|
Gassman Indole Synthesis
The Gassman indole synthesis is a series of chemical reactions used to synthesize substituted indoles by addition of an aniline and a ketone bearing a thioether substituent. This is a one-pot chemical reaction, and none of the intermediates are isolated. R1 can be hydrogen or alkyl, while R2 works best with aryl, but can also be alkyl. Electron-rich anilines, such as 4-methoxyaniline, tend to fail in this reaction. The 3-position thiomethyl group is often removed using Raney nickel to give the 3-H-indole. Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism of the Gassman indole synthesis is divided among three steps. The first step is the oxidation of the aniline 1 using ''tert''-butyl hypochlorite (tBuOCl) to give the chloramine 2. The second step is the addition of the keto-thioether to give the sulfonium ion 3, and is typically done at low temperatures (−78 °C). The third and final step is the addition of a base, which in this case is triethylamine. Upon warming to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (chemistry), products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmatropic Rearrangement
A sigmatropic reaction in organic chemistry is a pericyclic reaction wherein the net result is one sigma bond, σ-bond is changed to another σ-bond in an uncatalyzed intramolecular reaction. The name ''sigmatropic'' is the result of a compound word, compounding of the long-established sigma designation from single carbon–carbon bonds and the Greek word ''tropos'', meaning turn. In this type of rearrangement reaction, a substituent moves from one part of a pi-bond, π-bonded system to another part in an intramolecular reaction with simultaneous rearrangement of the π system. True sigmatropic reactions are usually uncatalyzed, although Lewis acid catalysis is possible. Sigmatropic reactions often have transition-metal catalysts that form intermediates in analogous reactions. The most well-known of the sigmatropic rearrangements are the [3,3] Cope rearrangement, Claisen rearrangement, Carroll rearrangement, and the Fischer indole synthesis. Overview of sigmatropic shifts Woodward� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
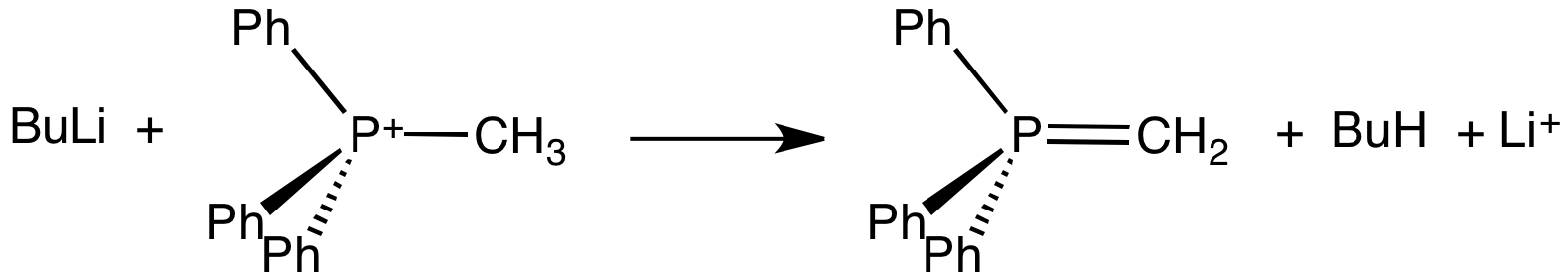
Ylide
An ylide or ylid () is a neutral dipolar molecule containing a formally negatively charged atom (usually a carbanion) directly attached to a heteroatom with a formal positive charge (usually nitrogen, phosphorus or sulfur), and in which both atoms have full octets of electrons. The result can be viewed as a structure in which two adjacent atoms are connected by both a covalent and an ionic bond; normally written X+–Y−. Ylides are thus 1,2- dipolar compounds, and a subclass of zwitterions. They appear in organic chemistry as reagents or reactive intermediates. The class name "ylide" for the compound should not be confused with the suffix "-ylide". Resonance structures Many ylides may be depicted by a multiple bond form in a resonance structure, known as the ylene form, while the actual structure lies in between both forms: : The actual bonding picture of these types of ylides is strictly zwitterionic (the structure on the right) with the strong Coulombic attraction between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deprotonation
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch331/protstructure/PS_2A3_AA_Charges.html, accessed 12/2/2020 The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when a proton is added (transferred) to a Brønsted–Lowry base, is protonation (or hydronation). The species formed is the conjugate acid of that base. A species that can either accept or donate a proton is referred to as amphiprotic. An example is the H2O (water) molecule, which can gain a proton to form the hydronium ion, H3O+, or lose a proton, leaving the hydroxide ion, OH−. The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its p''K''a value. A low p''K''a value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA is also a common abbreviation. It is a colourless volatile liquid with a strong fishy odor reminiscent of ammonia. Like diisopropylethylamine (Hünig's base), triethylamine is commonly employed in organic synthesis, usually as a base. Synthesis and properties Triethylamine is prepared by the alkylation of ammonia with ethanol: :NH3 + 3 C2H5OH → N(C2H5)3 + 3 H2O The pKa of protonated triethylamine is 10.75,David Evans Research Group and it can be used to prepare buffer solutions at that pH. The [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base (chemistry)
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances that react with acids, as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century. In 1884, Svante Arrhenius proposed that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to form Hydroxide ions OH−. These ions can react with hydrogen ions (H+ according to Arrhenius) from the dissociation of acids to form water in an acid–base reaction. A base was therefore a metal hydroxide such as NaOH or Ca(OH)2. Such aqueous hydroxide solutions were also described by certain characteristic properties. They are slippery to the touch, can taste bitter and change the color of pH indicators (e.g., turn red litmus paper blue). In water, by altering the autoionization equilibrium, bases yield solutions in which the hydrogen ion activity is lower than it is in pure water, i.e., the water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonium
In organic chemistry, a sulfonium ion, also known as sulphonium ion or sulfanium ion, is a positively-charged ion (a "cation") featuring three organic substituents attached to sulfur. These organosulfur compounds have the formula . Together with a negatively-charged counterion, they give sulfonium salts. They are typically colorless solids that are soluble in organic solvent. Synthesis Sulfonium compounds are usually synthesized by the reaction of thioethers with alkyl halides. For example, the reaction of dimethyl sulfide with iodomethane yields trimethylsulfonium iodide: : + → The reaction proceeds by a nucleophilic substitution mechanism (SN2). Iodide is the leaving group departs. The rate of methylation is faster with more electrophilic methylating agents, such as methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate. Inversion Sulfonium ions with three different substituents are chiral owing to their pyramidal structure. Unlike the isoelectronic oxonium ions (R3O+), chiral sulfon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloramine
Chloramines refer to derivatives of ammonia and organic amines wherein one or more N-H bonds have been replaced by N-Cl bonds. Two classes of compounds are considered: inorganic chloramines and organic chloramines. Inorganic chloramines Inorganic chloramines comprise three compounds: monochloramine (NH2Cl), dichloramine (NHCl2), and nitrogen trichloride (NCl3). Monochloramine is of broad significance as a disinfectant for water. Organic chloramines 144px, ''N''-Chloropiperidine is a rare example of an organic chloramine. 144px, Chloramine-T is often referred to as a chloramine, but it is really a salt (CH3C6H4SO2NClNa) derived from a chloramine. Organic chloramines feature the NCl functional group attached to an organic substituent. Examples include ''N''-chloromorpholine (ClN(CH2CH2)2O), ''N''-chloropiperidine, and ''N''-chloroquinuclidinium chloride. Chloramines are commonly produced by the action of bleach on secondary amines: :R2NH + NaOCl → R2NCl + NaOH ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gassman Mechanism Scheme
Gassman is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Alessandro Gassman (born 1965), Italian actor * David Gassman (born 1949), American politician * Tedd Gassman (born 1943), American politician *Vittorio Gassman (1922–2000), Italian theatre and film actor and director See also *Gassman indole synthesis, indole forming reaction *Gasman (other) Gasman may refer to: * One who works for a gas company, reading gas meters * Gasman (surname) * Gasman, a character in the ''Maximum Ride'' book series * ''Gasman'' (film), a 1997 short film directed by Lynne Ramsay * Gasman, Iran * '' The Gas ... {{surname Jewish surnames Germanic-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





3S _in_the_BPh4-_salt_(code_HEYZAM).png)