|
Gangpunch (computing)
The IBM 101 Electronic Statistical Machine, introduced in 1952, combines in one unit the functions of Sorting algorithm, sorting, counting, accumulating, balancing, editing, and printing of summaries of facts recorded in Punched card, IBM cards. The 101 could sort cards based on multiple columns. For example, if a card had multiple 3-column test scores, the 101 could be wired to sort into pocket 0 those cards with no scores over 090, into pocket 1 those with one score over 090, and so on; logic limited only by the number of relays available. A. Ross Eckler suggests the development of the 101, with functions similar to earlier multicolumn sorters and unit counters developed by the Census Bureau, "was apparently a direct result of the transfer to IBM of Lawrence Wilson, who had served as chief of the Census Bureau's Machine Tabulation Division". Functions The following operations may be performed at the rate of 450 cards per minute: * Sort Punched cards, IBM cards into numeric or alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorting Algorithm
In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a List (computing), list into an Total order, order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending. Efficient sorting is important for optimizing the Algorithmic efficiency, efficiency of other algorithms (such as search algorithm, search and merge algorithm, merge algorithms) that require input data to be in sorted lists. Sorting is also often useful for Canonicalization, canonicalizing data and for producing human-readable output. Formally, the output of any sorting algorithm must satisfy two conditions: # The output is in monotonic order (each element is no smaller/larger than the previous element, according to the required order). # The output is a permutation (a reordering, yet retaining all of the original elements) of the input. Although some algorithms are designed for sequential access, the highest-performing algorithms assum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a stiff paper-based medium used to store digital information via the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Developed over the 18th to 20th centuries, punched cards were widely used for data processing, the control of automated machines, and computing. Early applications included controlling weaving looms and recording census data. Punched cards were widely used in the 20th century, where unit record equipment, unit record machines, organized into data processing systems, used punched cards for Input (computer science), data input, data output, and data storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and Data (computing), data. Punched cards were used for decades before being replaced by magnetic storage and terminals. Their influence persists in cultural references, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Cards
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a stiff paper-based medium used to store digital information via the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Developed over the 18th to 20th centuries, punched cards were widely used for data processing, the control of automated machines, and computing. Early applications included controlling weaving looms and recording census data. Punched cards were widely used in the 20th century, where unit record machines, organized into data processing systems, used punched cards for data input, data output, and data storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and data. Punched cards were used for decades before being replaced by magnetic storage and terminals. Their influence persists in cultural references, standardized data layouts, and computing conventions such as 80-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Tabulation
In statistics, a contingency table (also known as a cross tabulation or crosstab) is a type of table in a matrix format that displays the multivariate frequency distribution of the variables. They are heavily used in survey research, business intelligence, engineering, and scientific research. They provide a basic picture of the interrelation between two variables and can help find interactions between them. The term ''contingency table'' was first used by Karl Pearson in "On the Theory of Contingency and Its Relation to Association and Normal Correlation", part of the '' Drapers' Company Research Memoirs Biometric Series I'' published in 1904. A crucial problem of multivariate statistics is finding the (direct-)dependence structure underlying the variables contained in high-dimensional contingency tables. If some of the conditional independences are revealed, then even the storage of the data can be done in a smarter way (see Lauritzen (2002)). In order to do this one can use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
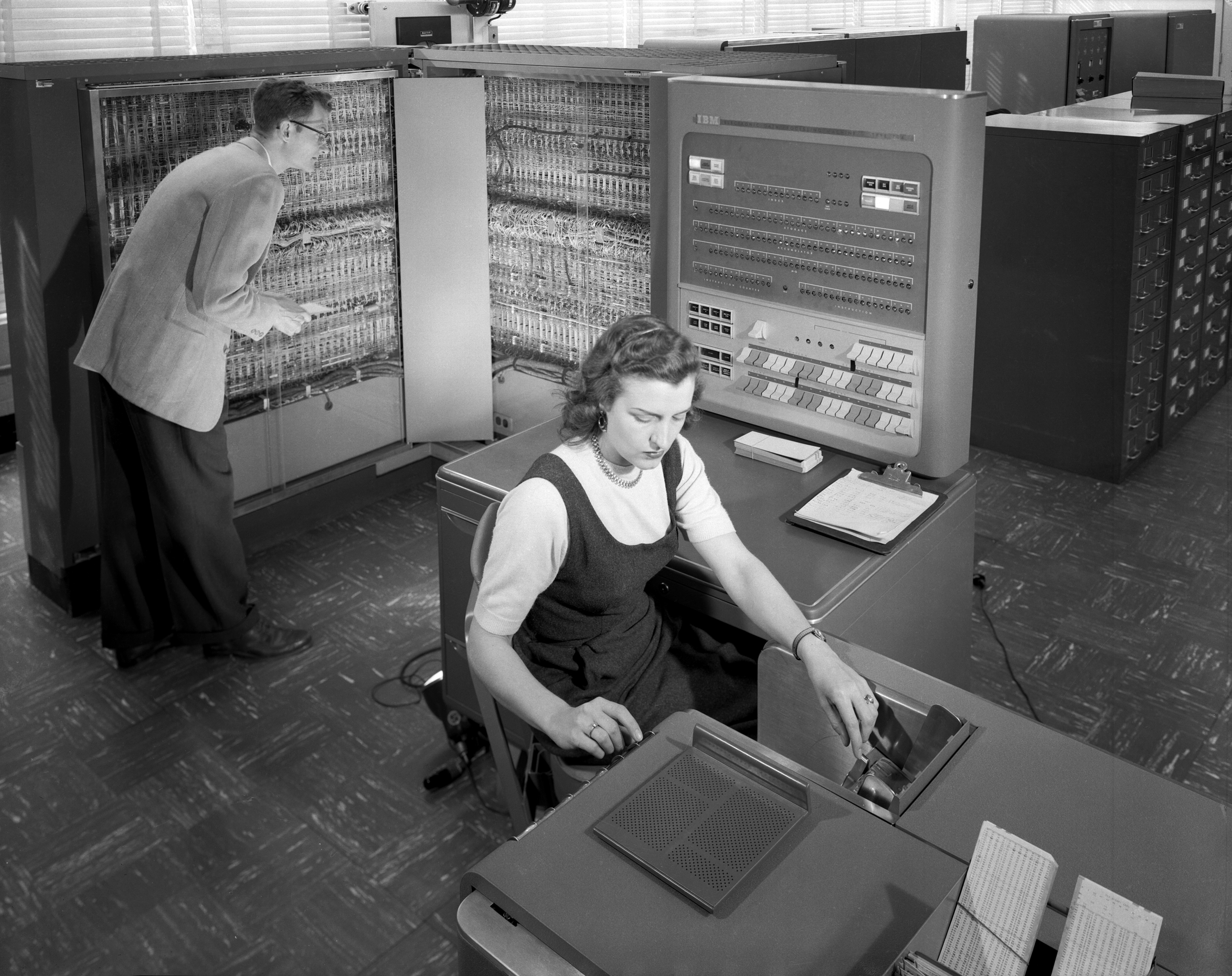
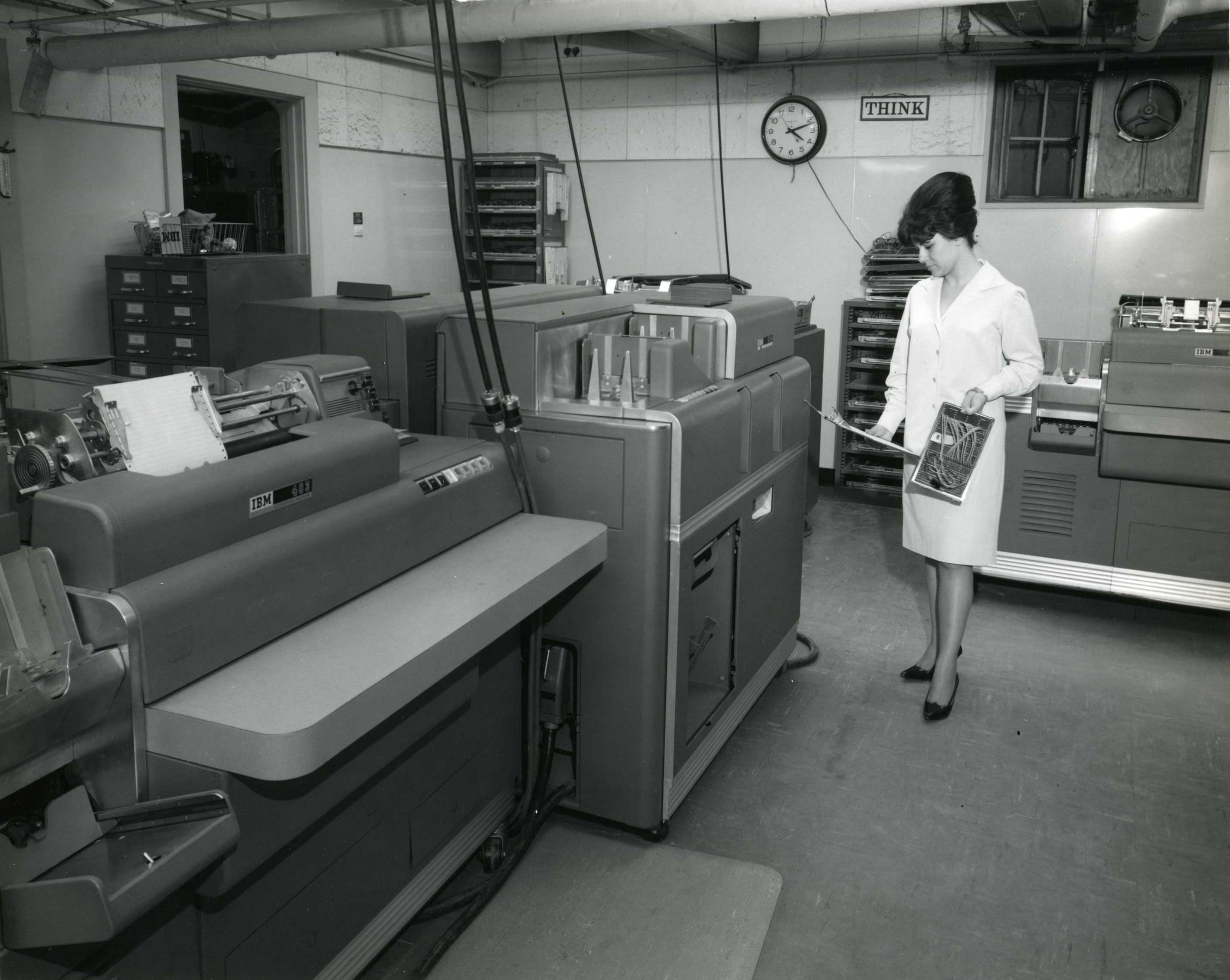
Unit Record Equipment
Starting at the end of the nineteenth century, well before the advent of electronic computers, data processing was performed using Electromechanics, electromechanical machines collectively referred to as unit record equipment, electric accounting machines (EAM) or tabulating machines. Unit record machines came to be as ubiquitous in industry and government in the first two-thirds of the twentieth century as computers became in the last third. They allowed large volume, sophisticated data-processing tasks to be accomplished before electronic computers were invented and while they were still in their infancy. This data processing was accomplished by processing punched cards through various unit record machines in a carefully choreographed progression. This progression, or flow, from machine to machine was often planned and documented with detailed flowcharts that used standardized symbols for documents and the various machine functions. All but the earliest machines had high-speed me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 524
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is a publicly traded company and one of the 30 companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average. IBM is the largest industrial research organization in the world, with 19 research facilities across a dozen countries; for 29 consecutive years, from 1993 to 2021, it held the record for most annual U.S. patents generated by a business. IBM was founded in 1911 as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR), a holding company of manufacturers of record-keeping and measuring systems. It was renamed "International Business Machines" in 1924 and soon became the leading manufacturer of punch-card tabulating systems. During the 1960s and 1970s, the IBM mainframe, exemplified by the System/360 and its successors, was the world's dominant computing platform, with the company p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plugboard
A plugboard or control panel (the term used depends on the application area) is an array of jack (connector), jacks or sockets (often called hubs) into which patch cords can be inserted to complete an electrical circuit. Control panels are sometimes used to direct the operation of unit record equipment, :Cryptographic hardware, cipher machines, and History of computing hardware#Digital computation, early computers. The array of holes is often contained in a flat removable panel that can be inserted into a machine and pressed against an array of contacts. This allows the machine to be quickly switched between different applications. The contacts on the machine are hard wired to the various devices that comprise the machine, such as relays, counters, inputs from each card reader column, outputs to a card punch column or printer position, and so on. The wiring on a plugboard connects these devices to perform a specific function, say reading cards and summing up the numbers punched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM 514
The IBM 519 Document-Originating Machine, introduced in 1946, was the last in a series of unit record machines designed for automated preparation of punched cards. Others in the series included the IBM 513 & IBM 514 Reproducing Punch. The 519, which was "state of the art for the time", could: * reproduce all or parts of the information on a set of cards * " gangpunch" - copy information from a master card into the following detail cards * print up to eight digits on the end of a card * compare two decks of cards * "summary punch" — create punch cards containing summary information provided by a connected accounting machine, such as totals from a group of processed cards * "mark sense" — detect marks made with an electrographic pencil in designated locations on a punched card and then punch holes corresponding to those marks into the card * number cards consecutively (an optional feature) The reproducing, gangpunching, summary punching, and comparing features of the IBM 519 ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a stiff paper-based medium used to store digital information via the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Developed over the 18th to 20th centuries, punched cards were widely used for data processing, the control of automated machines, and computing. Early applications included controlling weaving looms and recording census data. Punched cards were widely used in the 20th century, where unit record equipment, unit record machines, organized into data processing systems, used punched cards for Input (computer science), data input, data output, and data storage. The IBM 12-row/80-column punched card format came to dominate the industry. Many early digital computers used punched cards as the primary medium for input of both computer programs and Data (computing), data. Punched cards were used for decades before being replaced by magnetic storage and terminals. Their influence persists in cultural references, sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |