|
French Cartography
The history of French cartography can be traced to developments in the Middle Ages. This period was marked by improvements in measuring instruments and also by an upgrade of work in registers of all types. What is thought to be the oldest land map in Europe, the Saint-Bélec slab, representing an area of the Odet valley, was found in 1900, and rediscovered in a castle cellar in France in 2014. The Bronze-Age stone is thought to be 4,000-years old. The first map of France was drawn by Oronce Finé and printed in woodcuts in 1525. It testifies to the will of the political power to mark its presence on the territory; to affirm, to build limits, borders, to arrange its territory, and to consolidate the internal economic markets. In the 16th century, Dieppe appeared as an important school of cartography. Pierre Desceliers allowed the realization of many maps. At the same time, the Portolan maps of the Portuguese sailors had the most recent knowledge obtained by the Dieppois sailors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1691 Sanson Map Of The World On Hemisphere Projection - Geographicus - World-sanson-1691
Events January–March * January 6 – King William III of England, who rules Scotland and Ireland as well as being the Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic, departs from Margate to tend to the affairs of the Netherlands. * January 14 – A fleet of ships carrying 827 Spanish Navy sailors and marines arrives at Manzanillo Bay on the island of Hispaniola in what is now the Dominican Republic and joins 700 Spanish cavalry, then proceeds westward to invade the French side of the island in what is now Haiti. * January 15 – King Louis XIV of France issues an order specifically prohibiting play of games of chance, specifically naming basset and similar games, on penalty of 1,000 livres for the first offence. * January 23 – Spanish colonial administrator Domingo Terán de los Ríos, most recently the governor of Sonora y Sinaloa on the east side of the Gulf of California, is assigned by the Viceroy of New Spain to administer a new province that governs lands on both sides o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominique, Comte De Cassini
Jean-Dominique, comte de Cassini (30 June 174818 October 1845) was a French astronomer, son of César-François Cassini de Thury and great-grandson of Giovanni Domenico Cassini. Cassini was born at the Paris Observatory. He succeeded his father as director of the observatory in 1784; but his plans for its restoration and re-equipment were wrecked in 1793 by the animosity of the National Assembly. His position having become intolerable, he resigned on 6 September and was thrown into prison in 1794, but released after seven months. He then withdrew to Thury, where he died in 1845. In 1770, he published an account of a voyage to America in 1768, undertaken as the commissary of the French Academy of Sciences with a view to testing Pierre Le Roy’s watches at sea. In 1783, he sent a memoir to the Royal Society in which he proposed a trigonometric survey connecting the observatories of Paris and Greenwich for the purpose of better determining the latitude and longitude of the lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Méchain
Pierre François André Méchain (; 16 August 1744 – 20 September 1804) was a French astronomer and surveyor who, with Charles Messier, was a major contributor to the early study of deep-sky objects and comets. Life Pierre Méchain was born in Laon, the son of the ceiling designer and plasterer Pierre François Méchain and Marie–Marguerite Roze. He displayed mental gifts in mathematics and physics but had to give up his studies for lack of money. However, his talents in astronomy were noticed by Jérôme Lalande, for whom he became a friend and proof-reader of the second edition of his book "L'Astronomie". Lalande then secured a position for him as assistant hydrographer with the Naval Depot of Maps and Charts at Versailles, where he worked through the 1770s engaged in hydrographic work and coastline surveying. It was during this time—approximately 1774—that he met Charles Messier, and apparently, they became friends. In the same year, he also produced his first astron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre
Jean Baptiste Joseph, chevalier Delambre (19 September 1749 – 19 August 1822) was a French mathematician, astronomer, historian of astronomy, and geodesist. He was also director of the Paris Observatory, and author of well-known books on the history of astronomy from ancient times to the 18th century. Biography After a childhood fever, he suffered from very sensitive eyes, and believed that he would soon go blind. For fear of losing his ability to read, he devoured any book available and trained his memory. He thus immersed himself in Greek and Latin literature, acquired the ability to recall entire pages verbatim weeks after reading them, became fluent in Italian, English and German and even wrote an unpublished ''Règle ou méthode facile pour apprendre la langue anglaise'' (Easy rule or method for learning English). Delambre's quickly achieved success in his career in astronomy, such that in 1788, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Scie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Meridian
The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the Paris Observatory in Paris, France – now longitude 2°20′14.02500″ East. It was a long-standing rival to the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian of the world. The "Paris meridian arc" or "French meridian arc" (French: ''la Méridienne de France'') is the name of the meridian arc measured along the Paris meridian. The French meridian arc was important for French cartography, inasmuch as the triangulations of France began with the measurement of the French meridian arc. Moreover, the French meridian arc was important for geodesy as it was one of the meridian arcs which were measured to determine the figure of the Earth via the arc measurement method. The determination of the figure of the Earth was a problem of the highest importance in astronomy, inasmuch as the diameter of the Earth was the unit to which all celestial distances had to be referred. History French cartography and the figure of the Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon Bonaparte, successful campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars, Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the First French Republic, French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in Hundred Days, 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers Napoleonic Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France Cotes Academie
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the French mainland, west of the Italian Peninsula and immediately north of the Italian island of Sardinia, which is the land mass nearest to it. A single chain of mountains makes up two-thirds of the island. , it had a population of 349,465. The island is a territorial collectivity of France. The regional capital is Ajaccio. Although the region is divided into two administrative departments, Haute-Corse and Corse-du-Sud, their respective regional and departmental territorial collectivities were merged on 1 January 2018 to form the single territorial collectivity of Corsica. As such, Corsica enjoys a greater degree of autonomy than other French regional collectivities; for example, the Corsican Assembly is permitted to exercise limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
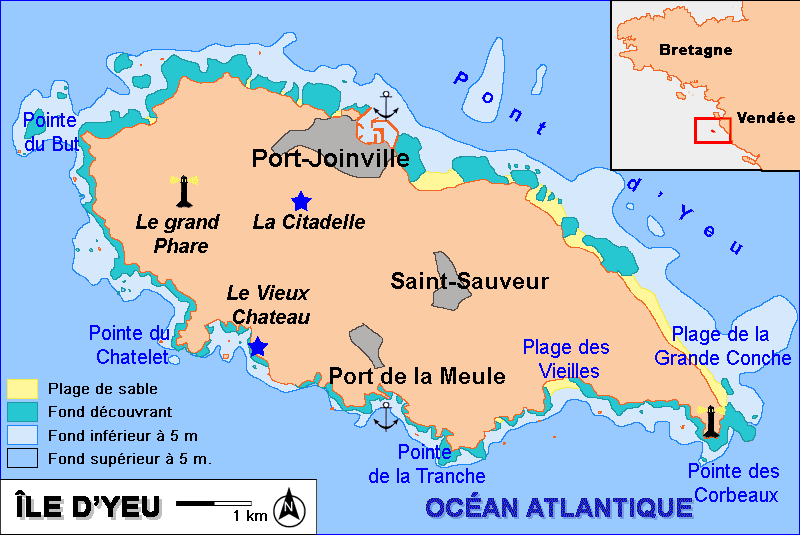
Île D'Yeu
Île d'Yeu () or L'Île-d'Yeu, is an island and commune just off the Vendée coast of western France. The island's two harbors, Port-Joinville in the north and Port de la Meule to the south, in a rocky inlet of the southern granite coast, are famous for tuna and lobster fishing, respectively. Administratively, the commune of L'Île-d'Yeu is part of the Vendée department and the Pays de la Loire region of France. History Neolithic markings in the native stone and an unusual concentration of megalithic dolmens and menhirs attest to the island's early sanctity. Irish monks from Bangor, County Down, dedicated their monastery on the Île d'Yeu to Hilaire; Saint Amand from Poitou received early training there, but it was destroyed by Viking raiders in the ninth century. During the tenth century, monks from Marmoutier near Tours and monks of Saint-Cyprien at Poitiers built a new monastery and dedicated it to Saint Stephen. The castle built on an islet linked to the coast by a brid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Alps
The Maritime Alps (french: Alpes Maritimes ; it, Alpi Marittime ) are a mountain range in the southwestern part of the Alps. They form the border between the regions of France, French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur and the regions of Italy, Italian regions of Piedmont and Liguria. They are the southernmost part of the Alps. Geography Administratively the range is divided between the Provinces of Italy, Italian provinces of Province of Cuneo, Cuneo and Province of Imperia, Imperia (eastern slopes) and the Departments of France, French department of Alpes-Maritimes (western slopes). The Maritime Alps are drained by the rivers Roya (river), Roya, Var River, Var and Verdon River, Verdon and their tributaries on the French side; by the Stura di Demonte and other tributaries of the Tanaro River, Tanaro and Po River, Po on the Italian side. There are many attractive perched villages, such as Belvédère at the entrance to the spectacular Gordolasque valley, some concealing unex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie (; Arpitan: ''Savouè d'Amont'' or ''Hiôta-Savouè''; en, Upper Savoy) or '; it, Alta Savoia. is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France, bordering both Switzerland and Italy. Its prefecture is Annecy. To the north is Lake Geneva; to the south and southeast are Mont Blanc and the Aravis mountain range. It holds its name from the Savoy historical region, as does the department of Savoie, located south of Haute-Savoie. In 2019, it had a population of 826,094.Populations légales 2019: 74 Haute-Savoie INSEE Its subprefectures are [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south. Savoy emerged as the feudal County of Savoy ruled by the House of Savoy during the 11th to 14th centuries. The original territory, also known as "ducal Savoy" or "Savoy proper", is largely co-terminous with the modern French Savoie and Haute-Savoie ''départements'', but the historical expansion of Savoyard territories, as the Duchy of Savoy (1416–1860) included parts of what is now western Italy and southwestern Switzerland. The current border between France and Italy is due to the Plombières Agreement of 1858, which in preparation for the unification of Italy ceded western Savoy to France, while the eastern territories in Piedmont and Liguria were retained by the House of Savoy, which was to become the ruling dynasty of Italy. Geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |