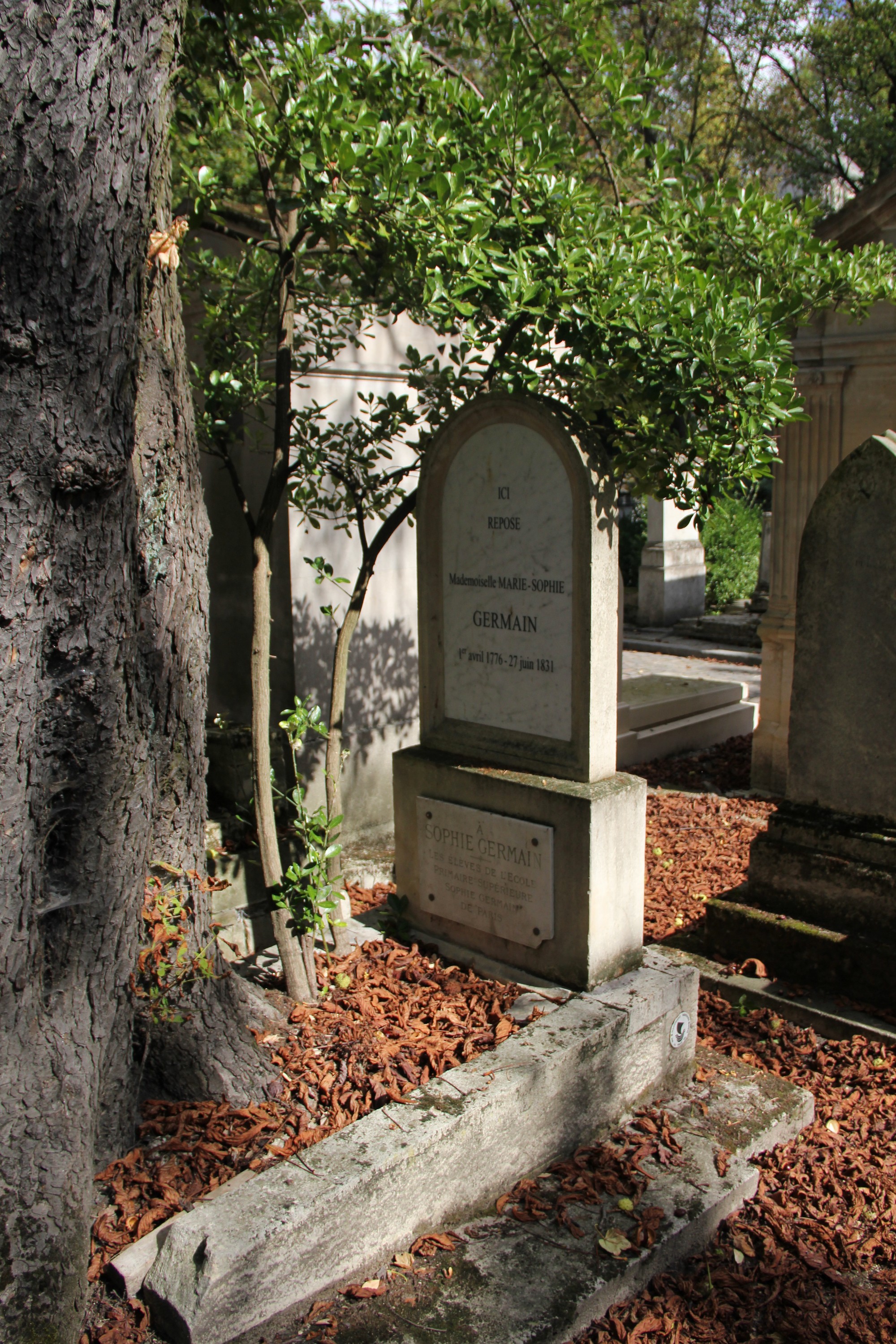|
G. W. Peck
G. W. Peck is a pseudonymous attribution used as the author or co-author of a number of published mathematics academic papers. Peck is sometimes humorously identified with George Wilbur Peck, a former governor of the United States, US state of Wisconsin.. Peck first appeared as the official author of a 1979 paper entitled "Maximum antichains of rectangular arrays". The name "G. W. Peck" is derived from the initials of the actual writers of this paper: Ronald Graham, Douglas West (mathematician), Douglas West, George B. Purdy, Paul Erdős, Fan Chung, and Daniel Kleitman. The paper initially listed Peck's affiliation as Shangdu, Xanadu, but the editor of the journal objected, so Ron Graham gave him a job at Bell Labs. Since then, Peck's name has appeared on some sixteen publications, primarily as a pseudonym of Daniel Kleitman. In reference to "G. W. Peck", Richard P. Stanley defined a Peck poset to be a graded poset, graded partially ordered set that is rank symmetric, rank unimod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudonym
A pseudonym (; ) or alias () is a fictitious name that a person or group assumes for a particular purpose, which differs from their original or true name (orthonym). This also differs from a new name that entirely or legally replaces an individual's own. Many pseudonym holders use pseudonyms because they wish to remain anonymous, but anonymity is difficult to achieve and often fraught with legal issues. Scope Pseudonyms include stage names, user names, ring names, pen names, aliases, superhero or villain identities and code names, gamer identifications, and regnal names of emperors, popes, and other monarchs. In some cases, it may also include nicknames. Historically, they have sometimes taken the form of anagrams, Graecisms, and Latinisations. Pseudonyms should not be confused with new names that replace old ones and become the individual's full-time name. Pseudonyms are "part-time" names, used only in certain contexts – to provide a more clear-cut separation between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MathSciNet
MathSciNet is a searchable online bibliographic database created by the American Mathematical Society in 1996. It contains all of the contents of the journal ''Mathematical Reviews'' (MR) since 1940 along with an extensive author database, links to other MR entries, citations, full journal entries, and links to original articles. It contains almost 3.6 million items and over 2.3 million links to original articles. Along with its parent publication ''Mathematical Reviews'', MathSciNet has become an essential tool for researchers in the mathematical sciences. Access to the database is by subscription only and is not generally available to individual researchers who are not affiliated with a larger subscribing institution. For the first 40 years of its existence, traditional typesetting was used to produce the Mathematical Reviews journal. Starting in 1980 bibliographic information and the reviews themselves were produced in both print and electronic form. This formed the basis of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Shared Pseudonyms
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophie Germain
Marie-Sophie Germain (; 1 April 1776 – 27 June 1831) was a French mathematician, physicist, and philosopher. Despite initial opposition from her parents and difficulties presented by society, she gained education from books in her father's library, including ones by Euler, and from correspondence with famous mathematicians such as Lagrange, Legendre, and Gauss (under the pseudonym of Monsieur LeBlanc). One of the pioneers of elasticity theory, she won the grand prize from the Paris Academy of Sciences for her essay on the subject. Her work on Fermat's Last Theorem provided a foundation for mathematicians exploring the subject for hundreds of years after. Because of prejudice against her sex, she was unable to make a career out of mathematics, but she worked independently throughout her life. Before her death, Gauss had recommended that she be awarded an honorary degree, but that never occurred. On 27 June 1831, she died from breast cancer. At the centenary of her life, a str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blanche Descartes
Blanche Descartes was a collaborative pseudonym used by the English mathematicians R. Leonard Brooks, Arthur Harold Stone, Cedric Smith, and W. T. Tutte. The four mathematicians met in 1935 as undergraduate students at Trinity College, Cambridge, where they joined the Trinity Mathematical Society and began meeting together to work on mathematical problems. Pseudonym The pseudonym originated by combining the initials of the mathematicians' given names (Bill, Leonard, Arthur, and Cedric) to form ''BLAC''. This was extended to ''BLAnChe''. The surname ''Descartes'' was chosen as a play on the common phrase ''carte blanche''. Publication Over 30 works were published under the name, including whimsical poetry and mathematical humour, but some serious mathematical results as well. Many of these publications appeared in ''Eureka'', a mathematical student magazine in Cambridge. Notably, the foursome proved several theorems in mathematical tessellation. In particular, they solved the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Rainwater
The fictitious mathematician John Rainwater was created as a student prank but has become known as the author of important results in functional analysis. At the University of Washington in 1952, John Rainwater was invented and enrolled in a mathematics course by graduate students who were in possession of a duplicate student-registration form. Later, mathematicians published under the pseudonym of John Rainwater. Papers were published under the name Rainwater mainly in functional analysis, particularly in the geometric theory of Banach spaces and in convex functions. Rainwater's theorem is an important result in summability theory and functional analysis. The University of Washington's seminar in functional analysis is called the Rainwater seminar, and the associated Rainwater notes have influenced Banach-space theory and convex analysis. The concept of a fictional pseudonym used by multiple people creating valuable mathematics is not unique. Most notably, Nicolas Bourbaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Besse
Arthur Besse is a pseudonym chosen by a group of French differential geometers, led by Marcel Berger, following the model of Nicolas Bourbaki. A number of monographs have appeared under the name. Bibliography * ** *Actes de la Table Ronde de Géométrie Différentielle. roceedings of the Roundtable on Differential GeometryEn l'honneur de Marcel Berger. n honor of Marcel BergerHeld in Luminy, July 12–18, 1992. Edited by Arthur L. Besse. Séminaires et Congrès eminars and Congresses 1. Société Mathématique de France, Paris; distributed by American Mathematical Society, Providence, RI, 1996. *Besse, Arthur L.: Some trends in Riemannian geometry. Duration and change, 71–105, Springer, Berlin, 1994 . *Besse, A. Многообразия Эйнштейна. Том I,II. (Russian) instein manifolds. Vol. I, IITranslated from the English and with a preface by D. V. Alekseevskiĭ. "Mir", Moscow, 1990. Vol. I: 320 pp.; Vol. II: pp. 321–704. *Besse, Arthur L.: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Bourbaki
Nicolas Bourbaki () is the collective pseudonym of a group of mathematicians, predominantly French alumni of the École normale supérieure - PSL (ENS). Founded in 1934–1935, the Bourbaki group originally intended to prepare a new textbook in analysis. Over time the project became much more ambitious, growing into a large series of textbooks published under the Bourbaki name, meant to treat modern pure mathematics. The series is known collectively as the '' Éléments de mathématique'' (''Elements of Mathematics''), the group's central work. Topics treated in the series include set theory, abstract algebra, topology, analysis, Lie groups and Lie algebras. Bourbaki was founded in response to the effects of the First World War which caused the death of a generation of French mathematicians; as a result, young university instructors were forced to use dated texts. While teaching at the University of Strasbourg, Henri Cartan complained to his colleague André Weil of the inade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poset
In mathematics, especially order theory, a partially ordered set (also poset) formalizes and generalizes the intuitive concept of an ordering, sequencing, or arrangement of the elements of a set. A poset consists of a set together with a binary relation indicating that, for certain pairs of elements in the set, one of the elements precedes the other in the ordering. The relation itself is called a "partial order." The word ''partial'' in the names "partial order" and "partially ordered set" is used as an indication that not every pair of elements needs to be comparable. That is, there may be pairs of elements for which neither element precedes the other in the poset. Partial orders thus generalize total orders, in which every pair is comparable. Informal definition A partial order defines a notion of comparison. Two elements ''x'' and ''y'' may stand in any of four mutually exclusive relationships to each other: either ''x'' ''y'', or ''x'' and ''y'' are ''incompa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strongly Sperner
In order-theoretic mathematics, a graded partially ordered set is said to have the Sperner property (and hence is called a Sperner poset), if no antichain within it is larger than the largest rank level (one of the sets of elements of the same rank) in the poset.. Since every rank level is itself an antichain, the Sperner property is equivalently the property that some rank level is a maximum antichain. The Sperner property and Sperner posets are named after Emanuel Sperner Emanuel Sperner (9 December 1905 – 31 January 1980) was a German mathematician, best known for two theorems. He was born in Waltdorf (near Neiße, Upper Silesia, now Nysa, Poland), and died in Sulzburg-Laufen, West Germany. He was a student at ..., who proved Sperner's theorem stating that the family of all subsets of a finite set (partially ordered by set inclusion) has this property. The lattice of partitions of a finite set typically lacks the Sperner property. Variations A ''k''-Sperner poset is a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rank Unimodal
Rank is the relative position, value, worth, complexity, power, importance, authority, level, etc. of a person or object within a ranking, such as: Level or position in a hierarchical organization * Academic rank * Diplomatic rank * Hierarchy * Hierarchy of the Catholic Church * Military rank * Police ranks of the United States * Ranking member, S politicsthe most senior member of a committee from the minority party, and thus second-most senior member of a committee * Imperial, royal and noble ranks Level or position in society * Social class * Social position * Social status Places * Rank, Iran, a village * Rank, Nepal, a village development committee People * Rank (surname), a list of people with the name Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''Rank'' (album), a live album by the Smiths * "Rank", a song by Artwork from '' A Bugged Out Mix'' Other arts, entertainment, and media * Rank (chess), a row of the chessboard * ''Rank'' (film), a short film directed by David Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rank Symmetric
Rank is the relative position, value, worth, complexity, power, importance, authority, level, etc. of a person or object within a ranking, such as: Level or position in a hierarchical organization * Academic rank * Diplomatic rank * Hierarchy * Hierarchy of the Catholic Church * Military rank * Police ranks of the United States * Ranking member, S politicsthe most senior member of a committee from the minority party, and thus second-most senior member of a committee * Imperial, royal and noble ranks Level or position in society * Social class * Social position * Social status Places * Rank, Iran, a village * Rank, Nepal, a village development committee People * Rank (surname), a list of people with the name Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''Rank'' (album), a live album by the Smiths * "Rank", a song by Artwork from '' A Bugged Out Mix'' Other arts, entertainment, and media * Rank (chess), a row of the chessboard * ''Rank'' (film), a short film directed by David Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |