|
Fryns Syndrome
Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome. Presentation Usually associated with diaphragmatic hernia, pulmonary hypoplasia, imperforate anus, micropenis, bilateral cryptorchidism, cerebral ventricular dilation, camptodactyly, agenesis of sacrum, low-set ear. Cytogenetics In a newborn boy thought to have Fryns syndrome, Clark and Fenner-Gonzales (1989) found mosaicism for a tandem duplication of 1q24-q31.2. They suggested that the gene for this disorder is located in that region. However, de Jong et al. (1989), Krassikoff and Sekhon (1990), and Dean et al. (1991) found possible Fryns syndrome associated with anomalies of chromosome 15, chromosome 6, chromosome 8 and chromosome 22, respectively. Thus, these cases may all represent mimics of the mendelian syndrome and have no significance as to the location of the gene for the recessive disorder. By array CGH, Slavo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proband
In medical genetics and other medical fields, a proband, proposito (male proband), or proposita (female proband)Bennett, RL. The Language of the Pedigree. In: ''The Practical Guide to the Genetic Family History''. Wiley-Liss. is a particular subject (human or other animal) being studied or reported on. On pedigrees, the proband is noted with a square (male) or circle (female) shaded accordingly. Denoting the proband is important, so the relationship to other individuals can be seen and patterns established. In most cases, the proband is the first affected family member who seeks medical attention for a genetic disorder. Among the ancestors of the proband, other subjects may manifest the disease, but the proband typically refers to the member seeking medical attention or being studied, even if affected ancestors are known. Often, affected ancestors are unknown due to the lack of information regarding those individuals or about the disease at the time they lived. Other ancestors mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrasomy 12p Mosaicism
A tetrasomy is a form of aneuploidy with the presence of four copies, instead of the normal two, of a particular chromosome. Causes Full Full tetrasomy of an individual occurs due to non-disjunction when the cells are dividing (meiosis I or II) to form egg and sperm cells (gametogenesis). This can result in extra chromosomes in a sperm or egg cell. After fertilization, the resulting fetus has 48 chromosomes instead of the typical 46. Autosomal tetrasomies * Cat eye syndrome where partial tetrasomy of chromosome 22 is present * Pallister-Killian syndrome (tetrasomy 12p) * Tetrasomy 9p * Tetrasomy 18p * Tetrasomy 21, a rare form of Down syndrome Sex-chromosome tetrasomies * Tetrasomy X * XXYY syndrome XXYY syndrome is a sex chromosome anomaly in which males have 2 extra chromosomes, one X and one Y chromosome. Human cells usually contain two sex chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father. Usually, females have two X chromosomes ( ... External links {{Chro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosaicism
Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in multicellular organisms in which a single organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized egg. Genetic mosaics may often be confused with chimerism, in which two or more genotypes arise in one individual similarly to mosaicism. In chimerism, though, the two genotypes arise from the fusion of more than one fertilized zygote in the early stages of embryonic development, rather than from a mutation or chromosome loss. Genetic mosaicism can result from many different mechanisms including chromosome nondisjunction, anaphase lag, and endoreplication. Anaphase lagging is the most common way by which mosaicism arises in the preimplantation embryo. Mosaicism can also result from a mutation in one cell during development, in which case the mutation will be passed on only to its daughter cells (and will be present only in certain adult cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysmorphic Syndrome
A dysmorphic feature is an abnormal difference in body structure. It can be an isolated finding in an otherwise normal individual, or it can be related to a congenital disorder, genetic syndrome or birth defect. Dysmorphology is the study of dysmorphic features, their origins and proper nomenclature. One of the key challenges in identifying and describing dysmorphic features is the use and understanding of specific terms between different individuals. Clinical geneticists and pediatricians are usually those most closely involved with the identification and description of dysmorphic features, as most are apparent during childhood. Dysmorphic features can vary from isolated, mild anomalies such as clinodactyly or synophrys to severe congenital anomalies, such as heart defects and holoprosencephaly. In some cases, dysmorphic features are part of a larger clinical picture, sometimes known as a sequence, syndrome or association. Recognizing the patterns of dysmorphic features is an imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pallister–Killian Syndrome
The Pallister–Killian syndrome (PKS), also termed tetrasomy 12p mosaicism or the Pallister mosaic aneuploidy syndrome, is an extremely rare and severe genetic disorder. PKS is due to the presence of an extra and abnormal chromosome termed a small supernumerary marker chromosome (sSMC). sSMCs contain copies of genetic material from parts of virtually any other chromosome and, depending on the genetic material they carry, can cause various genetic disorders and neoplasms. The sSMC in PKS consists of multiple copies of the short (i.e. "p") arm of chromosome 12. Consequently, the multiple copies of the genetic material in the sSMC plus the two copies of this genetic material in the two normal chromosome 12's are overexpressed and thereby cause the syndrome. Due to a form of genetic mosaicism, however, individuals with PKS differ in the tissue distributions of their sSMC and therefore show different syndrome-related birth defects and disease severities. For example, individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book ''The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as cad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natal Teeth
Natal teeth are teeth that are present above the gumline (have already erupted) at birth, and neonatal teeth are teeth that emerge through the gingiva during the first month of life (the neonatal period). The incidence of neonatal teeth varies considerably, between 1:700 and 1:30,000 depending on the type of study; the highest prevalence is found in the only study that relies on personal examination of patients. Natal teeth, and neonatal teeth, can be the baby's normal deciduous teeth, sprouting prematurely. These should be preserved, if possible. Alternately, they could be supernumary teeth, extra teeth, not part of the normal allotment of teeth. Signs and symptoms Most often natal teeth are mandibular central incisors. They have little root structure and are attached to the end of the gum by soft tissue and are often mobile. Causes Most of the time, natal teeth are not related to a medical condition. However, sometimes they may be associated with: * Ellis–van Creveld syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisor are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typically, the mandibular central incisors erupt first, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Termination Of Pregnancy
Abortion is the termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. An abortion that occurs without intervention is known as a miscarriage or "spontaneous abortion"; these occur in approximately 30% to 40% of pregnancies. When deliberate steps are taken to end a pregnancy, it is called an induced abortion, or less frequently "induced miscarriage". The unmodified word ''abortion'' generally refers to an induced abortion. The reasons why women have abortions are diverse and vary across the world. Reasons include maternal health, an inability to afford a child, domestic violence, lack of support, feeling they are too young, wishing to complete education or advance a career, and not being able or willing to raise a child conceived as a result of rape or incest. When properly done, induced abortion is one of the safest procedures in medicine. In the United States, the risk of maternal mortality is 14 times lower after induced abortion than after childb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
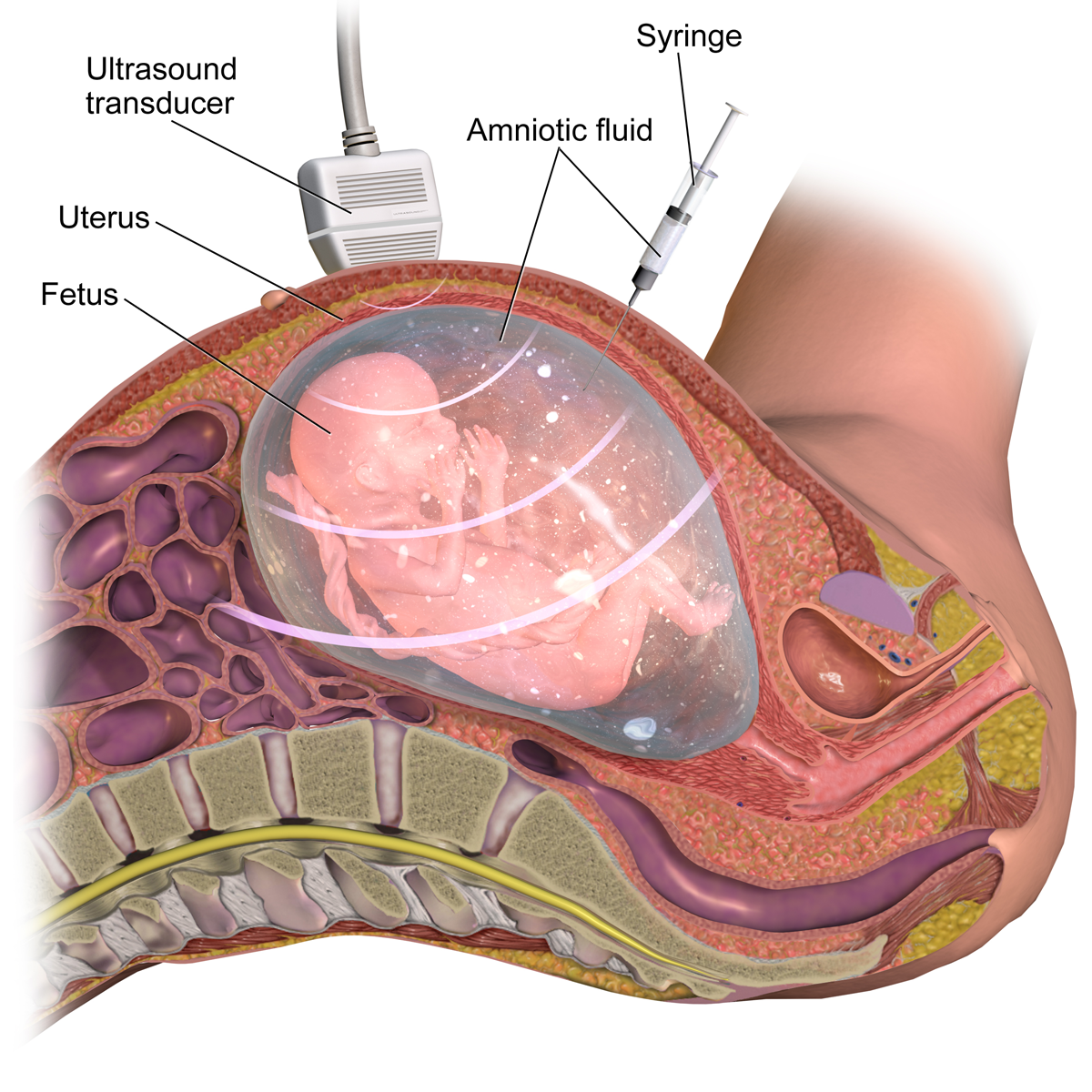
Sonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequency, frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenatal Diagnosis
Prenatal testing consists of prenatal screening and prenatal diagnosis, which are aspects of prenatal care that focus on detecting problems with the pregnancy as early as possible. These may be anatomic and physiologic problems with the health of the zygote, embryo, or fetus, either before gestation even starts (as in preimplantation genetic diagnosis) or as early in gestation as practicable. Screening can detect problems such as neural tube defects, chromosome abnormalities, and gene mutations that would lead to genetic disorders and birth defects, such as spina bifida, cleft palate, Down syndrome, Tay–Sachs disease, sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophy, and fragile X syndrome. Some tests are designed to discover problems which primarily affect the health of the mother, such as PAPP-A to detect pre-eclampsia or glucose tolerance tests to diagnose gestational diabetes. Screening can also detect anatomical defects such as hydrocephalus, anencephal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |