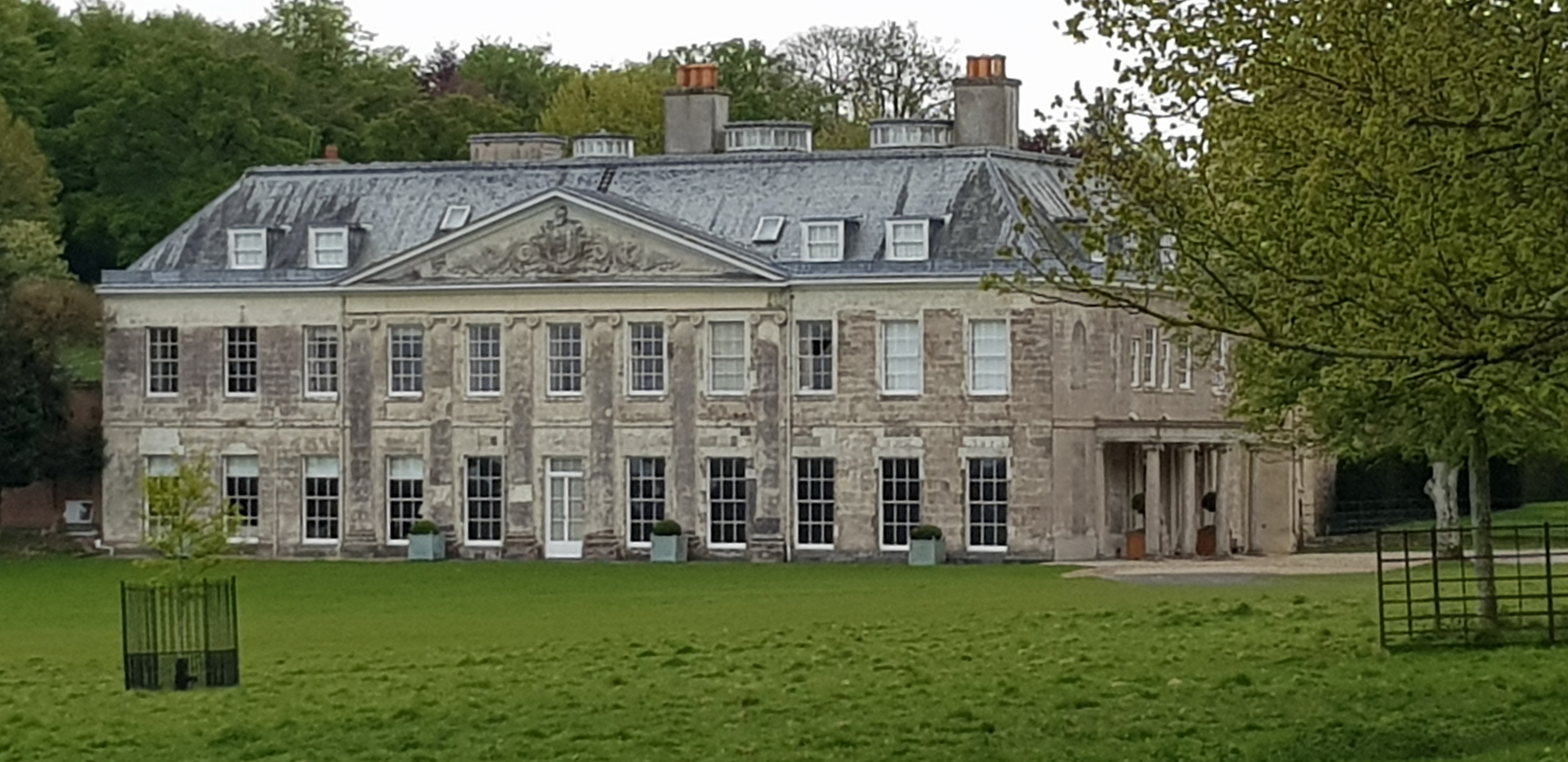
Charborough Park
Charborough House, also known as Charborough Park, is a Grade I listed building, the manor house of the ancient manor of Charborough. The house is between the villages of Sturminster Marshall and Bere Regis in Dorset, England. The grounds, which include a deer park and gardens, adjoin the villages of Winterborne Zelston, Newton Peveril and Lytchett Matravers: they are Grade II* listed in the National Register of Historic Parks and Gardens, and have been called the most splendid parkland in Dorset. Descent The estate is listed as a manor in the Domesday Book of 1086. Erle The Erle (''alias'' Earl, Earle, etc.) family originated in east Devon and moved to neighbouring Dorset in about 1500, but died out in the male line on the death of General Thomas III Erle (1650–1720) without male progeny. His daughter and sole heiress Frances Erle (d.1728) married Edward Ernle, to which family the estate passed. Female heiresses subsequently brought the Erle/Ernle estates to owners with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldermaston Court
Aldermaston Court is a country house and private park built in the Victorian era for Daniel Higford Davall Burr with incorporations from a Stuart house. It is south-east of the village nucleus of Aldermaston in the English county of Berkshire. The predecessor manor house became a mansion from the wealth of its land and from assistance to Charles I during the English Civil War under ownership of the Forster baronets of Aldermaston after which the estate has alternated between the names Aldermaston Park and Aldermaston Manor. The estate became dominated by its neo-Elizabethan mansion after a fire of 1843 destroyed one third of the predecessor and various landscape features were added which have resulted in building and grounds being Grade II* listed. Between the turn of the 21st century and its closure in 2012, the estate has been a wedding venue, a conference centre, and a hotel. Aside from the manor house and its immediate surroundings, the park is home to office building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)