|
Galvani Potential
In electrochemistry, the Galvani potential (also called Galvani potential difference, or inner potential difference, Δφ, delta phi) is the electric potential difference between two points in the bulk of two phases. These phases can be two different solids (e.g., two metals joined), or a solid and a liquid (e.g., a metal electrode submerged in an electrolyte). The Galvani potential is named after Luigi Galvani. Galvani potential between two metals First, consider the Galvani potential between two metals. When two metals are electrically isolated from each other, an arbitrary voltage difference may exist between them. However, when two different metals are brought into electronic contact, electrons will flow from the metal with a lower voltage to the metal with the higher voltage until the Fermi level of the electrons in the bulk of both phases are equal. The actual numbers of electrons that passes between the two phases is small (it depends on the capacitance between the objects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvani Volta Surface Potential
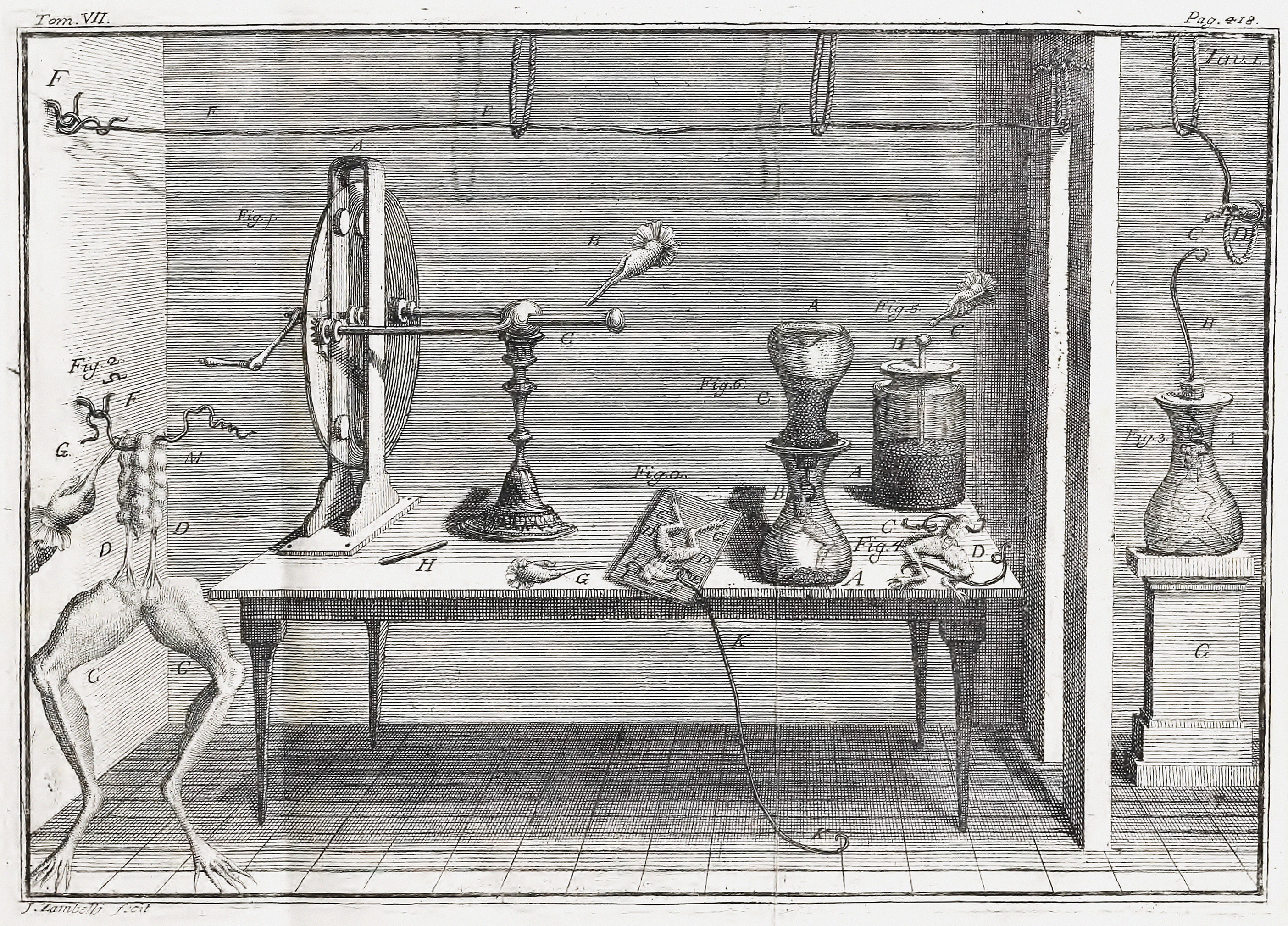
Luigi Galvani ( , , ; ; 9 September 1737 – 4 December 1798) was an Italian physician, physicist, biologist and philosopher who studied animal electricity. In 1780, using a frog, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs twitched when struck by an electrical spark. This was an early study of bioelectricity, following experiments by John Walsh and Hugh Williamson. Early life Luigi Galvani was born to Domenico Galvani and Barbara Caterina Foschi, in Bologna, then part of the Papal States. The house in which he was born may still be seen on Via Marconi, 25, in the center of Bologna. Domenico was a goldsmith. His family had produced several illustrious men. Galvani then began taking an interest in the field of "medical electricity". This field emerged in the middle of the 18th century, following electrical researches and the discovery of the effects of electricity on the human body by scientists including Bertrand Bajon and Ramón María Termeyer in the 1760s, and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical Potential
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the aforementioned electronically conducting circuit. This phenomenon is what distinguishes an electrochemical reaction from a conventional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donnan Potential
Donnan potential is the difference in the Galvani potentials which appears as a result of Donnan equilibrium, named after Frederick G. Donnan, which refers to the distribution of ion species between two ionic solutions separated by a semipermeable membrane or boundary.{{GoldBookRef , title=Donnan emf (Donnan potential) , file=MD01830 The boundary layer maintains an unequal distribution of ionic solute concentration by acting as a selective barrier to ionic diffusion. Some species of ions may pass through the barrier while others may not. The solutions may be gels or colloids as well as ionic liquids, and as such the phase boundary between gels or a gel and a liquid can also act as a selective barrier. The Electric potential that arises between two solutions is called Donnan potential. Donnan equilibrium is prominent in the triphasic model for articular cartilage proposed by Mow and Ratcliffe, as well as in electrochemical fuel cells and dialysis. The Donnan effect is extra o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volta Potential
The Volta potential (also called Volta effect, Volta potential difference, contact potential difference, outer potential difference, Δψ, or "delta psi") in electrochemistry, is the electrostatic potential difference between two metals (or one metal and one electrolyte) that are in contact and are in thermodynamic equilibrium. Specifically, it is the potential difference between a point close to the surface of the first metal and a point close to the surface of the second metal (or electrolyte). The Volta potential is named after Alessandro Volta. Description When two metals are electrically isolated from each other, an arbitrary potential difference may exist between them. However, when two different neutral metal surfaces are brought into electrical contact (even indirectly, say, through a long electro-conductive wire), electrons will flow from the metal with the higher Fermi level to the metal with the lower Fermi level until the Fermi levels in the two phases are equal. On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITIES
In electrochemistry, ITIES (interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions) is an electrochemical interface that is either polarisable or polarised. An ITIES is polarisable if one can change the Galvani potential difference, or in other words the difference of inner potentials between the two adjacent phases, without noticeably changing the chemical composition of the respective phases (i.e. without noticeable electrochemical reactions taking place at the interface). An ITIES system is polarised if the distribution of the different charges and redox species between the two phases determines the Galvani potential difference. Usually, one electrolyte is an aqueous electrolyte composed of hydrophilic ions such as NaCl dissolved in water and the other electrolyte is a lipophilic salt such as tetrabutylammonium tetraphenylborate dissolved in an organic solvent immiscible with water such as nitrobenzene, or 1,2-dichloroethane. Charge transfer reactions of an ITIES Three major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode Potential
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a Electronic circuit, circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a variety of materials (chemicals) depending on the type of cell. An electrode may be called either a cathode or anode according to the direction of the electric current, unrelated to the potential difference between electrodes. Michael Faraday coined the term "" in 1833; the word recalls the Greek ἤλεκτρον (, "amber") and ὁδός (, "path, way"). The Electrophorus, electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke in 1762, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any Electric battery, battery. The first electrochemical battery was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absolute Electrode Potential
Absolute electrode potential, in electrochemistry, according to an IUPAC definition, is the electrode potential of a metal measured with respect to a universal reference system (without any additional metal–solution interface). Definition According to a more specific definition presented by Trasatti, the absolute electrode potential is the difference in electronic energy between a point inside the metal (Fermi level) of an electrode and a point outside the electrolyte in which the electrode is submerged (an electron at rest in vacuum just above the electrolyte surface). This potential is difficult to determine accurately. For this reason, a standard hydrogen electrode is typically used for reference potential. The absolute potential of the SHE is 4.44 ± 0.02 V at 25 °C. Therefore, for any electrode at 25 °C: :E^M_ = E^M_+(4.44 \pm 0.02)\ where: : is electrode potential :V is the unit volt :''M'' denotes the electrode made of metal M :(abs) denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvanic Cell
A galvanic cell or voltaic cell, named after the scientists Luigi Galvani and Alessandro Volta, respectively, is an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous oxidation–reduction reactions. An example of a galvanic cell consists of two different metals, each immersed in separate beakers containing their respective metal ions in solution that are connected by a salt bridge or separated by a porous membrane. Volta was the inventor of the voltaic pile, the first electrical battery. Common usage of the word ''battery'' has evolved to include a single Galvanic cell, but the first batteries had many Galvanic cells. History In 1780, Luigi Galvani discovered that when two different metals (e.g., copper and zinc) are in contact and then both are touched at the same time to two different parts of a muscle of a frog leg, to close the circuit, the frog's leg contracts. He called this " animal electricity". The frog's leg, as well as being a detector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Constant
In physical chemistry, the Faraday constant (symbol , sometimes stylized as ℱ) is a physical constant defined as the quotient of the total electric charge () by the amount () of elementary charge carriers in any given sample of matter: it is expressed in units of coulombs per mole (C/mol). As such, it represents the " molar elementary charge", that is, the electric charge of one mole of elementary carriers (e.g., protons). It is named after the English scientist Michael Faraday. Since the 2019 revision of the SI, the Faraday constant has an exactly defined value, the product of the elementary charge (, in coulombs) and the Avogadro constant (, in reciprocal moles): : Derivation The Faraday constant can be thought of as the proportionality factor between the charge in coulombs (used in physics and in practical electrical measurements) and the amount of substance in moles (used in chemistry), and is therefore of particular use in electrochemistry, particularly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Potential
In thermodynamics, the chemical potential of a Chemical specie, species is the energy that can be absorbed or released due to a change of the particle number of the given species, e.g. in a chemical reaction or phase transition. The chemical potential of a species in a mixture is defined as the rate of change of Thermodynamic free energy, free energy of a thermodynamic system with respect to the change in the number of atoms or molecules of the species that are added to the system. Thus, it is the partial derivative of the free energy with respect to the amount of the species, all other species' concentrations in the mixture remaining constant. When both temperature and pressure are held constant, and the number of particles is expressed in moles, the chemical potential is the partial Molar concentration, molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibrium, the total sum of the product of chemical potentials and stoichiometric coefficients is zero, as the free en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Layer (surface Science)
Double layer may refer to: * Double layer (biospecific), the surface where two different phases of matter are in contact * Double layer (plasma physics), a structure in a plasma and consists of two parallel layers with opposite electrical charge * Double layer (surface science), a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is placed into a liquid * Double layer forces, which occur between charged objects across liquids * Double layer potential, a solution of Laplace's equation * Double layer suturing, two layers of sutures, first in a deep level of a tissue and then at a more superficial level * DVD+R DL or Double layer, a DVD format {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between Electric potential, electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve Electron, electrons moving via an electronically conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in Electroless nickel-phosphorus plating, electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic chemical species, species in a Solution (chemistry), solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical Voltage, potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the aforementioned electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |