|
Galapagar
Galapagar is a town and municipality northwest of Madrid, Spain, situated in the autonomous community of the Community of Madrid. Of all the towns in the area, it was experiencing the most growth, mostly because of immigration and the conversion of old livestock fields into terrain for construction. The name Galapagar comes from the Spanish ''galápago'', meaning turtle, as the town centre was settled near a lake full of turtles. The town first appears as a village in the eleventh century, its importance due to the frequent hunting expeditions by the Spanish royalty, and being a main stop on the road from the capital to the Royal Monastery of San Lorenzo de El Escorial. Sights in the town include the church of The Asunción (Assumption). Galapagar is served by lines C-3, C-8 and C-10 of the Cercanías Madrid commuter rail service at its Galapagar-La Navata train station; and by 9 lines of Interurban Bus Service linking it to Moncloa district of Madrid. Jacinto Benavente, one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Negrales
Los Negrales is a residential zone in the municipal area of Collado Villalba, Alpedrete, Saint Lorenzo de El Escorial, Guadarrama and Galapagar (municipalities of the northwest of the Community of Madrid, Spain), consisting mostly of detached houses. Although it was divided in three administrative zones, Los Negrales is a contiguous residential area. This residential zone was built gradually. The oldest houses date to the first half of the 20th century, and building has continued until contemporary times. A significant part of the houses are second residences of their owners, therefore, in summer and in holidays the population doubles. Los Negrales is situated near the Sierra de Guadarrama and near the centre of Collado Villalba, which makes it a favorable place to spend the holidays. The short distance to Collado Villalba facilitates shopping and leisure. Los Negrales has considerable public facilities (parish church, public schools, a sports center, a municipal park and a phar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones develop from ribs that grow sideways and develop into broad flat plates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Tomás (bullfighter)
José Tomás Pérez Sellés (26 August 1934, in Alicante – 7 August 2001) was a Spanish classical guitarist and teacher. Considered a major influence on the evolution of classical guitar technique in the second half of the 20th century, he trained many guitarists from all over the world.Iborra, Mario Alcaraz and Soto, Roberto Díaz''La guitarra: Historia, organología y repertorio'' Editorial Club Universitario, 2009, p. 170. (in Spanish) Biography José Tomás began his musical studies with Óscar Esplá. He would later transcribe Esplá's piano suite, ''Levante'', for the guitar as well as re-discover and transcribe Esplá's previously unknown work, ''Tempo di Sonata''. The sonata, originally composed for the harp, was given its first performance in 1978 by Tomás himself. Tomás was initially a self-taught guitarist, but then continued his studies with Regino Sainz de la Maza, Emilio Pujol, and Alirio Diaz. On Diaz's recommendation, he went to study with Andrés Segovia in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock-breeding
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starting with the Neolithic Revolution when animals were first domesticated, from around 13,000 BC onwards, predating farming of the first crops. By the time of early civilisations such as ancient Egypt, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs were being raised on farms. Major changes took place in the Columbian exchange, when Old World livestock were brought to the New World, and then in the British Agricultural Revolution of the 18th century, when livestock breeds like the Dishley Longhorn cattle and Lincoln Longwool sheep were rapidly improved by agriculturalists, such as Robert Bakewell, to yield more meat, milk, and wool. A wide range of other species, such as horse, water buffalo, llama, rabbit, and guinea pig, are used as livestock in some pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullfighting
Bullfighting is a physical contest that involves a bullfighter attempting to subdue, immobilize, or kill a bull, usually according to a set of rules, guidelines, or cultural expectations. There are several variations, including some forms which involve dancing around or leaping over a cow or bull or attempting to grasp an object tied to the animal's horns. The best-known form of bullfighting is Spanish-style bullfighting, practiced in Spain, Portugal, Southern France, Mexico, Colombia, Ecuador, Venezuela, and Peru. The Spanish Fighting Bull is bred for its aggression and physique, and is raised free-range with little human contact. The practice of bullfighting is controversial because of a range of concerns including animal welfare, funding, and religion. While some forms are considered a blood sport, in some countries, for example Spain, it is defined as an art form or cultural event, and local regulations define it as a cultural event or heritage. Bullfighting is illegal in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Literature
) , image = Nobel Prize.png , caption = , awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature , presenter = Swedish Academy , holder = Annie Ernaux (2022) , location = Stockholm, Sweden , year = 1901 , reward = 10 million SEK (2022) , website = , year2 = 2022 , holder_label = Currently held by , previous = 2021 , main = 2022 , next = 2023 The Nobel Prize in Literature (here meaning ''for'' literature) is a Swedish literature prize that is awarded annually, since 1901, to an author from any country who has, in the words of the will of Swedish industrialist Alfred Nobel, "in the field of literature, produced the most outstanding work in an idealistic direction" (original Swedish: ''den som inom litteraturen har producerat det utmärktaste i idealisk rigtning''). Though individual works are sometimes cited as being particularly noteworthy, the award is based on an author's body of work as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacinto Benavente
Jacinto Benavente y Martínez (12 August 1866 – 14 July 1954) was one of the foremost Spanish dramatists of the 20th century. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1922 "for the happy manner in which he has continued the illustrious traditions of the Spanish drama". Biography Born in Madrid, the son of a celebrated pediatrician, he returned drama to reality by way of social criticism: declamatory verse giving way to prose, melodrama to comedy, formula to experience, impulsive action to dialogue and the play of minds. Benavente showed a preoccupation with aesthetics and later with ethics. A liberal monarchist and a critic of socialism, he was a reluctant supporter of Francoist Spain as the only viable alternative to what he considered the disastrous republican experiment of 1931–1936. In 1936 Benavente's name became associated with the assassination of the Spanish poet and dramatist Federico García Lorca. This happened when the Nationalist newspapers ''Estampa'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moncloa
Moncloa-Aravaca is a district of the municipality of Madrid, Spain. It is located to the northwest of the city centre, spanning across both banks of the Manzanares. It is made up of the neighborhoods of Aravaca, Argüelles, Casa de Campo, Ciudad Universitaria, El Plantío, Valdemarín and Valdezarza. The Palace of Moncloa, located in Ciudad Universitaria, is the residence of the Spanish Prime Minister. Geography Subdivision The district is administratively divided into 7 neighborhoods (): Education The ''Colegio Japonés de Madrid'', the Japanese international school in Madrid, is located in the El Plantío area. " Archive '' |
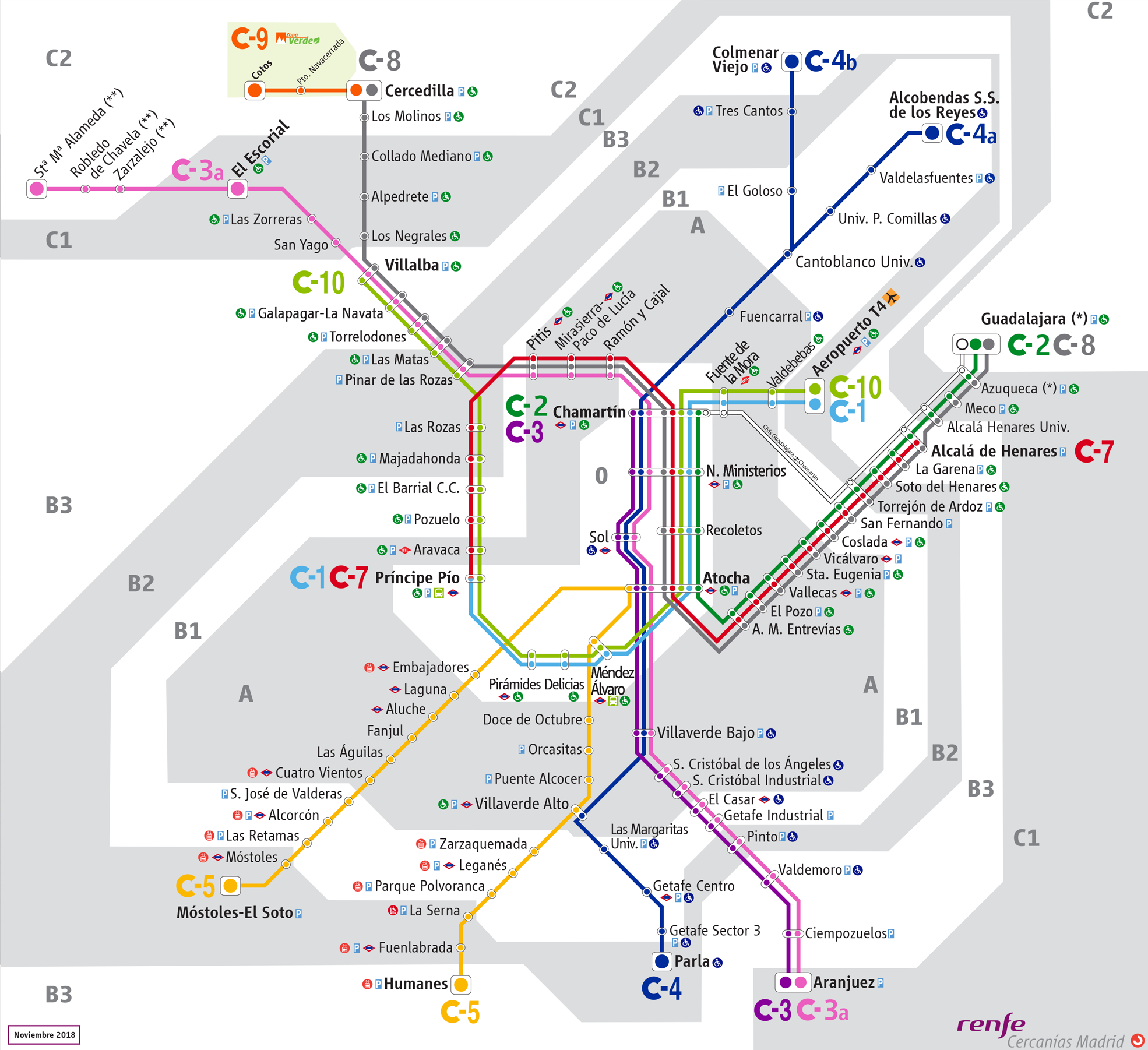
Cercanías Madrid
Cercanías Madrid is the commuter rail service that serves Madrid, the capital of Spain, and its metropolitan area. It is operated by Cercanías Renfe, the commuter rail division of Renfe, the former monopoly of rail services in Spain. Its total length is 370 km. History Until 1989 The first railroad line departing from Madrid (the second in Spain and the third in the Iberian Peninsula) was built in 1851 between Madrid and Aranjuez. Soon the growing Spanish railway system was dominated by two large companies: the ''Compañía del Norte'' (Northern Company), who operated the lines between Madrid and the Atlantic North of Spain from the ''Estación del Norte'' (now Príncipe Pío),and the Madrid-Zaragoza-Alicante (MZA) who operated the lines between the capital and the Mediterranean and Andalusian cities from the Atocha station. Another station, Delicias, served the line to Lisbon. Other smaller companies operated from Madrid, mostly in narrow gauge. After the Civi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asunción (Galapagar)
Asunción (, , ) is the capital and the largest city of Paraguay. The city stands on the eastern bank of the Paraguay River, almost at the confluence of this river with the Pilcomayo River. The Paraguay River and the Bay of Asunción in the northwest separate the city from the Occidental Region of Paraguay and from Argentina in the south part of the city. The rest of the city is surrounded by the Central Department. Asunción is one of the oldest cities in South America and the longest continually inhabited area in the Río de la Plata Basin; for this reason it is known as "the Mother of Cities". From Asunción, Spanish colonial expeditions departed to found other cities, including the second foundation of Buenos Aires, that of other important cities such as Villarrica, Corrientes, Santa Fe, Córdoba, Santa Cruz de la Sierra and 65 more. Administratively, the city forms an autonomous capital district, not a part of any department. The metropolitan area, called ''Gran Asunci� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Escorial
El Escorial, or the Royal Site of San Lorenzo de El Escorial ( es, Monasterio y Sitio de El Escorial en Madrid), or Monasterio del Escorial (), is a historical residence of the King of Spain located in the town of San Lorenzo de El Escorial, up the valley ( road distance) from the town of El Escorial and about northwest of the Spanish capital Madrid. Built between 1563 and 1584 by order of King Philip II (who reigned 1556–1598), El Escorial is the largest Renaissance building in the world. It is one of the Spanish royal sites and functions as a monastery, basilica, royal palace, pantheon, library, museum, university, school, and hospital. El Escorial consists of two architectural complexes of great historical and cultural significance: the royal monastery itself and '' La Granjilla de La Fresneda'', a royal hunting lodge and monastic retreat about 5 kilometres away. These sites have a dual nature: during the 16th and 17th centuries, they were places in which the power of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Spain
The municipality ( es, municipio, , ca, municipi, gl, concello, eu, udalerria, ast, conceyu)In other languages of Spain: * Catalan/Valencian (), sing. ''municipi''. * Galician () or (), sing. ''municipio''/''bisbarra''. *Basque (), sing. ''udalerria''. * Asturian (), sing. ''conceyu''. is the basic local administrative division in Spain together with the province. Organisation Each municipality forms part of a province which in turn forms part or the whole of an autonomous community (17 in total plus Ceuta and Melilla): some autonomous communities also group municipalities into entities known as ''comarcas'' (districts) or ''mancomunidades'' (commonwealths). There are a total of 8,131 municipalities in Spain, including the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla. In the Principality of Asturias, municipalities are officially named ''concejos'' (councils). The average population of a municipality is about 5,300, but this figure masks a huge range: the most populo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)