|
GAAFET
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be controlled by a single gate electrode, wherein the multiple gate surfaces act electrically as a single gate, or by independent gate electrodes. A multigate device employing independent gate electrodes is sometimes called a multiple-independent-gate field-effect transistor (MIGFET). The most widely used multi-gate devices are the FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) and the GAAFET (gate-all-around field-effect transistor), which are non-planar transistors, or 3D transistors. Multi-gate transistors are one of the several strategies being developed by MOS semiconductor manufacturers to create ever-smaller microprocessors and memory cells, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's law (in its narrow, specific version concerning density scaling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAAFET
A multigate device, multi-gate MOSFET or multi-gate field-effect transistor (MuGFET) refers to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) that has more than one gate on a single transistor. The multiple gates may be controlled by a single gate electrode, wherein the multiple gate surfaces act electrically as a single gate, or by independent gate electrodes. A multigate device employing independent gate electrodes is sometimes called a multiple-independent-gate field-effect transistor (MIGFET). The most widely used multi-gate devices are the FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) and the GAAFET (gate-all-around field-effect transistor), which are non-planar transistors, or 3D transistors. Multi-gate transistors are one of the several strategies being developed by MOS semiconductor manufacturers to create ever-smaller microprocessors and memory cells, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's law (in its narrow, specific version concerning density scaling, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moore's Law
Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of physics, it is an empirical relationship linked to gains from experience in production. The observation is named after Gordon Moore, the co-founder of Fairchild Semiconductor and Intel (and former CEO of the latter), who in 1965 posited a doubling every year in the number of components per integrated circuit, and projected this rate of growth would continue for at least another decade. In 1975, looking forward to the next decade, he revised the forecast to doubling every two years, a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 41%. While Moore did not use empirical evidence in forecasting that the historical trend would continue, his prediction held since 1975 and has since become known as a "law". Moore's prediction has been used in the semiconductor industry to g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor DG MOSFET 1
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanoelectronics
Nanoelectronics refers to the use of nanotechnology in electronic components. The term covers a diverse set of devices and materials, with the common characteristic that they are so small that inter-atomic interactions and quantum mechanical properties need to be studied extensively. Some of these candidates include: hybrid molecular/semiconductor electronics, one-dimensional nanotubes/nanowires (e.g. silicon nanowires or carbon nanotubes) or advanced molecular electronics. Nanoelectronic devices have critical dimensions with a size range between 1 nm and 100 nm. Recent silicon MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) technology generations are already within this regime, including 22 nanometers CMOS (complementary MOS) nodes and succeeding 14 nm, 10 nm and 7 nm FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) generations. Nanoelectronics is sometimes considered as disruptive technology because present candidates are significantly different f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FinFET
A fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is a multigate device, a MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) built on a substrate where the gate is placed on two, three, or four sides of the channel or wrapped around the channel, forming a double or even multi gate structure. These devices have been given the generic name "FinFETs" because the source/drain region forms fins on the silicon surface. The FinFET devices have significantly faster switching times and higher current density than planar CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) technology. FinFET is a type of non-planar transistor, or "3D" transistor. It is the basis for modern nanoelectronic semiconductor device fabrication. Microchips utilizing FinFET gates first became commercialized in the first half of the 2010s, and became the dominant gate design at 14 nm, 10 nm and 7 nm process nodes. It is common for a single FinFET transistor to contain several fins, arranged side by side and all covered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational corporation, multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of the Samsung chaebol, accounting for 70% of the group's revenue in 2012. Samsung Electronics has played a key role in the group's corporate governance due to circular ownership. Samsung Electronics has Assembly line, assembly plants and sales networks in 74 countries and employs around 290,000 people. It is majority-owned by foreign investors. Samsung Electronics is the world's List of largest technology companies by revenue, second-largest technology company by revenue, and its market capitalization stood at US$520.65 billion, the 12th largest in the world. Samsung is a major manufacturer of Electronic component, Electronic Components such as lithium-ion batteries, semiconductors, image sensors, camera modules, and Display device, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC; also called Taiwan Semiconductor) is a Taiwanese multinational corporation, multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is the world's most valuable semiconductor company, the world's largest dedicated independent (Pure-play semiconductor foundry, pure-play) Foundry (electronics), semiconductor foundry, and one of Taiwan's largest companies, with its headquarters and main operations located in the Hsinchu Science Park in Hsinchu. It is majority owned by foreign investors. Founded in Taiwan in 1987 by Morris Chang, TSMC was the world's first dedicated semiconductor foundry and has long been the leading company in its field. When Chang retired in 2018, after 31 years of TSMC leadership, Mark Liu became chairman and C. C. Wei became Chief Executive. It has been listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange (TWSE: 2330) since 1993; in 1997 it became the first Taiwanese company to be listed on the New York ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
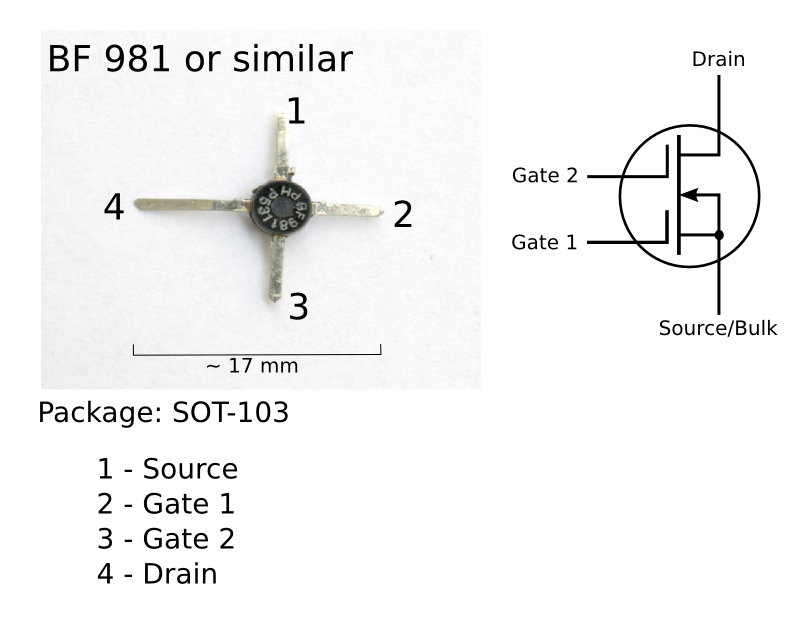
Gate (transistor)
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessors
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a single or a few integrated circuits using Very-Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) greatly reduced the cost o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
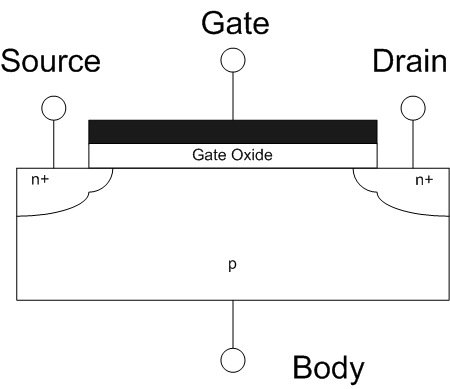
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. A metal-insulator-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MISFET) is a term almost synonymous with MOSFET. Another synonym is IGFET for insulated-gate field-effect transistor. The basic principle of the field-effect transistor was first patented by Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.Lilienfeld, Julius Edgar (1926-10-08) "Method and apparatus for controlling electric currents" upright=1.6, Two power MOSFETs in V_in_the_''off''_state,_and_can_conduct_a_continuous_current_of_30 surface-mount_packages._Operating_as_switches,_each_of_these_components_can_su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-κ Dielectric
The term high-κ dielectric refers to a material with a high dielectric constant (κ, kappa), as compared to silicon dioxide. High-κ dielectrics are used in semiconductor manufacturing processes where they are usually used to replace a silicon dioxide gate dielectric or another dielectric layer of a device. The implementation of high-κ gate dielectrics is one of several strategies developed to allow further miniaturization of microelectronic components, colloquially referred to as extending Moore's Law. Sometimes these materials are called "high-k" (pronounced "high kay"), instead of "high-κ" (high kappa). Need for high-κ materials Silicon dioxide () has been used as a gate oxide material for decades. As metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) have decreased in size, the thickness of the silicon dioxide gate dielectric has steadily decreased to increase the gate capacitance (per unit area) and thereby drive current (per device width), raising device perfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)