|
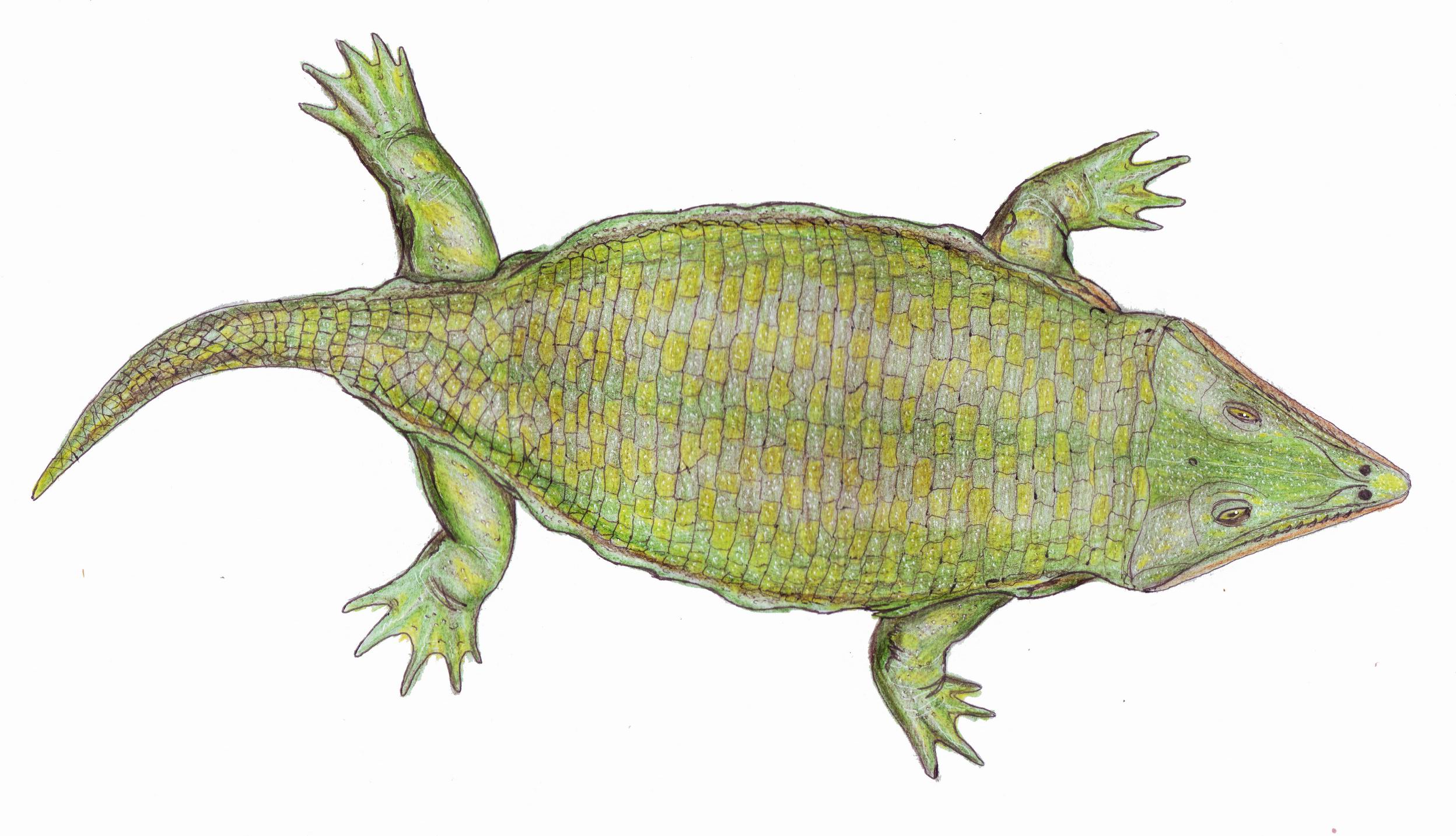
Garjainia
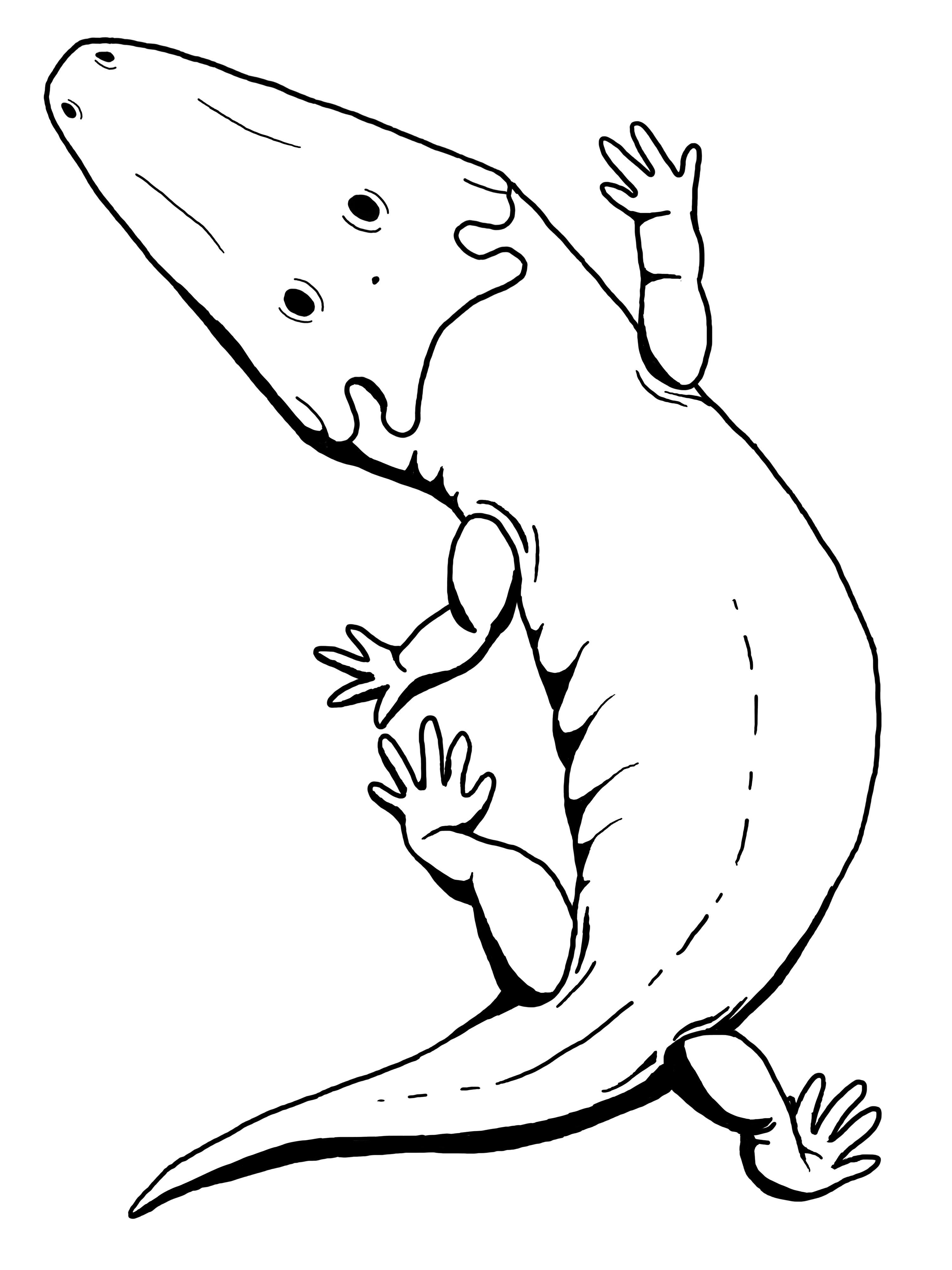
''Garjainia'' is an extinct genus of erythrosuchid archosauriform reptile from the Olenekian of Russia and South Africa. It was approximately 1.50–2 m (5–6 ft 8 in) long. It contained two species, ''Garjainia prima'' from the Yarengian/Yarkenskian Supergorizont of Russia, and ''Garjainia madiba'' from the Burgersdorp Formation ( ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone A) of South Africa. "''Vjuskovia triplicostata''", a name assigned to some erythrosuchid fossils from Russia, has been synonymized with ''Garjainia prima''. Discovery ''Garjainia prima'' was first discovered in a small village in Russia by a farmer. The exact date of the discovery is not known but its believed to have been found some time in the early 1950s. An later find is ''G. madiba'', which was found in South Africa in the 1960s. In the same locality another much larger erythrosuchid was also found, called '' Erythrosuchus africanus'', which was the one of the largest terrestrial predators of the Early Tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vjushkovia
''Garjainia'' is an extinct genus of erythrosuchid archosauriform reptile from the Olenekian of Russia and South Africa. It was approximately 1.50–2 m (5–6 ft 8 in) long. It contained two species, ''Garjainia prima'' from the Yarengian/Yarkenskian Supergorizont of Russia, and ''Garjainia madiba'' from the Burgersdorp Formation ( ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone A) of South Africa. "''Vjuskovia triplicostata''", a name assigned to some erythrosuchid fossils from Russia, has been synonymized with ''Garjainia prima''. Discovery ''Garjainia prima'' was first discovered in a small village in Russia by a farmer. The exact date of the discovery is not known but its believed to have been found some time in the early 1950s. An later find is ''G. madiba'', which was found in South Africa in the 1960s. In the same locality another much larger erythrosuchid was also found, called '' Erythrosuchus africanus'', which was the one of the largest terrestrial predators of the Early Tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garjainia Madiba
''Garjainia'' is an extinct genus of erythrosuchid archosauriform reptile from the Olenekian of Russia and South Africa. It was approximately 1.50–2 m (5–6 ft 8 in) long. It contained two species, ''Garjainia prima'' from the Yarengian/Yarkenskian Supergorizont of Russia, and ''Garjainia madiba'' from the Burgersdorp Formation ( ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone A) of South Africa. "''Vjuskovia triplicostata''", a name assigned to some erythrosuchid fossils from Russia, has been synonymized with ''Garjainia prima''. Discovery ''Garjainia prima'' was first discovered in a small village in Russia by a farmer. The exact date of the discovery is not known but its believed to have been found some time in the early 1950s. An later find is ''G. madiba'', which was found in South Africa in the 1960s. In the same locality another much larger erythrosuchid was also found, called '' Erythrosuchus africanus'', which was the one of the largest terrestrial predators of the Early Tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgersdorp Formation
The ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod biozone utilized in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. It is equivalent to the Burgersdorp Formation, the youngest lithostratigraphic formation in the Beaufort Group, which is part of the fossiliferous and geologically important Karoo Supergroup. The ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest of the eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be late Early Triassic (Olenekian) to early Middle Triassic (Anisian) in age (around 247 Ma). The name of the biozone refers to '' Cynognathus crateronotus'', a large and carnivorous cynodont therapsid which occurs throughout the entire biozone. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the current eight biozones were discovered by Andrew Geddes Bain in 1856. However, it was not until 1892 that it was observed that the geological strata of the Beaufort Group could be differentiated based on their fossil taxa. The initial underta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynognathus Assemblage Zone
The ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod biozone utilized in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. It is equivalent to the Burgersdorp Formation, the youngest lithostratigraphic formation in the Beaufort Group, which is part of the fossiliferous and geologically important Karoo Supergroup. The '' Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest of the eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be late Early Triassic (Olenekian) to early Middle Triassic (Anisian) in age (around 247 Ma). The name of the biozone refers to '' Cynognathus crateronotus'', a large and carnivorous cynodont therapsid which occurs throughout the entire biozone. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the current eight biozones were discovered by Andrew Geddes Bain in 1856. However, it was not until 1892 that it was observed that the geological strata of the Beaufort Group could be differentiated based on their fossil taxa. The initial undert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
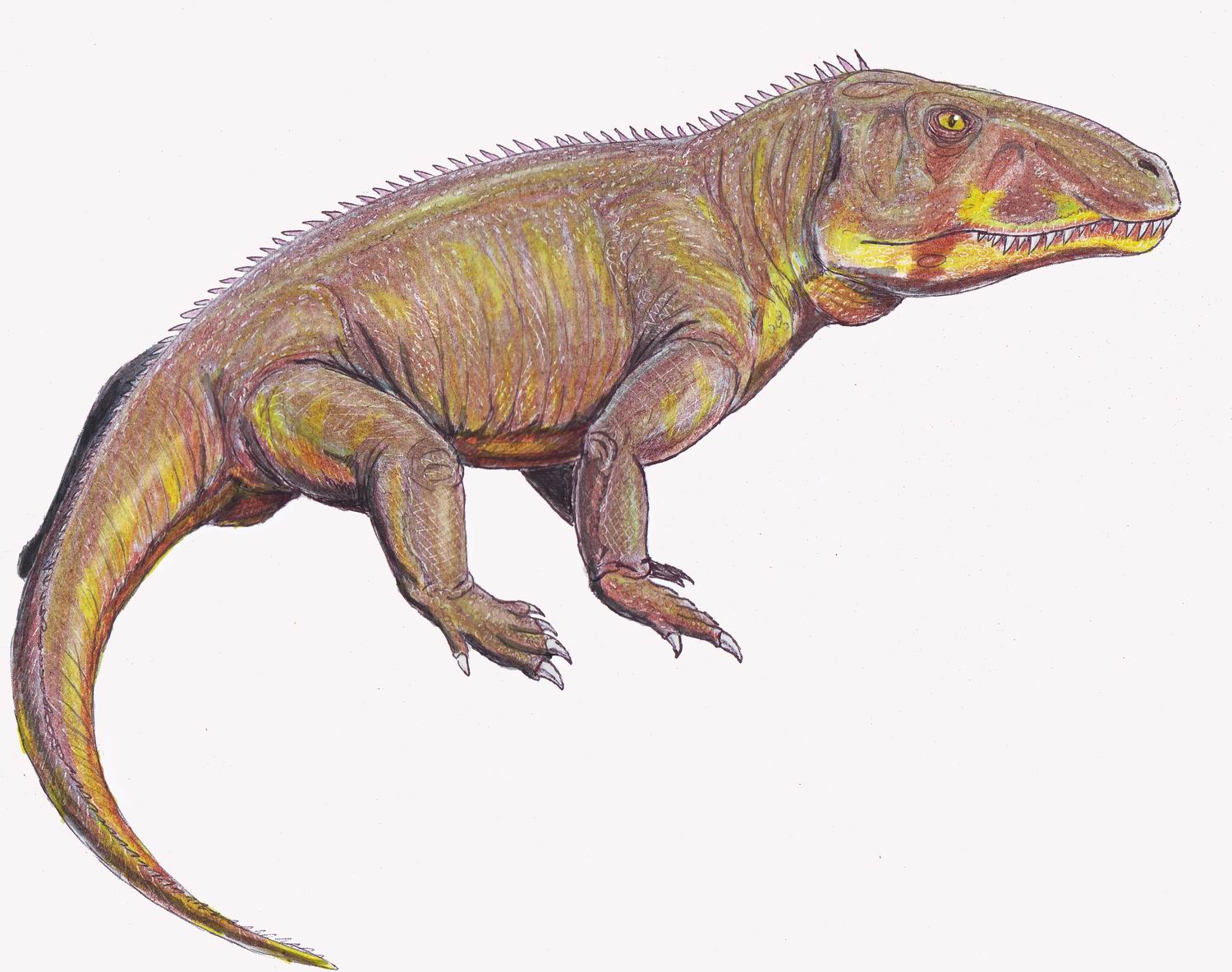
Erythrosuchids
Erythrosuchidae (meaning "red crocodiles" in Greek) are a family of large basal archosauriform carnivores that lived from the later Early Triassic (Olenekian) to the early Middle Triassic (Anisian). Naming The family Erythrosuchidae was named by David Meredith Seares Watson in 1917.D.M.S. Watson. 1917. "A sketch classification of the Pre-Jurassic tetrapod vertebrates". ''Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London'' 1917: 167–186 Description They were the apex predators of their day, with lengths of to almost . Their fossil remains are known to date from South Africa (Beaufort Group of the Karoo Basin), China, India and European Russia, from the Early to Middle Triassic. Erythrosuchids were unusually large and robust archosauromorphs. Several features set them apart from other archosauriformes and are also seen in later, more derived archosaurs. For example, they lack teeth on the palate, which are found in other early archosauriformes, such as ''Doswellia'' and eupark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrosuchidae
Erythrosuchidae (meaning "red crocodiles" in Greek) are a family of large basal archosauriform carnivores that lived from the later Early Triassic (Olenekian) to the early Middle Triassic (Anisian). Naming The family Erythrosuchidae was named by David Meredith Seares Watson in 1917.D.M.S. Watson. 1917. "A sketch classification of the Pre-Jurassic tetrapod vertebrates". ''Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London'' 1917: 167–186 Description They were the apex predators of their day, with lengths of to almost . Their fossil remains are known to date from South Africa (Beaufort Group of the Karoo Basin), China, India and European Russia, from the Early to Middle Triassic. Erythrosuchids were unusually large and robust archosauromorphs. Several features set them apart from other archosauriformes and are also seen in later, more derived archosaurs. For example, they lack teeth on the palate, which are found in other early archosauriformes, such as ''Doswellia'' and eupar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythrosuchid
Erythrosuchidae (meaning "red crocodiles" in Greek) are a family of large basal archosauriform carnivores that lived from the later Early Triassic (Olenekian) to the early Middle Triassic (Anisian). Naming The family Erythrosuchidae was named by David Meredith Seares Watson in 1917.D.M.S. Watson. 1917. "A sketch classification of the Pre-Jurassic tetrapod vertebrates". ''Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London'' 1917: 167–186 Description They were the apex predators of their day, with lengths of to almost . Their fossil remains are known to date from South Africa (Beaufort Group of the Karoo Basin), China, India and European Russia, from the Early to Middle Triassic. Erythrosuchids were unusually large and robust archosauromorphs. Several features set them apart from other archosauriformes and are also seen in later, more derived archosaurs. For example, they lack teeth on the palate, which are found in other early archosauriformes, such as ''Doswellia'' and eupark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fugusuchus
''Fugusuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform, probably the basal-most member of the family Erythrosuchidae. The genus is known from a single fossil from the middle Early Triassic Heshanggou Formation in Shanxi, China. The partial skeleton consists of an incomplete skull, parts of the right forelimb, and an intercentrum. The skeleton, known as GMB V 313, is currently in the Geological Museum of China in Beijing. ''Fugusuchus'' was a medium-sized archosauriform. It has a long and relatively low skull, unlike the higher more pointed skulls of related genera such as ''Erythrosuchus''. In ''Fugusuchus'', the tooth row of the upper jaw extends beneath the orbit, or eye socket. This feature distinguishes it from more advanced erythrosuchids such as ''Garjainia ''Garjainia'' is an extinct genus of erythrosuchid archosauriform reptile from the Olenekian of Russia and South Africa. It was approximately 1.50–2 m (5–6 ft 8 in) long. It contained two species, ''Garjainia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shansisuchus
''Shansisuchus'' (meaning "Shansi Province crocodile") is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile belonging to the family Erythrosuchidae that lived during the Middle Triassic in what is now China. The first fossils of ''Shansisuchus'' were discovered from the Ermaying Formation of Shansi Province in 1964 by Chinese paleontologist Yang Zhongjian. Like other erythrosuchids, ''Shansisuchus'' was a large-bodied carnivore with a large, deep skull. ''Shansisuchus'' is unique among early archosauriforms in having a hole in its skull called a subnarial fenestra. Description ''Shansisuchus'' is a large erythrosuchid distinguished from other members of the group by two characters: a tongue-and-groove articulation between the premaxilla and nasal bones of the skull and the presence of a subnarial fenestra. In ''Shansisuchus'' the premaxilla, a bone that makes up the front of the snout, projects backward and fits into a groove in the nasal, a bone that makes up the top of the snout. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterosuchus
''Proterosuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptiles that lived during the Early Triassic. It contains three valid species: the type species ''P. fergusi'' and the referred species ''P. alexanderi'' and ''P. goweri''. All three species lived in what is now South Africa. The genus was named in 1903 by the South African paleontologist Robert Broom. The well-known genus ''Chasmatosaurus'' is a junior synonym of ''Proterosuchus''. ''Proterosuchus'' was a mid-sized quadrupedal reptile with a sprawling stance that could reach a length of up to . It had a large head and distinctively hooked snout. It was a predator, which may have hunted prey such as ''Lystrosaurus''. The lifestyle of ''Proterosuchus'' remains debated; it may have been terrestrial or it may have been a semiaquatic ambush predator similar to modern crocodiles. ''Proterosuchus'' is one of the earliest members of the clade Archosauriformes, which also includes crocodilians, pterosaurs, and dinosaurs, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic Reptiles Of Africa
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia Other uses * ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early (name) * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early Records, a record label * the early part of the morning See also * Earley (other) Earley is a town in England. Earley may also refer to: * Earley (surname), a list of people with the surname Earley * Earley (given name), a variant of the given name Earlene * Earley Lake, a lake in Minnesota *Earley parser, an algorithm *Earley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about ance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |