|
Gas Chromatography-olfactometry
Gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O) is a technique that integrates the separation of volatile compounds using a gas chromatograph with the detection of odour using an olfactometer (human assessor). It was first invented and applied in 1964 by Fuller and co-workers. While GC separates and quantifies volatile compounds from an extract, human olfaction detects the odour activity of each eluting compound. In this olfactometric detection, a human assessor may qualitatively determine whether a compound has odour activity or describe the odour perceived, or quantitatively evaluate the intensity of the odour or the duration of the odour activity. The olfactometric detection of compounds allows the assessment of the relationship between a quantified substance and the human perception of its odour, without instrumental detection limits present in other kinds of detectors. Olfactory perception The properties of a compound relating to human olfactory perception includes its odour quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture. Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Gas chromatography is the process of separating compounds in a mixture by injecting a gaseous or liquid sample into a mobile phase, typically called the carrier gas, and passing the gas through a stationary phase. The mobile phase is usually an inert gas or an unreactive gas such as helium, argon, nitrogen or hydrogen. The stationary phase is a microscopic la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven's Power Law
Stevens' power law is an empirical relationship in psychophysics between an increased intensity or strength in a physical stimulus and the perceived magnitude increase in the sensation created by the stimulus. It is often considered to supersede the Weber–Fechner law, which is based on a logarithmic relationship between stimulus and sensation, because the power law describes a wider range of sensory comparisons, down to zero intensity. The theory is named after psychophysicist Stanley Smith Stevens (1906–1973). Although the idea of a power law had been suggested by 19th-century researchers, Stevens is credited with reviving the law and publishing a body of psychophysical data to support it in 1957. The general form of the law is :\psi(I) = k I ^a, where ''I'' is the intensity or strength of the stimulus in physical units (energy, weight, pressure, mixture proportions, etc.), ψ(''I'') is the magnitude of the sensation evoked by the stimulus, ''a'' is an exponent that depends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
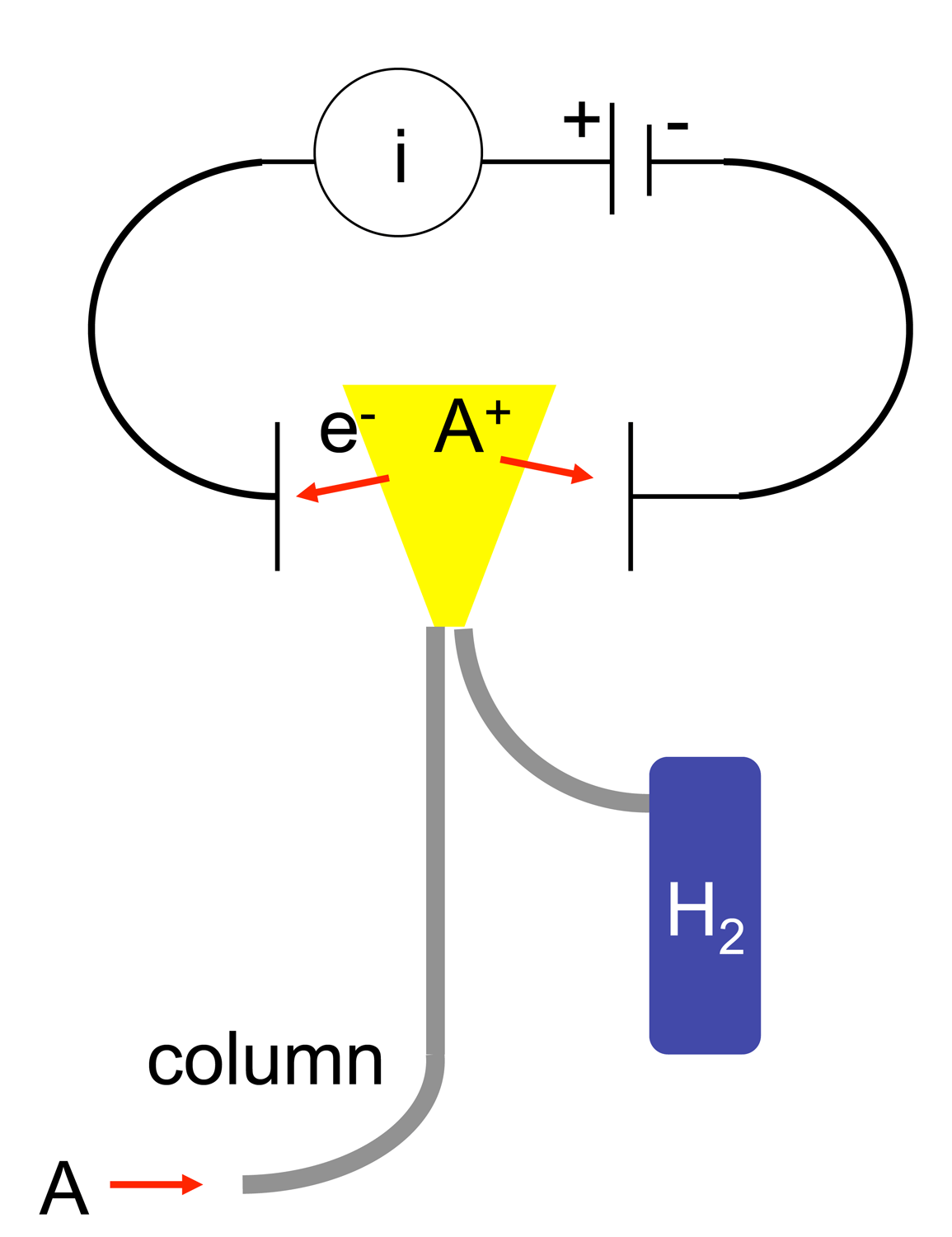
Retention Time
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be preparative or analytical. The purpose of preparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial Dilution
A serial dilution is the stepwise dilution of a substance in solution. Usually the dilution factor at each step is constant, resulting in a geometric progression of the concentration in a logarithmic fashion. A ten-fold serial dilution could be 1 M, 0.1 M, 0.01 M, 0.001 M ... Serial dilutions are used to accurately create highly diluted solutions as well as solutions for experiments resulting in concentration curves with a logarithmic scale. A tenfold dilution for each step is called a logarithmic dilution or log-dilution, a 3.16-fold (100.5-fold) dilution is called a half-logarithmic dilution or half-log dilution, and a 1.78-fold (100.25-fold) dilution is called a quarter-logarithmic dilution or quarter-log dilution. Serial dilutions are widely used in experimental sciences, including biochemistry, pharmacology, microbiology, and physics. In biology and medicine In biology and medicine, besides the more conventional uses described above, serial dilution may also be used to red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometer
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Ionization Detector
A flame ionization detector (FID) is a scientific instrument that measures analytes in a gas stream. It is frequently used as a detector in gas chromatography. The measurement of ion per unit time make this a mass sensitive instrument. Standalone FIDs can also be used in applications such as landfill gas monitoring, fugitive emissions monitoring and internal combustion engine emissions measurement in stationary or portable instruments. History The first flame ionization detectors were developed simultaneously and independently in 1957 by McWilliam and Dewar at Imperial Chemical Industries of Australia and New Zealand (ICIANZ, see Orica history) Central Research Laboratory, Ascot Vale, Melbourne, Australia. and by Harley and Pretorius at the University of Pretoria in Pretoria, South Africa. In 1959, Perkin Elmer Corp. included a flame ionization detector in its Vapor Fractometer. Operating principle The operation of the FID is based on the detection of ions formed during co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present. Humidity depends on the temperature and pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is the dew point. The amount of water vapor needed to achieve saturation increases as the temperature increases. As the temperature of a parcel of air decreases it will eventually reach the saturation point without adding or losing water mass. The amount of water vapor contained within a parcel of air can vary significantly. For example, a parcel of air near saturation may contain 28 g of water per cubic metre of air at , but only 8 g of water per cubic metre of air at . Three primary measurements of humidity are widely employed: absolute, relative, and specific. Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the state of matter from the gas phase into the liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. The word most often refers to the water cycle. It can also be defined as the change in the state of water vapor to liquid water when in contact with a liquid or solid surface or cloud condensation nuclei within the atmosphere. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition. Initiation Condensation is initiated by the formation of atomic/molecular clusters of that species within its gaseous volume—like rain drop or snow flake formation within clouds—or at the contact between such gaseous phase and a liquid or solid surface. In clouds, this can be catalyzed by water-nucleating proteins, produced by atmospheric microbes, which are capable of binding gaseous or liquid water molecules. Reversibility scenarios A few distinct reversibility scenarios emerge here with respect to the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. It is one of the best-known and widely applied PFAS. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a spin-off from DuPont, which originally discovered the compound in 1938. Polytetrafluoroethylene is a fluorocarbon solid, as it is a high-molecular-weight polymer consisting wholly of carbon and fluorine. PTFE is hydrophobic: neither water nor water-containing substances wet PTFE, as fluorocarbons exhibit only small London dispersion forces due to the low electric polarizability of fluorine. PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. Polytetrafluoroethylene is used as a non-stick coating for pans and other cookware. It is non-reactive, partly because of the strength of carbon–fluorine bonds, so it is often used in containers and pipework for reactive and corrosive chemicals. Where used as a lubricant, PTFE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nose Cone
A nose cone is the conically shaped forwardmost section of a rocket, guided missile or aircraft, designed to modulate oncoming airflow behaviors and minimize aerodynamic drag. Nose cones are also designed for submerged watercraft such as submarines, submersibles and torpedoes, and in high-speed land vehicles such as rocket cars and velomobiles. Rockets On a suborbital rocket vehicle it consists of a chamber or chambers in which instruments, animals, plants, or auxiliary equipment may be carried, and an outer surface built to withstand high temperatures generated by aerodynamic heating. Much of the fundamental research related to hypersonic flight was done towards creating viable nose cone designs for the atmospheric reentry of spacecraft and ICBM reentry vehicles. In a satellite launch vehicle, the nose cone may become the satellite itself after separating from the final stage of the rocket, or it may be used as a payload fairing to shield the satellite until out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflection Point
In differential calculus and differential geometry, an inflection point, point of inflection, flex, or inflection (British English: inflexion) is a point on a smooth plane curve at which the curvature changes sign. In particular, in the case of the graph of a function, it is a point where the function changes from being concave (concave downward) to convex (concave upward), or vice versa. For the graph of a function of differentiability class (''f'', its first derivative ''f, and its second derivative ''f'''', exist and are continuous), the condition ''f'' = 0'' can also be used to find an inflection point since a point of ''f'' = 0'' must be passed to change ''f'''' from a positive value (concave upward) to a negative value (concave downward) or vice versa as ''f'''' is continuous; an inflection point of the curve is where ''f'' = 0'' and changes its sign at the point (from positive to negative or from negative to positive). A point where the second derivative vanishes but do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odour
An odor (American English) or odour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds that are generally found in low concentrations that humans and animals can perceive via their sense of smell. An odor is also called a "smell" or a "scent", which can refer to either a pleasant or an unpleasant odor. While "odor" and "smell" can refer to pleasant and unpleasant odors, the terms "scent", "aroma", and "fragrance" are usually reserved for pleasant-smelling odors and are frequently used in the food and cosmetic industry to describe floral scents or to refer to perfumes. Physiology of smell Sense of smell The perception of odors, or sense of smell, is mediated by the olfactory nerve. The olfactory receptor (OR) cells are neurons present in the olfactory epithelium, which is a small patch of tissue at the back of the nasal cavity. There are millions of olfactory receptor neurons that act as sensory signaling cells. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)