Paris Meridian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the
The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the
 In the year 1634, France ruled by
In the year 1634, France ruled by  In 1740 an account was published in the Paris ''Mémoires'', by
In 1740 an account was published in the Paris ''Mémoires'', by
 Cesar-François Cassini de Thury completed the
Cesar-François Cassini de Thury completed the 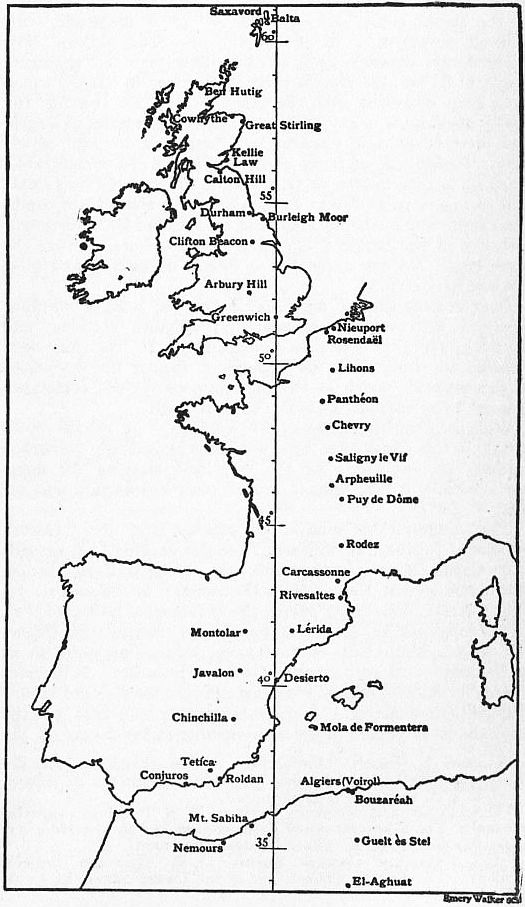 In the second half of the 19th century, Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero directed the survey of Spain. From 1870 to 1894 the Paris meridan's arc was remeasured by
In the second half of the 19th century, Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero directed the survey of Spain. From 1870 to 1894 the Paris meridan's arc was remeasured by
 In 1994 the Arago Association and the city of Paris commissioned a Dutch conceptual artist,
In 1994 the Arago Association and the city of Paris commissioned a Dutch conceptual artist,
The Arago medallions on Google Earth
Full Meridian of Glory: Perilous Adventures in the Competition to Measure the Earth
history of science book by Prof. Paul Murdin
The Greenwich Meridian, by Graham Dolan
Named meridians Geography of Paris Geography of France History of Paris Prime meridians Geodesy Metrology Geography of England Geography of Spain Geography of Algeria Paris Observatory
 The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the
The Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its histor ...
in Paris, France – now longitude 2°20′14.02500″ East. It was a long-standing rival to the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great c ...
of the world. The "Paris meridian arc" or "French meridian arc" (French: ''la Méridienne de France'') is the name of the meridian arc measured along the Paris meridian.
The French meridian arc was important for French cartography
The history of French cartography can be traced to developments in the Middle Ages. This period was marked by improvements in measuring instruments and also by an upgrade of work in registers of all types. What is thought to be the oldest land map ...
, inasmuch as the triangulations of France began with the measurement of the French meridian arc. Moreover, the French meridian arc was important for geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
as it was one of the meridian arcs which were measured to determine the figure of the Earth
Figure of the Earth is a Jargon, term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A Spherical Earth, sphere is a well-k ...
via the arc measurement
Arc measurement, sometimes degree measurement (german: Gradmessung), is the astrogeodetic technique of determining of the radius of Earth – more specifically, the local Earth radius of curvature of the figure of the Earth – by relating the la ...
method. The determination of the figure of the Earth was a problem of the highest importance in astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
, inasmuch as the diameter of the Earth was the unit to which all celestial distances had to be referred.
History
French cartography and the figure of the Earth
 In the year 1634, France ruled by
In the year 1634, France ruled by Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown ...
and Cardinal Richelieu, decided that the Ferro Meridian should be used as the reference on maps, since El Hierro
El Hierro, nicknamed ''Isla del Meridiano'' (the "Meridian Island"), is the second-smallest and farthest-south and -west of the Canary Islands (an autonomous community of Spain), in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa, with a populatio ...
(Ferro) was the most western position of the Ptolemy's world map
The Ptolemy world map is a map of the world known to Greco-Roman societies in the 2nd century. It is based on the description contained in Ptolemy's book ''Geography'', written . Based on an inscription in several of the earliest surviving manusc ...
. It was also thought to be exactly 20 degrees west of Paris. The astronomers of the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific me ...
, founded in 1666, managed to clarify the position of El Hierro
El Hierro, nicknamed ''Isla del Meridiano'' (the "Meridian Island"), is the second-smallest and farthest-south and -west of the Canary Islands (an autonomous community of Spain), in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa, with a populatio ...
relative to the meridian of Paris, which gradually supplanted the Ferro meridian. In 1666, Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Versa ...
had authorized the building of the Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its histor ...
. On Midsummer's Day
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer usually held at a date around the summer solstice. It has pagan pre-Christian roots in Europe.
The undivided Christianity, Christian Church designated June 24 as the feast day of the early Chri ...
1667, members of the Academy of Sciences traced the future building's outline on a plot outside town near the Port Royal abbey, with Paris meridian exactly bisecting the site north–south. French cartographers would use it as their prime meridian for more than 200 years. Old maps from continental Europe often have a common grid with Paris degrees at the top and Ferro degrees offset by 20 at the bottom.
A French astronomer, Abbé Jean Picard, measured the length of a degree of latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
along the Paris meridian (arc measurement
Arc measurement, sometimes degree measurement (german: Gradmessung), is the astrogeodetic technique of determining of the radius of Earth – more specifically, the local Earth radius of curvature of the figure of the Earth – by relating the la ...
) and computed from it the size of the Earth
Figure of the Earth is a term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A sphere is a well-known historical approxima ...
during 1668–1670. The application of the telescope to angular instruments was an important step. He was the first who in 1669, with the telescope, using such precautions as the nature of the operation requires, measured a precise arc of meridian (Picard's arc measurement
Jean Picard (21 July 1620 – 12 July 1682) was a French astronomer and priest born in La Flèche, where he studied at the Jesuit Collège Royal Henry-Le-Grand.
He is principally notable for his accurate measure of the size of the Earth, ba ...
). He measured with wooden rods a baseline of 5,663 toise
A toise (; symbol: T) is a unit of measure for length, area and volume originating in pre-revolutionary France. In North America, it was used in colonial French establishments in early New France, French Louisiana (''Louisiane''), Acadia (''Acadi ...
s, and a second or base of verification of 3,902 toises; his triangulation network
In surveying, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by measuring only angles to it from known points at either end of a fixed baseline by using trigonometry, rather than measuring distances to the point directly as ...
extended from Malvoisine, near Paris, to Sourdon
Sourdon (; pcd, Sordon) is a commune in the Somme department in the Hauts-de-France region of France.
Geography
Sourdon is situated south of Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, ...
, near Amiens
Amiens (English: or ; ; pcd, Anmien, or ) is a city and commune in northern France, located north of Paris and south-west of Lille. It is the capital of the Somme department in the region of Hauts-de-France. In 2021, the population of ...
. The angles of the triangles were measured with a quadrant furnished with a telescope having cross-wires. The difference of latitude of the terminal stations was determined by observations made with a sector on a star in Cassiopeia, giving 1° 22′ 55″ for the amplitude. The terrestrial degree measurement gave the length of 57,060 toises, whence he inferred 6,538,594 toises for the Earth's diameter.
Four generations of the Cassini family headed the Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its histor ...
. They directed the surveys of France for over 100 years. Hitherto geodetic observations had been confined to the determination of the magnitude of the Earth considered as a sphere, but a discovery made by Jean Richer
Jean Richer (1630–1696) was a French astronomer and assistant (''élève astronome'') at the French Academy of Sciences, under the direction of Giovanni Domenico Cassini.
Between 1671 and 1673 he performed experiments and carried out celestial ...
turned the attention of mathematicians to its deviation from a spherical form. This astronomer, having been sent by the Academy of Sciences of Paris to the island of Cayenne (now in French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic ...
) in South America, for the purpose of investigating the amount of astronomical refraction and other astronomical objects, observed that his clock, which had been regulated at Paris to beat seconds, lost about two minutes and a half daily at Cayenne, and that to bring it to measure mean solar time it was necessary to shorten the pendulum by more than a line (about 1⁄12th of an in.). This fact, which was scarcely credited till it had been confirmed by the subsequent observations of Varin and Deshayes on the coasts of Africa and America, was first explained in the third book of Newton’s '' Principia'', who showed that it could only be referred to a diminution of gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
arising either from a protuberance of the equatorial parts of the Earth and consequent increase of the distance from the centre, or from the counteracting effect of the centrifugal force. About the same time (1673) appeared Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists of ...
’ ''De Horologio Oscillatorio'', in which for the first time were found correct notions on the subject of centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is paralle ...
. It does not, however, appear that they were applied to the theoretical investigation of the figure of the Earth before the publication of Newton's ''Principia''. In 1690 Huygens published his ''De Causa Gravitatis'', which contains an investigation of the figure of the Earth on the supposition that the attraction of every particle is towards the centre.
Between 1684 and 1718 Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini, also known as Jean-Dominique Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian (naturalised French) mathematician, astronomer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the ...
and Jacques Cassini
Jacques Cassini (18 February 1677 – 16 April 1756) was a French astronomer, son of the famous Italian astronomer Giovanni Domenico Cassini.
Cassini was born at the Paris Observatory. Admitted at the age of seventeen to membership of the French ...
, along with Philippe de La Hire, carried a triangulation, starting from Picard's base in Paris and extending it northwards to Dunkirk and southwards to Collioure
Collioure (; ca, Cotlliure, ) is a commune in the southern French department of Pyrénées-Orientales.
Geography
The town of Collioure is on the Côte Vermeille (Vermilion Coast), in the canton of La Côte Vermeille and in the arrondissement ...
. They measured a base of 7,246 toises near Perpignan, and a somewhat shorter base near Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.spheroid
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters. A spheroid has cir ...
. This conclusion was totally opposed to the theoretical investigations of Newton and Huygens, and accordingly the Academy of Sciences of Paris determined to apply a decisive test by the measurement of arcs at a great distance from each other – one in the neighbourhood of the equator, the other in a high latitude. Thus arose the celebrated , to the Equator and to Lapland, the latter directed by Pierre Louis Maupertuis
Pierre Louis Moreau de Maupertuis (; ; 1698 – 27 July 1759) was a French mathematician, philosopher and man of letters. He became the Director of the Académie des Sciences, and the first President of the Prussian Academy of Science, at the ...
.
 In 1740 an account was published in the Paris ''Mémoires'', by
In 1740 an account was published in the Paris ''Mémoires'', by Cassini de Thury Cassini may refer to:
People
* Cassini (surname)
* Oleg Cassini (1913-2006), American fashion designer
:Cassini family:
* Giovanni Domenico Cassini (1625–1712), Italian mathematician, astronomer, engineer, and astrologer
* Jacques Cassini (167 ...
, of a remeasurement by himself and Nicolas Louis de Lacaille
Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille (; 15 March 171321 March 1762), formerly sometimes spelled de la Caille, was a French astronomer and geodesist who named 14 out of the 88 constellations. From 1750 to 1754, he studied the sky at the Cape of Goo ...
of the meridian of Paris. With a view to determine more accurately the variation of the degree along the meridian, they divided the distance from Dunkirk to Collioure into four partial arcs of about two degrees each, by observing the latitude at five stations. The results previously obtained by Giovanni Domenico and Jacques Cassini were not confirmed, but, on the contrary, the length of the degree derived from these partial arcs showed on the whole an increase with increasing latitude.
The West Europe-Africa Meridian-arc
 Cesar-François Cassini de Thury completed the
Cesar-François Cassini de Thury completed the Cassini map
The Cassini Map or Academy's Map is the first topographic and geometric map made of the Kingdom of France as a whole. It was compiled by the Cassini family, mainly César-François Cassini (Cassini III) and his son Jean-Dominique Cassini (Ca ...
, which was published by his son Cassini IV in 1790. Moreover, the Paris meridian was linked with international collaboration in geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equivale ...
and metrology
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in Fran ...
. Cesar-François Cassini de Thury (1714–1784) expressed the project to extend the French geodetic network all around the world and to connect the Paris and Greenwich observatories. In 1783 the French Academy of Science
The French Academy of Sciences (French: ''Académie des sciences'') is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at t ...
presented his proposal to King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
. This connection and a proposal from General William Roy led to the first triangulation of Great Britain. France and Great Britain surveys' connection was repeated by French astronomers and geodesists in 1787 by Cassini IV, in 1823–1825 by François Arago and in 1861–1862 by François Perrier.
Between 1792 and 1798 Pierre Méchain
Pierre François André Méchain (; 16 August 1744 – 20 September 1804) was a French astronomer and surveyor who, with Charles Messier, was a major contributor to the early study of deep-sky objects and comets.
Life
Pierre Méchain was born i ...
and Jean-Baptiste Delambre surveyed the Paris meridian arc between Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
(see meridian arc of Delambre and Méchain). They extrapolated from this measurement the distance from the North Pole to the Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
which was 5,130,740 toise
A toise (; symbol: T) is a unit of measure for length, area and volume originating in pre-revolutionary France. In North America, it was used in colonial French establishments in early New France, French Louisiana (''Louisiane''), Acadia (''Acadi ...
s. As the metre had to be equal to one ten-millionth of this distance, it was defined as 0,513074 toises or 443,296 ligne
The ''ligne'' ( ), or line or Paris line, is a historic unit of length used in France and elsewhere prior to the adoption of the metric system in the late 18th century, and used in various sciences after that time. The ''loi du 19 frimaire an V ...
s of the Toise of Peru (see below) and of the double-toise N° 1 of the apparatus which had been devised by Lavoisier and Borda for this survey at specified temperatures.
In the early 19th century, the Paris meridian's arc was recalculated with greater precision between Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
and the Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands ( es, Islas Baleares ; or ca, Illes Balears ) are an archipelago in the Balearic Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago is an autonomous community and a province of Spain; its capital is ...
by the astronomer François Arago, whose name now appears on the plaques or medallions tracing the route of the meridian through Paris (see below). Biot
The British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) is an Overseas Territory of the United Kingdom situated in the Indian Ocean, halfway between Tanzania and Indonesia. The territory comprises the seven atolls of the Chagos Archipelago with over 1,000 ...
and Arago published their work as a fourth volume following the three volumes of "''Bases du système métrique décimal ou mesure de l'arc méridien compris entre les parallèles de Dunkerque et Barcelone''" (Basis for the decimal metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the Decimal, decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in French Revolution, France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the d ...
or measurement of the meridian arc comprised between Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
) by Delambre
Jean Baptiste Joseph, chevalier Delambre (19 September 1749 – 19 August 1822) was a French mathematician, astronomer, historian of astronomy, and geodesist. He was also director of the Paris Observatory, and author of well-known books on th ...
and Méchain.
 In the second half of the 19th century, Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero directed the survey of Spain. From 1870 to 1894 the Paris meridan's arc was remeasured by
In the second half of the 19th century, Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero directed the survey of Spain. From 1870 to 1894 the Paris meridan's arc was remeasured by Perrier
Perrier ( , also , ) is a French brand of natural bottled mineral water obtained at its source in Vergèze, located in the Gard ''département''. Perrier is known for its carbonation and its distinctive green bottle.
Perrier was part of the ...
and Bassot in France and Algeria. In 1879, Ibáñez de Ibero for Spain and François Perrier for France directed the junction of the Spanish geodetic network with Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
. This connection was a remarkable enterprise where triangles with a maximum length of 270 km were observed from mountain stations over the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. The triangulation of France was then connected to those of Great Britain, Spain and Algeria and thus the Paris meridian's arc measurement extended from Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the no ...
to the Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
.
The fundamental co-ordinates of the Panthéon
The Panthéon (, from the Classical Greek word , , ' empleto all the gods') is a monument in the 5th arrondissement of Paris, France. It stands in the Latin Quarter, atop the , in the centre of the , which was named after it. The edifice was b ...
were also obtained anew, by connecting the Panthéon
The Panthéon (, from the Classical Greek word , , ' empleto all the gods') is a monument in the 5th arrondissement of Paris, France. It stands in the Latin Quarter, atop the , in the centre of the , which was named after it. The edifice was b ...
and the Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its histor ...
with the five stations of Bry-sur-Marne, Morlu, Mont Valérien, Chatillon and Montsouris, where the observations of latitude and azimuth were effected.
Geodesy and metrology
In 1860, the Russian Government at the instance ofOtto Wilhelm von Struve
Otto Wilhelm von Struve (May 7, 1819 (Julian calendar: April 25) – April 14, 1905) was a Russian astronomer of Baltic German origins. In Russian, his name is normally given as Otto Vasil'evich Struve (Отто Васильевич Струв ...
invited the Governments of Belgium, France, Prussia and England to connect their triangulations to measure the length of an arc of parallel in latitude 52° and to test the accuracy of the figure and dimensions of the Earth, as derived from the measurements of arc of meridian. To combine the measurements it was necessary to compare the geodetic standards of length used in the different countries. The British Government invited those of France, Belgium, Prussia, Russia, India, Australia, Austria, Spain, United States and Cape of Good Hope to send their standards to the Ordnance Survey
, nativename_a =
, nativename_r =
, logo = Ordnance Survey 2015 Logo.svg
, logo_width = 240px
, logo_caption =
, seal =
, seal_width =
, seal_caption =
, picture =
, picture_width =
, picture_caption =
, formed =
, preceding1 =
, di ...
office in Southampton. Notably the geodetic standards of France, Spain and United States were based on the metric system, whereas those of Prussia, Belgium and Russia where calibrated against the toise
A toise (; symbol: T) is a unit of measure for length, area and volume originating in pre-revolutionary France. In North America, it was used in colonial French establishments in early New France, French Louisiana (''Louisiane''), Acadia (''Acadi ...
, of which the oldest physical representative was the Toise of Peru. The Toise of Peru had been constructed in 1735 for Bouguer and De La Condamine as their standard of reference in the French Geodesic Mission
The French Geodesic Mission to the Equator (french: Expédition géodésique française en Équateur, also called the French Geodesic Mission to Peru and the Spanish-French Geodesic Mission) was an 18th-century expedition to what is now Ecuador c ...
, conducted in actual Ecuador from 1735 to 1744 in collaboration with the Spanish officers Jorge Juan and Antonio de Ulloa
Antonio de Ulloa y de la Torre-Giralt, FRS, FRSA, KOS (12 January 1716 – 3 July 1795) was a Spanish naval officer, scientist, and administrator. At the age of nineteen, he joined the French Geodesic Mission to what is now the country o ...
.
Alexander Ross Clarke
Col Alexander Ross Clarke FRS FRSE (1828–1914) was a British geodesist, primarily remembered for his calculation of the Principal Triangulation of Britain (1858), the calculation of the Figure of the Earth (1858, 1860, 1866, 1880) and one ...
and Henry James published the first results of the standards' comparisons in 1867. The same year Russia, Spain and Portugal joined the ''Europäische Gradmessung'' and the General Conference of the association proposed the metre as a uniform length standard for the Arc measurement and recommended the establishment of an International Metre Commission.
The ''Europäische Gradmessung'' decided the creation of an international geodetic standard at the General Conference held in Paris in 1875. The Metre Convention
The Metre Convention (french: link=no, Convention du Mètre), also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations (Argentina, Austria-Hungary, Belgium, Brazi ...
was signed in 1875 in Paris and the International Bureau of Weights and Measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (french: Bureau international des poids et mesures, BIPM) is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act together on measurement standards in four areas: chemistry, ...
was created under the supervision of the International Committee for Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (GCWM; french: Conférence générale des poids et mesures, CGPM) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established i ...
. The first president of the International Committee for Weights and Measures
The General Conference on Weights and Measures (GCWM; french: Conférence générale des poids et mesures, CGPM) is the supreme authority of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM), the intergovernmental organization established i ...
was the Spanish geodesist Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero. He also was the president of the Permanent Commission of the ''Europäische Gradmessung'' from 1874 to 1886. In 1886 the association changed name for the International Geodetic Association )
, merged =
, successor =
, formation =
, founder =
, founding_location =
, extinction =
, merger =
, type = scholarly society
, tax_id ...
(German: ''Internationale Erdmessung'') and Carlos Ibáñez e Ibáñez de Ibero was reelected as president. He remained in this position until his death in 1891. During this period the International Geodetic Association )
, merged =
, successor =
, formation =
, founder =
, founding_location =
, extinction =
, merger =
, type = scholarly society
, tax_id ...
gained worldwide importance with the joining of United States, Mexico, Chile, Argentina and Japan. In 1883 the General Conference of the ''Europäische Gradmessung'' proposed to select the Greenwich meridian
The historic prime meridian or Greenwich meridian is a geographical reference line that passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, Royal Observatory, Greenwich, in London, England. The modern IERS Reference Meridian widely used today ...
as the prime meridian in the hope that Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
would accede to the Metre Convention
The Metre Convention (french: link=no, Convention du Mètre), also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations (Argentina, Austria-Hungary, Belgium, Brazi ...
.
From the Paris meridian to the Greenwich meridian
The United States passed an Act of Congress on 3 August 1882, authorizing PresidentChester A. Arthur
Chester Alan Arthur (October 5, 1829 – November 18, 1886) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 21st president of the United States from 1881 to 1885. He previously served as the 20th vice president under President James ...
to call an international conference to fix on a common prime meridian for time and longitude throughout the world. Before the invitations were sent out on 1 December, the joint efforts of Abbe, Fleming and William Frederick Allen, Secretary of the US railways' ''General Time Convention'' and Managing Editor of the ''Travellers' Official Guide to the Railways'', had brought the US railway companies to an agreement which led to standard railway time being introduced at noon on 18 November 1883 across the nation. Although this was not legally established until 1918, there was thus a strong sense of ''fait accompli'' that preceded the International Meridian Conference
The International Meridian Conference was a conference held in October 1884 in Washington, D.C., in the United States, to determine a prime meridian for international use. The conference was held at the request of U.S. President Chester A. ...
, although setting local times was not part of the remit of the conference.
In 1884, at the International Meridian Conference
The International Meridian Conference was a conference held in October 1884 in Washington, D.C., in the United States, to determine a prime meridian for international use. The conference was held at the request of U.S. President Chester A. ...
in Washington DC, the Greenwich meridian was adopted as the prime meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrary meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. Together, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian in a 360°-system) form a great c ...
of the world. San Domingo, now the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares wit ...
, voted against. France and Brazil abstained. The United Kingdom acceded to the Metre Convention
The Metre Convention (french: link=no, Convention du Mètre), also known as the Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by representatives of 17 nations (Argentina, Austria-Hungary, Belgium, Brazi ...
in 1884 and to the International Geodetic Association )
, merged =
, successor =
, formation =
, founder =
, founding_location =
, extinction =
, merger =
, type = scholarly society
, tax_id ...
in 1898. In 1911, Alexander Ross Clarke
Col Alexander Ross Clarke FRS FRSE (1828–1914) was a British geodesist, primarily remembered for his calculation of the Principal Triangulation of Britain (1858), the calculation of the Figure of the Earth (1858, 1860, 1866, 1880) and one ...
and Friedrich Robert Helmert
Friedrich Robert Helmert (31 July 1843 – 15 June 1917) was a German geodesist and statistician with important contributions to the theory of errors.
Career
Helmert was born in Freiberg, Kingdom of Saxony. After schooling in Freiberg and ...
stated in the Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
:
"According to the calculations made at the central bureau of the international association on the great meridian arc extending from the Shetland Islands, through Great Britain, France and Spain to El Aghuat in Algeria, ''a'' equatorial_radius_of_the_Earth.html" ;"title="Earth_radius.html" ;"title="he equatorial_radius_of_the_Earth">Earth_radius.html"_;"title="he_Earth_radius">equatorial_radius_of_the_Earth=_6,377,935_metres,_the_Flattening.html" "title="Earth radius">equatorial radius of the Earth">Earth_radius.html" ;"title="he Earth radius">equatorial radius of the Earth= 6,377,935 metres, the Flattening">ellipticity
Flattening is a measure of the compression of a circle or sphere along a diameter to form an ellipse or an ellipsoid of revolution (spheroid) respectively. Other terms used are ellipticity, or oblateness. The usual notation for flattening is ...
being assumed as 1/299.15. [...] The net does not follow the meridian exactly, but deviates both to the west and to the east; actually, the Prime meridian (Greenwich), meridian of Greenwich is nearer the mean than that of Paris (Helmert, ''Grösse d. Erde'')."
The French clung to the Paris meridian as a rival to Greenwich until 1911 for timekeeping purposes and 1914 for navigation. To this day, French cartographers continue to indicate the Paris meridian on some maps.
From wireless telegraphy to Coordinated Universal Time
With the arrival of wireless telegraphy, France established a transmitter on theEiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower ( ; french: links=yes, tour Eiffel ) is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower.
Locally nicknamed "'' ...
to broadcast a time signal. The creation of the International Time Bureau
The International Time Bureau (french: Bureau International de l'Heure, abbreviated BIH), seated at the Paris Observatory, was the international bureau responsible for combining different measurements of Universal Time.
The bureau also played an i ...
, seated at the Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (french: Observatoire de Paris ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centers in the world. Its histor ...
, was decided upon during the 1912 ''Conférence internationale de l'heure radiotélégraphique''. The following year an attempt was made to regulate the international status of the bureau through the creation of an international convention
International law (also known as public international law and the law of nations) is the set of rules, norms, and standards generally recognized as binding between states. It establishes normative guidelines and a common conceptual framework for ...
. However, the convention wasn't ratified by its member countries due to the outbreak of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. In 1919, after the war, it was decided upon to make the bureau the executive body of the ''International Commission of Time'', one of the commissions of the then newly founded International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
(IAU).
From 1956 until 1987 the International Time Bureau
The International Time Bureau (french: Bureau International de l'Heure, abbreviated BIH), seated at the Paris Observatory, was the international bureau responsible for combining different measurements of Universal Time.
The bureau also played an i ...
was part of the Federation of Astronomical and Geophysical Data Analysis Services (FAGS). In 1987 the bureau's tasks of combining different measurements of Atomic Time
International Atomic Time (abbreviated TAI, from its French name ) is a high-precision atomic coordinate time standard based on the notional passage of proper time on Earth's geoid. TAI is a weighted average of the time kept by over 450 atomic ...
were taken over by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (french: Bureau international des poids et mesures, BIPM) is an intergovernmental organisation, through which its 59 member-states act together on measurement standards in four areas: chemistry, ...
(BIPM). Its tasks related to the correction of time with respect to the celestial
Celestial may refer to:
Science
* Objects or events seen in the sky and the following astronomical terms:
** Astronomical object, a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe
** Celes ...
reference frame
In physics and astronomy, a frame of reference (or reference frame) is an abstract coordinate system whose origin (mathematics), origin, orientation (geometry), orientation, and scale (geometry), scale are specified by a set of reference point ...
and the Earth's rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in retrograd ...
to realize the Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is within about one second of mean solar time (such as UT1) at 0° longitude (at the IERS Reference Meridian as the currently used ...
(UTC) were taken over by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS) which was established in its present form in 1987 by the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
and the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics
The International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG; french: Union géodésique et géophysique internationale, UGGI) is an international non-governmental organization dedicated to the scientific study of Earth and its space environment us ...
(IUGG).
The Arago medallions
 In 1994 the Arago Association and the city of Paris commissioned a Dutch conceptual artist,
In 1994 the Arago Association and the city of Paris commissioned a Dutch conceptual artist, Jan Dibbets
Jan Dibbets (born 9 May 1941, in Weert) is an Amsterdam-based Dutch conceptual artist. His work is influenced by mathematics and works mainly with photography.
Life and career
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, he started as an art teacher at the ...
, to create a memorial to Arago. Dibbets came up with the idea of setting 135 bronze medallions (although only 121 are documented in the official guide to the medallions) into the ground along the Paris meridian between the northern and southern limits of Paris: a total distance of 9.2 kilometres/5.7 miles. Each medallion is 12 cm in diameter and marked with the name ARAGO plus N and S pointers.
Another project, the Green Meridian (''An 2000 – La Méridienne Verte''), aimed to establish a plantation of trees along the entire length of the meridian arc in France. Several missing Arago medallions appear to have been replaced with the newer 'An 2000 – La Méridienne Verte' markers.
Unfounded speculation
In certain circles, some kind ofoccult
The occult, in the broadest sense, is a category of esoteric supernatural beliefs and practices which generally fall outside the scope of religion and science, encompassing phenomena involving otherworldly agency, such as magic and mysticism a ...
or esoteric
Western esotericism, also known as esotericism, esoterism, and sometimes the Western mystery tradition, is a term scholars use to categorise a wide range of loosely related ideas and movements that developed within Western society. These ideas a ...
significance is ascribed to the Paris meridian; sometimes it is even perceived as a sinister axis. Dominique Stezepfandts, a French conspiracy theorist, attacks the Arago medallions that supposedly trace the route of "an occult geographical line". To him the Paris meridian is a "Masonic axis" or even "the heart of the Devil."
Henry Lincoln
Henry Soskin (12 February 1930 – 23 February 2022), better known as Henry Lincoln, was a British author, television presenter, scriptwriter, and actor. He co-wrote three '' Doctor Who'' multi-part serials in the 1960s, and — starting in t ...
, in his book ''The Holy Place'', argues that various ancient structures are aligned according to the Paris meridian. They even include medieval churches, built long before the meridian was established according to conventional history, and Lincoln finds it obvious that the meridian "was based upon the 'cromlech
A cromlech (sometimes also spelled "cromleh" or "cromlêh"; cf Welsh ''crom'', "bent"; ''llech'', "slate") is a megalithic construction made of large stone blocks. The word applies to two different megalithic forms in English, the first being an ...
intersect division line'." David Wood, in his book ''Genesis'', likewise ascribes a deeper significance to the Paris meridian and takes it into account when trying to decipher the geometry of the myth-encrusted village of Rennes-le-Château
Rennes-le-Château (; oc, Rènnas del Castèl) is a commune approximately 5 km (3 miles) south of Couiza, in the Aude department in the Occitanie region in Southern France. In 2018, it had a population of 91.
This hilltop village is k ...
: The meridian passes about 350 metres (1,150 ft) west of the site of the so-called " Poussin tomb," an important location in the legends and esoteric theories relating to that place. A sceptical discussion of these theories, including the supposed alignments, can be found in Bill Putnam and Edwin Wood's book ''The Treasure of Rennes-le-Château – A mystery solved''.
In fiction
The meridian line, dubbed the "Rose Line" by authorDan Brown
Daniel Gerhard Brown (born June 22, 1964) is an American author best known for his Thriller (genre), thriller novels, including the Robert Langdon novels ''Angels & Demons'' (2000), ''The Da Vinci Code'' (2003), ''The Lost Symbol'' (2009), ''In ...
appeared in the novel ''The Da Vinci Code
''The Da Vinci Code'' is a 2003 mystery thriller novel by Dan Brown. It is Brown's second novel to include the character Robert Langdon: the first was his 2000 novel ''Angels & Demons''. ''The Da Vinci Code'' follows symbologist Robert Langdon ...
''.
See also
*Cartography of France
The history of French cartography can be traced to developments in the Middle Ages. This period was marked by improvements in measuring instruments and also by an upgrade of work in registers of all types. What is thought to be the oldest land map ...
* Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790)
The Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) was the geodetic survey to measure the relative position of Greenwich Observatory and the Paris Observatory via triangulation. The English operations, executed by William Roy, consisted of the measureme ...
* Principal Triangulation of Great Britain
The Principal Triangulation of Britain was the first high-precision triangulation survey of the whole of Great Britain (including Ireland), carried out between 1791 and 1853 under the auspices of the Board of Ordnance. The aim of the survey was ...
* Meridian arc
In geodesy and navigation, a meridian arc is the curve between two points on the Earth's surface having the same longitude. The term may refer either to a segment of the meridian, or to its length.
The purpose of measuring meridian arcs is to de ...
* History of geodesy
The history of geodesy deals with the historical development of measurements and representations of the Earth. The corresponding scientific discipline, '' geodesy'' ( /dʒiːˈɒdɪsi/), began in pre-scientific antiquity and blossomed during th ...
*History of the metre
The history of the metre starts with the Scientific Revolution that is considered to have begun with Nicolaus Copernicus's publication of '' De revolutionibus orbium coelestium'' in 1543. Increasingly accurate measurements were required, and ...
*Seconds pendulum
A seconds pendulum is a pendulum whose period is precisely two seconds; one second for a swing in one direction and one second for the return swing, a frequency of 0.5 Hz.
Pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that ...
* Struve Geodetic Arc
The Struve Geodetic Arc is a chain of survey triangulations stretching from Hammerfest in Norway to the Black Sea, through ten countries and over , which yielded the first accurate measurement of a meridian arc.
The chain was established ...
References
External links
* {{cite EB1911, wstitle=Earth, Figure of the , last1= Clarke , first1 = Alexander Ross , last2 = Helmert , first2 = Friedrich Robert , volume= 08 , pages = 801–814 Better formatted mathematics atWikisource
Wikisource is an online digital library of free-content textual sources on a wiki, operated by the Wikimedia Foundation. Wikisource is the name of the project as a whole and the name for each instance of that project (each instance usually rep ...
.
The Arago medallions on Google Earth
Full Meridian of Glory: Perilous Adventures in the Competition to Measure the Earth
history of science book by Prof. Paul Murdin
The Greenwich Meridian, by Graham Dolan
Named meridians Geography of Paris Geography of France History of Paris Prime meridians Geodesy Metrology Geography of England Geography of Spain Geography of Algeria Paris Observatory