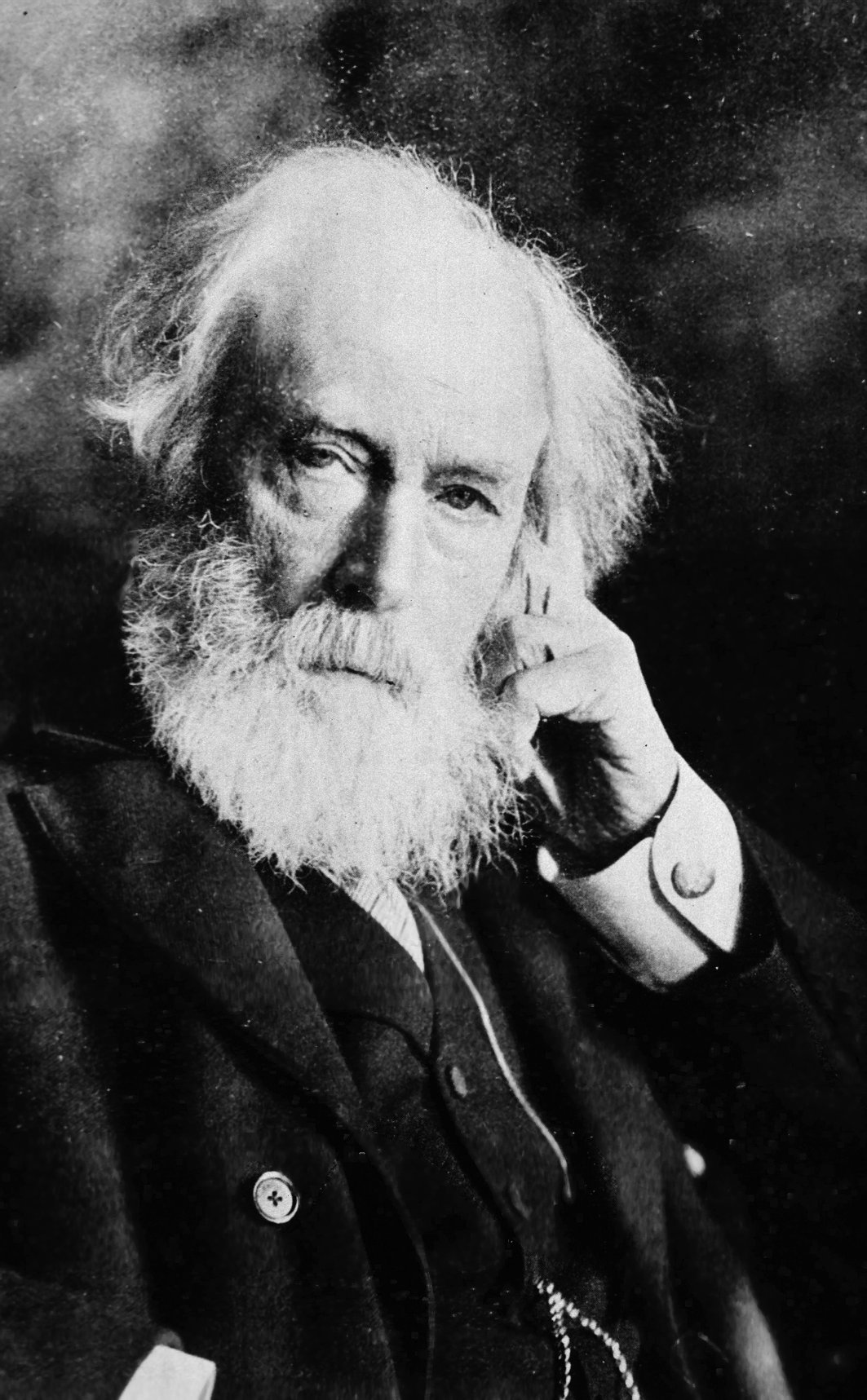|
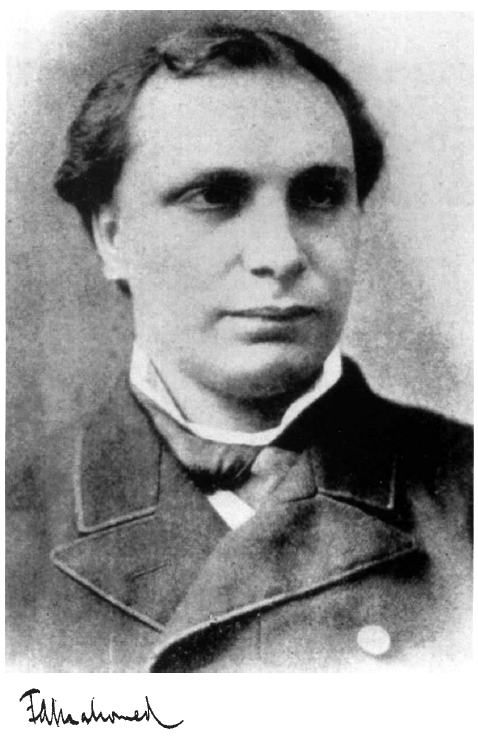
Frederick Akbar Mahomed
Frederick Henry Horatio Akbar Mahomed (11 April 1849 – 22 November 1884) was an internationally known British physician from Brighton, England. Family and personal life Frederick Henry Horatio Akbar Mahomed was born on 11 April 1849 in Brighton. He was the eldest son of Frederick Mahomed (1818–1888) and his second wife, Sarah Hodgkinson (1816–1905). He was also the grandson of the pioneering Indian traveller, author and entrepreneur Sake Dean Mahomed. Frederick Akbar Mahomed's father, Frederick Mahomed, ran a fencing, gymnastics and callisthenics academy in Hove, which included boxing instruction. Cameron and Hicks dispute the suggestion that he ran Turkish baths at Brighton attributing this to a confusion of Mahomed's father Frederick with his uncle, Arthur. Mahomed had three brothers (Arthur George Suleiman, James Deen Kerriman and Henry), and one sister (Adeline). He was educated privately in Brighton prior to attending medical school. On June 14, 1873, at the parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Mahomed
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Nobility Anhalt-Harzgerode *Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) Austria * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans Baden * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden Bohemia * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia Britain * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain Brandenburg/Prussia * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), Margrave of Brandenburg * Frederick William, Elector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Newspaper Archive
The British Newspaper Archive web site provides access to searchable digitized archives of British and Irish newspapers. It was launched in November 2011. History The British Library Newspapers section was based in Colindale in north London, until 2013, and is now divided between the St Pancras and Boston Spa sites. The library has an almost complete collection of British and Irish newspapers since 1840. This is partly because of the legal deposit legislation of 1869, which required newspapers to supply a copy of each edition of a newspaper to the library. London editions of national daily and Sunday newspapers are complete back to 1801. In total, the collection consists of 660,000 bound volumes and 370,000 reels of microfilm containing tens of millions of newspapers with 52,000 titles on 45 km of shelves. After the closure of Colindale in November 2013, access to the 750 million original printed pages was maintained via an automated and climate-controlled storage facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a desire to eliminate their presence, and fear of losing national, ethnic, or racial identity.Guido Bolaffi. ''Dictionary of race, ethnicity and culture''. SAGE Publications Ltd., 2003. Pp. 332. Alternate definitions A 1997 review article on xenophobia holds that it is "an element of a political struggle about who has the right to be cared for by the state and society: a fight for the collective good of the modern state." According to Italian sociologist Guido Bolaffi, xenophobia can also be exhibited as an "''uncritical exaltation of another culture''" which is ascribed "''an unreal, stereotyped and exotic quality''". History Ancient Europe An early example of xenophobic sentiment in Western culture is the Ancient Greek denigratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Garrett Anderson
Elizabeth Garrett Anderson (9 June 1836 – 17 December 1917) was an English physician and suffragist. She was the first woman to qualify in Britain as a physician and surgeon. She was the co-founder of the first hospital staffed by women, the first dean of a British medical school, the first woman in Britain to be elected to a school board and, as mayor of Aldeburgh, the first female mayor in Britain. Early life Elizabeth was born in Whitechapel, London, and the second of eleven children of Newson Garrett (1812–1893), from Leiston, Suffolk, and his wife, Louisa (born Dunnell; 1813–1903), from London. The Garrett ancestors had been ironworkers in East Suffolk since the early seventeenth century. Newson was the youngest of three sons and not academically inclined, although he possessed the family's entrepreneurial spirit. When he finished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Paget
Sir James Paget, 1st Baronet FRS HFRSE (11 January 1814 – 30 December 1899) (, rhymes with "gadget") was an English surgeon and pathologist who is best remembered for naming Paget's disease and who is considered, together with Rudolf Virchow, as one of the founders of scientific medical pathology. His famous works included ''Lectures on Tumours'' (1851) and ''Lectures on Surgical Pathology'' (1853). There are several medical conditions which were described by, and later named after, Paget: * Paget's disease of bone * Paget's disease of the nipple (a form of intraductal breast cancer spreading into the skin around the nipple) ** Extramammary Paget's disease refers to a group of similar, more rare skin lesions discovered by Radcliffe Crocker in 1889 which affect the male and female genitalia. * Paget–Schroetter disease * Paget's abscess, an abscess that recurs at the site of a former abscess which had resolved. Life Paget was born in Great Yarmouth, England, on 11 January ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Wilks
Sir Samuel Wilks, 1st Baronet, (2 June 1824 – 8 November 1911) was a British physician and biographer. Early life Samuel Wilks was born on 2 June 1824 in Camberwell, London, the second son of Joseph Barber Wilks, a cashier at the East India House. After attending Aldenham School and University College School he was apprenticed to Richard Prior, a doctor in Newington. Career In 1842 he entered Guy's Hospital to study medicine. After graduating MB in 1848 he was hired as a physician to the Surrey Infirmary (1853). In 1856 he returned to Guy's Hospital, first as assistant physician and curator of its museum (a post he held for nine years), then as physician and lecturer on medicine (1857). From 1866 to 1870 he was examiner in the practice of medicine at the University of London and from 1868 to 1875 examiner in medicine at the Royal College of Surgeons. Achievements Among his major discoveries, Wilks recognised ulcerative colitis in 1859, differentiating it from bacterial dyse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Gull
Sir William Withey Gull, 1st Baronet (31 December 181629 January 1890) was an English physician. Of modest family origins, he established a lucrative private practice and served as Governor of Guy's Hospital, Fullerian Professor of Physiology and President of the Clinical Society. In 1871, having successfully treated the Prince of Wales during a life-threatening attack of typhoid fever, he was created a Baronet and appointed to be one of the Physicians-in-Ordinary to Queen Victoria. Gull made some significant contributions to medical science, including advancing the understanding of myxoedema, Bright's disease, paraplegia and anorexia nervosa (for which he first established the name). A widely discredited masonic/royal conspiracy theory created in the 1970s alleged that Gull knew the identity of Jack the Ripper, or even that he himself was the murderer. Although scholars have dismissed it, and Gull was 71 years old and in ill health when the murders were committed, it has bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highgate Cemetery
Highgate Cemetery is a place of burial in north London, England. There are approximately 170,000 people buried in around 53,000 graves across the West and East Cemeteries. Highgate Cemetery is notable both for some of the people buried there as well as for its ''de facto'' status as a nature reserve. The Cemetery is designated Grade I on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. It is one of the Magnificent Seven cemeteries in London. Location The cemetery is in Highgate N6, next to Waterlow Park, in the London Borough of Camden. It comprises two sites, on either side of Swains Lane. The main gate is on Swains Lane just north of Oakshott Avenue. There is another, disused, gate on Chester Road. The nearest public transport ( Transport for London) is the C11 bus, Brookfield Park stop, and Archway tube station. History and setting The cemetery in its original formthe northwestern wooded areaopened in 1839, as part of a plan to provide seven large, modern cemeteries, now known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Fever Hospital
The London Fever Hospital was a voluntary hospital financed from public donations in Liverpool Road in London. It was one of the first fever hospitals in the country. History Originally established with 15 beds in 1802 in Gray's Inn Road, it moved in 1815 to the west wing of the Smallpox Hospital at Battle Bridge where it had 120 beds. After the Northern Railway bought the original site for Kings Cross station the compensation money paid enabled the charity to commission a new Hospital on Kettle Field, a 4-acre site in Liverpool Road, Islington with 200 beds. The new hospital, which was designed by Charles Fowler, opened in 1848. By 1924 it had about 150 beds. A new wing was opened by the Duchess of York in 1928 and a new isolation block was opened by the Duke of Kent in 1938. In 1948, the hospital joined the National Health Service under the same management as the Royal Free Hospital. After services had been transferred to the Royal Free Hospital, the hospital closed in 1975. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected, but they are still able to spread the disease. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''S. enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, peyers patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |