|
GRB7
Growth factor receptor-bound protein 7, also known as GRB7, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GRB7'' gene. Function The product of this gene belongs to a small family of adaptor proteins that are known to interact with a number of receptor tyrosine kinases and signaling molecules. This gene encodes a growth factor receptor-binding protein that interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ephrin receptors. The protein plays a role in the integrin signaling pathway and cell migration by binding with focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms, although the full-length natures of only two of the variants have been determined to date. Clinical significance GRB7 is an SH2-domain adaptor protein that binds to receptor tyrosine kinases and provides the intra-cellular direct link to the Ras proto-oncogene. Human GRB7 is located on the long arm of chromosome 17, next to the ERBB2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
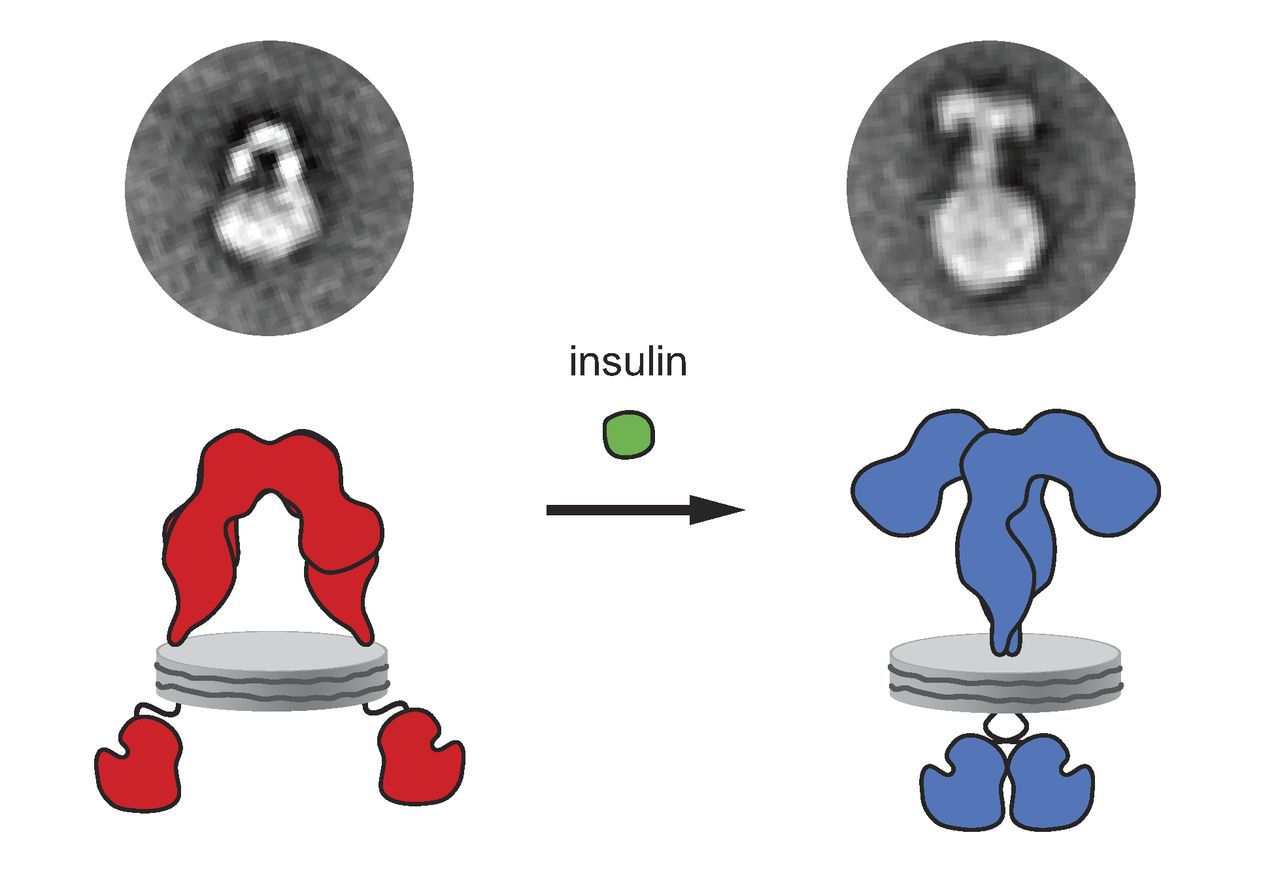
Insulin Receptor
The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis, a functional process that under degenerate conditions may result in a range of clinical manifestations including diabetes and cancer. Insulin signalling controls access to blood glucose in body cells. When insulin falls, especially in those with high insulin sensitivity, body cells begin only to have access to lipids that do not require transport across the membrane. So, in this way, insulin is the key regulator of fat metabolism as well. Biochemically, the insulin receptor is encoded by a single gene , from which alternate splicing during transcription results in either IR-A or IR-B isoforms. Downstream post-translational events of either isoform result in the formation of a proteolytically cleaved α and β subunit, which upon com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RET Proto-oncogene
The ''RET'' proto-oncogene encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase for members of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family of extracellular signalling molecules. ''RET'' loss of function mutations are associated with the development of Hirschsprung's disease, while gain of function mutations are associated with the development of various types of human cancer, including medullary thyroid carcinoma, multiple endocrine neoplasias type 2A and 2B, pheochromocytoma and parathyroid hyperplasia. Structure ''RET'' is an abbreviation for "rearranged during transfection", as the DNA sequence of this gene was originally found to be rearranged within a 3T3 fibroblast cell line following its transfection with DNA taken from human lymphoma cells. The human gene ''RET'' is localized to chromosome 10 (10q11.2) and contains 21 exons. The natural alternative splicing of the ''RET'' gene results in the production of 3 different isoforms of the protein RET. RET51, RET43 and RET9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rnd1
Rnd1 is a small (~21 kDa) signaling G protein (to be specific, a GTPase), and is a member of the Rnd subgroup of the Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RND1. It contributes to regulating the organization of the actin cytoskeleton in response to extracellular growth factors (Nobes et al., 1998). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> Interactions Rnd1 has been shown to interact with GRB7, PLXNB1, PDE6D, ARHGAP5 Rho GTPase-activating protein 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ARHGAP5'' gene. Function Rho GTPase activating protein 5 negatively regulates RHO GTPases, a family that may mediate cytoskeleton changes by stimulating the hydrol ... and UBXD5. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB-1; HER1 in humans) is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family (EGF family) of extracellular protein ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR (ErbB-1), HER2/neu (ErbB-2), Her 3 (ErbB-3) and Her 4 (ErbB-4). In many cancer types, mutations affecting EGFR expression or activity could result in cancer. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor was discovered by Stanley Cohen of Vanderbilt University. Cohen shared the 1986 Nobel Prize in Medicine with Rita Levi-Montalcini for their discovery of growth factors. Deficient signaling of the EGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases in humans is associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's, while over-expression is associated with the development of a wide variety of tumors. Interruption of EGFR signalling, either by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HER2/neu
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ERBB2'' gene. ERBB is abbreviated from erythroblastic oncogene B, a gene originally isolated from the avian genome. The human protein is also frequently referred to as ''HER2'' (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) or CD340 (cluster of differentiation 340). HER2 is a member of the human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER/EGFR/ERBB) family. But contrary to other member of the ERBB family, HER2 does not directly bind ligand. HER2 activation results from heterodimerization with another ERBB member or by homodimerization when HER2 concentration are high, for instance in cancer. Amplification or over-expression of this oncogene has been shown to play an important role in the development and progression of certain aggressive types of breast cancer. In recent years the protein has become an important biomarker and target of therapy for approximately 30% of breast cancer patients. Name ''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 17 (human)
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 17 contains the Homeobox B gene cluster. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 17. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 17. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. The following are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTK2
PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2), also known as focal adhesion kinase (FAK), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''PTK2'' gene. PTK2 is a focal adhesion-associated protein kinase involved in cellular adhesion (how cells stick to each other and their surroundings) and spreading processes (how cells move around). It has been shown that when FAK was blocked, breast cancer cells became less metastatic due to decreased mobility. Function The PTK2 gene encodes a cytosolic protein tyrosine kinase that is found concentrated in the focal adhesions that form among cells attaching to extracellular matrix constituents. The encoded protein is a member of the FAK subfamily of protein tyrosine kinases that included PYK2, but lacks significant sequence similarity to kinases from other subfamilies. It also includes a large FERM domain. With the exception of certain types of blood cells, most cells express FAK. FAK tyrosine kinase activity can be activated, which plays a key ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EPH Receptor B1
Ephrin type-B receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EPHB1'' gene. Function Ephrin receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, mediate numerous developmental processes, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for ephrin-B family members. Interactions EPH receptor B1 has been shown to interact with: * ACP1 * GRB7 and * NCK1 * Ephrin-B2 Ephrin-B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNB2'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knockout Mouse
A knockout mouse, or knock-out mouse, is a genetically modified mouse (''Mus musculus'') in which researchers have inactivated, or "knocked out", an existing gene by replacing it or disrupting it with an artificial piece of DNA. They are important animal models for studying the role of genes which have been sequenced but whose functions have not been determined. By causing a specific gene to be inactive in the mouse, and observing any differences from normal behaviour or physiology, researchers can infer its probable function. Mice are currently the laboratory animal species most closely related to humans for which the knockout technique can easily be applied. They are widely used in knockout experiments, especially those investigating genetic questions that relate to human physiology. Gene knockout in rats is much harder and has only been possible since 2003. The first recorded knockout mouse was created by Mario R. Capecchi, Martin Evans, and Oliver Smithies in 1989, for whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
The Wellcome Sanger Institute, previously known as The Sanger Centre and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, is a non-profit British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust. It is located on the Wellcome Genome Campus by the village of Hinxton, outside Cambridge. It shares this location with the European Bioinformatics Institute. It was established in 1992 and named after double Nobel Laureate Frederick Sanger. It was conceived as a large scale DNA sequencing centre to participate in the Human Genome Project, and went on to make the largest single contribution to the gold standard sequence of the human genome. From its inception the institute established and has maintained a policy of data sharing, and does much of its research in collaboration. Since 2000, the institute expanded its mission to understand "the role of genetics in health and disease". The institute now employs around 900 people and engages in five main areas of research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |