|
GWR 3232 Class
The 3232 Class, 20 locomotives designed by William Dean and built at Swindon Works for the Great Western Railway in 1892–93, were the GWR's last completely new 2-4-0 design. Their number series was 3232–3251. Design They resembled Dean's own 2201 Class and thus also Armstrong Armstrong may refer to: Places * Armstrong Creek (other), various places Antarctica * Armstrong Reef, Biscoe Islands Argentina * Armstrong, Santa Fe Australia * Armstrong, Victoria Canada * Armstrong, British Columbia * Armstrong ...'s 806 Class, though they had larger cylinders and a shorter wheelbase. All received Belpaire boilers in the course of the normal varied reboilerings. Use At the start of their careers these engines replaced their sister 2201s on Swindon-Weymouth trains, on South Wales expresses, and on fast North-to-West trains. Others were in the London and Reading areas, where others also moved when s displaced them from express working. A few went later to Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dean (engineer)
William Dean (8 January 1840 – 24 September 1905) was an English railway engineer. He was the second son of Henry Dean, who was the manager of the Hawes Soap Factory in New Cross, London. William was educated at the Haberdashers' Company School. He became the Chief Locomotive Engineer for the Great Western Railway from 1877, when he succeeded Joseph Armstrong. He retired from the post in 1902 and was replaced by George Jackson Churchward. He designed famous steam locomotive classes such as the Duke Class, the Bulldog Class and the long-lived 2301 Class. Apprenticeship He was apprenticed at the age of fifteen to Joseph Armstrong at the Great Western Railway's Wolverhampton Stafford Road Works. During his eight-year apprenticeship he attended Wolverhampton Working Men's College in the evening, excelling in mathematics and engineering. Upon completion of his apprentice years in 1863 he was made Joseph Armstrong's chief assistant. Posts with GWR A year later, Joseph Armst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swindon Works
Swindon railway works was opened by the Great Western Railway in 1843 in Swindon, Wiltshire, England. It served as the principal west England maintenance centre until closed in 1986. History In 1835 Parliament approved the construction of the Great Western Main Line between London and Bristol by the Great Western Railway (GWR). Its Chief Engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. From 1836, Brunel had been buying locomotives from various makers for the new railway. Brunel's general specifications gave the locomotive makers a free hand in design, although subject to certain constraints such as piston speed and axle load, resulting in a diverse range of locomotives of mixed quality. In 1837, Brunel recruited Daniel Gooch and gave him the job of rectifying the heavy repair burden of the GWR's mixed bag of purchased locomotives. It became clear that the GWR needed a central repair works so, in 1840 Gooch identified a site at Swindon because it was at the junction of the Golden Valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as stratum, rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ... with the southwest, west and West Midlands (region), West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838 with the initial route completed between London and Bristol in 1841. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of —later slightly widened to —but, from 1854, a series of Consolidation (business), amalgamations saw it also operate Standard gauge, standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892. The GWR was the only company to keep its identity through the Railways Act 1921, which ama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 2201 Class
The GWR 2201 Class was a class of steam locomotives built at Swindon Works under the aegis of William Dean for express passenger service on the Great Western Railway The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran .... Built in 1881–82, they were numbered 2201 to 2220. Design They were, in essentials, a continuation of Joseph Armstrong's 806 Class of 1873. They differed from the originals in having a cab and a domeless boiler from the start. Use The 2201s were widely distributed over the GWR system. Members of the class were in use on the Didcot, Newbury and Southampton Railway around 1910. They were all withdrawn by the end of 1921. References Sources * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Gwr 2201 Class 2201 2-4-0 locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1881 Standard gaug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Armstrong (engineer)
Joseph Armstrong (born Bewcastle, Cumberland, 21 September 1816, died Matlock Bath 5 June 1877) was an English locomotive engineer and the second locomotive superintendent of the Great Western Railway. His younger brother George and one of his sons ("Young Joe") also became outstanding engineers in the employment of the GWR. Career Early years to 1847 After a spell in Canada, in 1824 Joseph's family took up residence in Newburn-on-Tyne, where his father Thomas became a bailiff to the Duke of Northumberland. Joseph attended Bruce's School in Newcastle, where Robert Stephenson had also been a pupil. In 1823 Robert Stephenson, in collaboration with his father George, had set up his locomotive works in the city. Moreover, Newburn was at one end of the Wylam Waggonway, where the sight of the famous locomotives Puffing Billy and Wylam Dilly must have inspired young Joseph's enthusiasm as an engineer. Newburn also had colliery railways worked by stationary engines, and it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 806 Class
The 806 Class (20 locomotives, nos. 806–825) was Joseph Armstrong's last design of mixed-traffic locomotives for the Great Western Railway, built at Swindon Works in 1873. A further 20 similar locomotives were added by Armstrong's successor William Dean in 1881-2; numbered 2201–2220, these had modern domeless boilers (see GWR 2201 Class The GWR 2201 Class was a class of steam locomotives built at Swindon Works under the aegis of William Dean for express passenger service on the Great Western Railway The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that link ...). The class had a similar appearance to the 717 Class but had driving wheels larger. Use Most of the Armstrong locomotives worked in the Southern Division, and carried Sir Daniel Class boilers; only Nos. 806, 807, 810 and 821 were Northern Division engines, and these were in due course fitted with Wolverhampton boilers. The four Northern engines were stationed at Wolverhampton and worked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
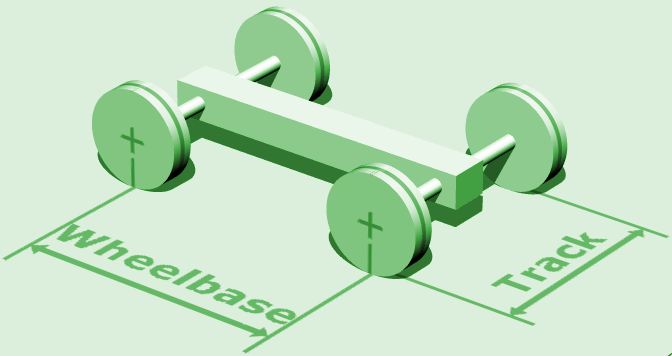
Wheelbase
In both road and rail vehicles, the wheelbase is the horizontal distance between the centers of the front and rear wheels. For road vehicles with more than two axles (e.g. some trucks), the wheelbase is the distance between the steering (front) axle and the centerpoint of the driving axle group. In the case of a tri-axle truck, the wheelbase would be the distance between the steering axle and a point midway between the two rear axles. Vehicles The wheelbase of a vehicle equals the distance between its front and rear wheels. At equilibrium, the total torque of the forces acting on a vehicle is zero. Therefore, the wheelbase is related to the force on each pair of tires by the following formula: :F_f = mg :F_r = mg where F_f is the force on the front tires, F_r is the force on the rear tires, L is the wheelbase, d_r is the distance from the center of mass (CM) to the rear wheels, d_f is the distance from the center of mass to the front wheels (d_f + d_r = L), m is the mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Correspondence And Travel Society
The Railway Correspondence and Travel Society (RCTS) is a national society founded in Cheltenham, England in 1928 to bring together those interested in rail transport and locomotives. Since 1929 the Society has published a regular journal ''The Railway Observer'' which records the current railway scene. It also has regional branches which organise meetings and trips to places of interest and an archive & library. It has published definitive multi-volume locomotive histories of the Great Western, Southern and London & North Eastern Railways, and has in progress similar works on the London, Midland & Scottish Railway and British Railways standard steam locomotives. It also has published many other historical railway books since the mid-1950s. On 2 November 2016, the RCTS become a Charitable Incorporated Organisation (CIO), registered number 1169995. Its new Archive and Library (located within the former station-master's house at Leatherhead station) was opened on 6 Octobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Western Railway Locomotives
Great may refer to: Descriptions or measurements * Great, a relative measurement in physical space, see Size Size in general is the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or dimensions of a thing. More specifically, ''geometrical size'' (or ''spatial size'') can refer to linear dimensions (length, width, height, diameter, perimeter), area, or volume ... * Greatness, being divine, majestic, superior, majestic, or transcendent People * List of people known as "the Great" * Artel Great (born 1981), American actor Other uses * ''Great'' (1975 film), a British animated short about Isambard Kingdom Brunel * ''Great'' (2013 film), a German short film * Great (supermarket), a supermarket in Hong Kong * GReAT, Graph Rewriting and Transformation, a Model Transformation Language * Gang Resistance Education and Training, or GREAT, a school-based and police officer-instructed program * Global Research and Analysis Team (GReAT), a cybersecurity team at Kaspersky Lab *'' Great!'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge Steam Locomotives Of Great Britain
Standard may refer to: Symbols * Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs * Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification Norms, conventions or requirements * Standard (metrology), an object that bears a defined relationship to a unit of measure used for calibration of measuring devices * Standard (timber unit), an obsolete measure of timber used in trade * Breed standard (also called bench standard), in animal fancy and animal husbandry * BioCompute Standard, a standard for next generation sequencing * ''De facto'' standard, product or system with market dominance * Gold standard, a monetary system based on gold; also used metaphorically for the best of several options, against which the others are measured * Internet Standard, a specification ratified as an open standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force * Learning standards, standards applied to education content * Standard displacement, a naval term describing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |