|
Gammacoronavirus
''Gammacoronavirus'' (Gamma-CoV) is one of the four genera (''Alpha''-, '' Beta-'', ''Gamma-'', and '' Delta-'') of coronaviruses. It is in the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'' of the family ''Coronaviridae''. They are enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses of zoonotic origin. Coronaviruses infect both animals and humans. While the alpha and beta genera are derived from the bat gene pool, the gamma and delta genera are derived from the avian and pig gene pools. Gamma-CoV also known as coronavirus group 3 are the avian coronaviruses. See also *Animal viruses * Positive/negative-sense *RNA virus An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses ... References External links CoronavirusesVirus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource (ViPR): Coronaviridae {{Taxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronaviruses
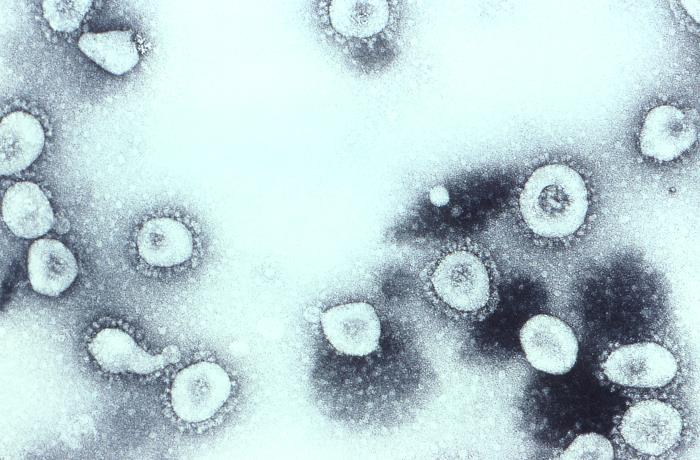
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family ''Coronaviridae'', order ''Nidovirales'' and realm ''Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which in electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthocoronavirinae
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family ''Coronaviridae'', order '' Nidovirales'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which in el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold (which is also caused by other viruses, predominantly rhinoviruses), while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19, which is causing the ongoing pandemic. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis. Coronaviruses constitute the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'', in the family ''Coronaviridae'', order '' Nidovirales'' and realm '' Riboviria''. They are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genome size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, one of the largest among RNA viruses. They have characteristic club-shaped spikes that project from their surface, which in electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avian Coronavirus
''Avian coronavirus'' is a species of virus from the genus ''Gammacoronavirus'' that infects birds; since 2018, all gammacoronaviruses which infect birds have been classified as this single species. The strain of avian coronavirus previously known as infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) is the only coronavirus that infects chickens. It causes avian infectious bronchitis, a highly infectious disease that affects the respiratory tract, gut, kidney and reproductive system. IBV affects the performance of both meat-producing and egg-producing chickens and is responsible for substantial economic loss within the poultry industry. The strain of avian coronavirus previously classified as Turkey coronavirus causes gastrointestinal disease in turkeys. Classification IBV is in the genus ''Gammacoronavirus'', or group 3, with a non-segmented, positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome. It was previously the type species of its genus '' Igacovirus''. When there was only one genus of coronavir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphacoronavirus
Alphacoronaviruses (Alpha-CoV) are members of the first of the four genera (''Alpha''-, '' Beta-'', '' Gamma-'', and '' Delta-'') of coronaviruses. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses that infect mammals, including humans. They have spherical virions with club-shaped surface projections formed by trimers of the spike protein, and a viral envelope. Alphacoronaviruses are in the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'' of the family ''Coronaviridae''. Both the ''Alpha''- and ''Betacoronavirus'' lineages descend from the bat viral gene pool. Alphacoronaviruses were previously known as "phylogroup 1 coronaviruses". The Alphacoronavirus genus is very diverse, particularly in bats. Most bat originating strains haven't been successfully isolated and cultured in laboratory. Alphacoronaviruses infecting other mammal species have been much better studied, see List of Coronavirus live isolates. Etymology The name alphacoronavirus is derived from Ancient Greek ἄλφα ( álp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deltacoronavirus (genus)
''Deltacoronavirus'' (Delta-CoV) is one of the four Genus, genera (''Alphacoronavirus, Alpha-'', ''Betacoronavirus, Beta-'', ''Gammacoronavirus, Gamma-'', and ''Delta-'') of coronaviruses. It is in the subfamily ''Orthocoronavirinae'' of the family ''Coronaviridae''. They are Viral envelope, enveloped, Sense (molecular biology), positive-sense, Base pair, single-stranded RNA viruses. Deltacoronaviruses infect mostly birds and some mammals. While the alpha and beta genera are derived from the Bat virome, bat viral gene pool, the gamma and delta genera are derived from the avian and pig viral gene pools. Genetic recombination, Recombination appears to be common among deltacoronaviruses.Lau SKP, Wong EYM, Tsang CC, Ahmed SS, Au-Yeung RKH, Yuen KY, Wernery U, Woo PCY. Discovery and Sequence Analysis of Four Deltacoronaviruses from Birds in the Middle East Reveal Interspecies Jumping with Recombination as a Potential Mechanism for Avian-to-Avian and Avian-to-Mammalian Transmission. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igacovirus
''Igacovirus'' is a subgenus of viruses in the genus ''Gammacoronavirus''. Species The genus consists of the following three species: * ''Avian coronavirus'' * ''Avian coronavirus 9203'' * ''Duck coronavirus 2714 ''Duck coronavirus 2714'' is a species of coronavirus in the genus ''Gammacoronavirus ''Gammacoronavirus'' (Gamma-CoV) is one of the four genera (''Alpha''-, '' Beta-'', ''Gamma-'', and '' Delta-'') of coronaviruses. It is in the subfamily ' ...'' References Virus subgenera Gammacoronaviruses {{Virus-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Virology
Veterinary virology is the study of viruses in non-human animals. It is an important branch of veterinary medicine. Rhabdoviruses Rhabdoviruses are a diverse family of single stranded, negative sense RNA viruses that infect a wide range of hosts, from plants and insects, to fish and mammals. The ''Rhaboviridae'' family consists of six genera, two of which, cytorhabdoviruses and nucleorhabdoviruses, only infect plants. Novirhabdoviruses infect fish, and vesiculovirus, lyssavirus and ephemerovirus infect mammals, fish and invertebrates. The family includes pathogens such as rabies virus, vesicular stomatitis virus and potato yellow dwarf virus that are of public health, veterinary, and agricultural significance. Foot-and-mouth disease virus Foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) is a member of the Aphthovirus genus in the Picornaviridae family and is the cause of foot-and-mouth disease in pigs, cattle, sheep and goats. It is a non-enveloped, positive strand, RNA virus. FMDV is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. Typically, the first infected human transmits the infectious agent to at least one other human, who, in turn, infects others. Major modern diseases such as Ebola virus disease and salmonellosis are zoonoses. HIV was a zoonotic disease transmitted to humans in the early part of the 20th century, though it has now evolved into a separate human-only disease. Most strains of influenza that infect humans are human diseases, although many strains of bird flu and swine flu are zoonoses; these viruses occasionally recombine with human strains of the flu and can cause pandemics such as the 1918 Spanish flu or the 2009 swine flu. ''Taenia solium'' infection is one of the neglected tropical diseases with public health and veterinary concern in en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Virus
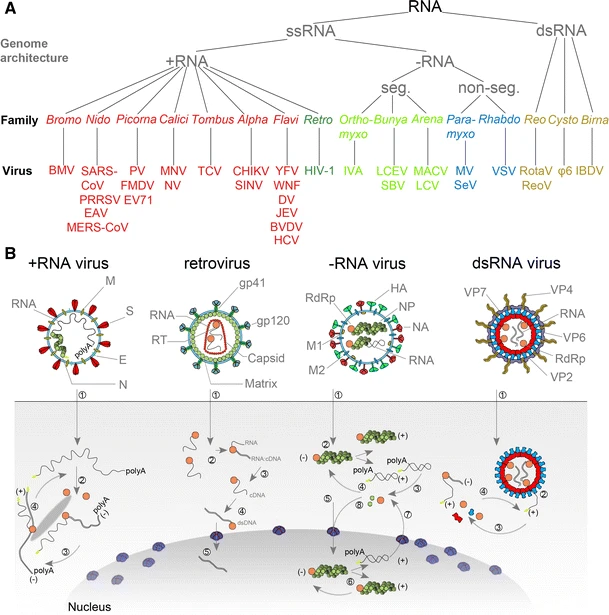
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA ( ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) classifies RNA viruses as those that belong to ''Group III'', ''Group IV'' or ''Group V'' of the Baltimore classification system. This category excludes ''Group VI'', viruses with RNA genetic material but which use DNA intermediates in their life cycle: these are called retroviruses, including HIV-1 and HIV-2 which cause AIDS. As of May 2020, all known RNA viruses encoding an RNA-directed RNA polymerase are believed to form a monophyletic group, known as the realm '' Riboviria''. The majority of such RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |