|
Gandhara Grave Culture
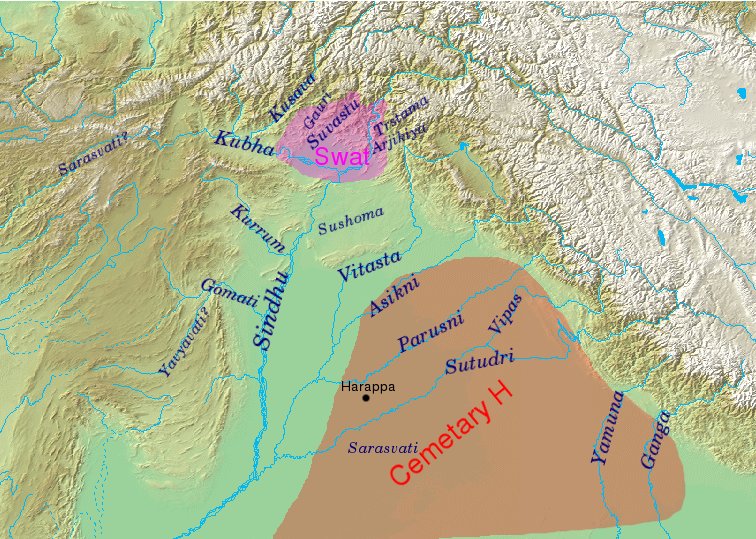
The Gandhara grave culture, also called Swat culture, or Swat Protohistoric Graveyards Complex, emerged ''c.'' 1400 BCE and lasted until 800 BCE, as recent fieldwork, along with subsequent analyses, have shown there are no burials with these features after 800 BCE. It is found in Middle Swat River course, even though earlier research considered it to be expanded to the Valleys of Dir, Kunar, Chitral, and Peshawar. It has been regarded as a token of the Indo-Aryan migrations, but has also been explained by local cultural continuity. Backwards projections, based on ancient DNA analyses, suggest ancestors of Swat culture people mixed with a population coming from the Inner Asian Mountain Corridor, which carried Steppe ancestry, sometime between 1900 and 1500 BCE. Location and characteristics Relevant finds, artifacts found primarily in graves, were distributed along the banks of the Swat and Dir rivers in the north, Taxila in the southeast, along the Gomal River to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigvedic Geography
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum. The ''Rigveda'' is the oldest known Vedic Sanskrit text. Its early layers are among the oldest extant texts in any Indo-European language. The sounds and texts of the ''Rigveda'' have been orally transmitted since the 2nd millennium BCE. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the bulk of the ''Rigveda'' Samhita was composed in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent (see) Rigvedic rivers), most likely between 1500 and 1000 BCE, although a wider approximation of 19001200 BCE has also been given. The text is layered, consisting of the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the Haripur District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. In 326 BCE, Alexander the Great gained control of the city without a battle, as it was immediately surrendered to him by Omphis. Old Taxila was an important city of ancient India, situated on the eastern shore of the Indus River—the pivotal junction of the Indian subcontinent and Central Asia;Raymond Allchin, Bridget Allchin''The Rise of Civilization in India and Pakistan''.Cambridge University Press, 1982 p.127 it was founded around 1000 BCE. Some ruins at Taxila date to the time of the Achaemenid Persian Empire, followed successively by the Maurya Empire, the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the Indo-Scythians, and the Kushan Empire. Owing to its strategic location, Taxila has ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Languages
The Indo-Aryan languages (or sometimes Indic languages) are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Maldives. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages. Modern Indo-Aryan languages descend from Old Indo-Aryan languages such as early Vedic Sanskrit, through Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Prakrits). The largest such languages in terms of first-speakers are Hindi–Urdu (),Standard Hindi first language: 260.3 million (2001), as second language: 120 million (199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upinder Singh
Upinder Singh is an Indian historian who is Professor of History and Dean of Faculty at Ashoka University. She is the former head of the History Department at the University of Delhi. She is also the recipient of the inaugural Infosys Prize in the category of Social Sciences (History).The Infosys Prize in Social Sciences – History Education and professional life Singh is an alumna of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronovo Culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo Problem: Studies of Cultural Genesis in the Eurasian Bronze Age" in Open Archaeology 2021 (7), p.3: "...By Andronovo cultures we may understand only Fyodorovka and Alakul cultures..."Parpola, Asko, (2020)"Royal 'Chariot' Burials of Sanauli near Delhi and Archaeological Correlates of Prehistoric Indo-Iranian Languages" in Studia Orientalia Electronica, Vol. 8, No. 1, Oct 23, 2020, p.188: "...the Alakul’ culture (c.2000–1700 BCE) in the west and the Fëdorovo culture (c.1850–1450 BCE) in the east..." in western Siberia and the central Eurasian Steppe. Some researchers have preferred to term it an archaeological complex or archaeological horizon. The slightly older Sintashta culture (2050–1900 BC), formerly included within the Androno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, southwestern Tajikistan and southeastern Uzbekistan. Called "beautiful Bactria, crowned with flags" by the Avesta, the region is one of the sixteen perfect Iranian lands that the supreme deity Ahura Mazda had created. One of the early centres of Zoroastrianism and capital of the legendary Kayanian kings of Iran, Bactria is mentioned in the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great as one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire; it was a special satrapy and was ruled by a crown prince or an intended heir. Bactria was the centre of Iranian resistance against the Macedonian invaders after the fall of the Achaemenid Empire in the 4th century BC, but eventually fell to Alexander the Great. After the death of Alexander, Bactria was annex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishkent Culture
The Bishkent culture or Beshkent culture is a late Bronze Age archaeological culture of southern Tajikistan, dating to c. 1700 – 1500 BC. It is primarily known from its cemeteries, which appear to have been used by mobile pastoralists. The Bishkent culture has been seen as a possible contributor to the Swat culture, which in turn is often associated with early Indo-Aryan movements into northwest India. See also * Vakhsh culture The Vakhsh culture is a Bronze Age culture which took place around 2500-1650 BC, as shown by radiocarbon dates, and flourished along the lower Vakhsh River in southern Tajikistan, earlier thought to be from ca. 1700 BC to 1500 BC. Earlier resear ... * Chust culture * Yaz culture Sources * Archaeological cultures of South Asia Bronze Age cultures of Asia Indo-Aryan archaeological cultures Iron Age cultures of Asia Archaeological cultures in Tajikistan {{Tajikistan-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vakhsh Culture
The Vakhsh culture is a Bronze Age culture which took place around 2500-1650 BC, as shown by radiocarbon dates, and flourished along the lower Vakhsh River in southern Tajikistan, earlier thought to be from ca. 1700 BC to 1500 BC. Earlier research seemed to show that Vakhsh culture had appeared somewhat later than the Bishkent culture, with which it shares many similarities. Settlements Evidence of settlements in the Vakhsh culture is scant. They made stone walls and mud-brick constructions. Houses on the site at Kangurt Tut in the Vaksh valley contained storage pits for grain and hearths. The grain storages had barley and wheat. Faunal remains have revealed dogs, deer, camels, donkeys, horses, sheep and goats.Mallory, J. P., & Douglas Q. Adams, (1997)"Vaksh Culture" in Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Taylor & Francis, p. 617. Burials The Vaksh culture is known chiefly for its burials. These were catacomb graves covered entirely over with a mound, and entrance shafts blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemetery H
The Cemetery H culture was a Bronze Age culture in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, from about 1900 BC until about 1300 BC. It is regarded as a regional form of the late phase of the Harappan (Indus Valley) civilisation (alongside the Jhukar culture of Sindh and Rangpur culture of Gujarat), but also as the manifestation of a first wave of Indo-Aryan migrations, predating the migrations of the proto-Rig Vedic people. Origins The Cemetery H culture was located in and around the Punjab region in present-day India and Pakistan. It was named after a cemetery found in "area H" at Harappa. Remains of the culture have been dated from about 1900 BC until about 1300 BC. According to Rafique Mughal, the Cemetery H culture developed out of the northern part of the Indus Valley civilization around 1700 BC, being part of the Punjab Phase, one of three cultural phases that developed in the Localization Era or "Late Harappan phase" of the Indus Valley T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asko Parpola
Asko Parpola (born 12 July 1941, in Forssa) is a Finnish Indologist, current professor emeritus of South Asian studies at the University of Helsinki The University of Helsinki ( fi, Helsingin yliopisto, sv, Helsingfors universitet, abbreviated UH) is a public research university located in Helsinki, Finland since 1829, but founded in the city of Turku (in Swedish ''Åbo'') in 1640 as the .... He specializes in Sindhology, specifically the study of the Indus script. Biography Parpola is a brother of the Akkadian language epigrapher Simo Parpola. He is married to Marjatta Parpola, who has authored a study on the traditions of Kerala's Nambudiri Brahmins. Scholarship Parpola's research and teaching interests fall within the following topics: * Indus Civilization / Indus script and religion / Corpus of Indus Seals and Inscriptions * Veda / Vedic ritual / Samaveda / Jaiminiya Samaveda texts and rituals / Purva-Mimamsa * South Asian religions / Hinduism / Saiva and Sakta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tureng Teppe
Tureng Tepe ( fa, تورنگ تپه, "Hill of the Pheasants"; alternatively spelled in English as Turang Tappe/Tape/Tappa/Tappeh) is a Neolithic and Chalcolithic archaeological site in northeastern Iran, in the Gorgan plain, approximately 17 km northeast of the town of Gorgan. Nearby is a village of Turang Tappeh. Description Tureng Tepe consists of a group of mounds interspersed with ponds and water courses. The whole archaeological pattern is about 800 – 900 m in diameter. Most of the mounds rise between 11 and 15 m above the level of the surrounding plan, but the steep central mound, marked A on the Wulsin's plan, is over 30 m high and dominated the entire site. The oldest remains on the site date to the Neolithic and Chalcolithic periods. The Bronze Age settlement portion of the site dates from approximately 3100-2900 BC through 1900 BC.Moreau, KathyTureng Tepe, Iran expedition records (finding aid)(University of Pennsylvania, Penn Museum Archives, 2010), Retrieved J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tepe Hissar
Tepe Hissar (also spelled Tappeh Hesār) is a prehistoric site located in the village Heydarabad just south of Damghan in Semnan Province in northeastern Iran. The site is notable for its uninterrupted occupational history from the 5th to the 2nd millennium BCE. The quantity and elaborateness of its excavated artifacts and funerary customs position the site prominently as a cultural bridge between Mesopotamia and Central Asia. Archaeology The overall site covers 200 hectares including multiple mounds and several middle Islamic fortresses. The main tell has an extent of 12 hectares. The site was firstly discovered in 1877 by Albert Houtum-Schindler and then investigated in 1931 and 1932 by Erich Schmidt, on behalf of the University of Pennsylvania Museum (Schmidt 1933). A surface survey was carried out in 1972, while in 1976 a re-study project was performed, utilizing modern methods of stratigraphic assessments, ceramic typological analysis and radiocarbon dating, by the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)






