|
Franz Daniel Kahn
Franz Daniel Kahn (1926–1998) was a mathematician and astrophysicist at the University of Manchester. He was Professor of Astronomy from 1966 to 1993, then Emeritus thereafter in the School of Physics and Astronomy. Education Kahn was educated at St Paul's School, London from 1940 to 1944, after which he secured an open scholarship to The Queen's College, Oxford. After graduating with first-class honours in mathematics in 1947 he moved to Balliol College, Oxford in 1948 as a Skynner senior student. He was awarded a Doctor of Philosophy degree in 1950 for research supervised by Sydney Chapman on the luminosity of the upper atmosphere. Research and career According to his certificate of election as a Fellow of the Royal Society: Awards and honours Kahn was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) in 1993. He was also a Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society (FRAS). In 1991 the International Astronomers Union named the asteroid Kahnia after him. Personal life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest city in Germany. On the Pegnitz River (from its confluence with the Rednitz in Fürth onwards: Regnitz, a tributary of the River Main) and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it lies in the Bavarian administrative region of Middle Franconia, and is the largest city and the unofficial capital of Franconia. Nuremberg forms with the neighbouring cities of Fürth, Erlangen and Schwabach a continuous conurbation with a total population of 800,376 (2019), which is the heart of the urban area region with around 1.4 million inhabitants, while the larger Nuremberg Metropolitan Region has approximately 3.6 million inhabitants. The city lies about north of Munich. It is the largest city in the East Franconian dialect area (colloquially: "F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow
A fellow is a concept whose exact meaning depends on context. In learned or professional societies, it refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements. Within the context of higher educational institutions, a fellow can be a member of a highly ranked group of teachers at a particular college or university or a member of the governing body in some universities (such as the Fellows of Harvard College); it can also be a specially selected postgraduate student who has been appointed to a post (called a fellowship) granting a stipend, research facilities and other privileges for a fixed period (usually one year or more) in order to undertake some advanced study or research, often in return for teaching services. In the context of research and development-intensive large companies or corporations, the title "fellow" is sometimes given to a small number of senior scientists and engineers. In the context of medical education in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 '' Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein–de Sitter Universe
The Einstein–de Sitter universe is a model of the universe proposed by Albert Einstein and Willem de Sitter in 1932. On first learning of Edwin Hubble's discovery of a linear relation between the redshift of the galaxies and their distance, Einstein set the cosmological constant to zero in the Friedmann equations, resulting in a model of the expanding universe known as the Friedmann–Einstein universe. In 1932, Einstein and De Sitter proposed an even simpler cosmic model by assuming a vanishing spatial curvature as well as a vanishing cosmological constant. In modern parlance, the Einstein–de Sitter universe can be described as a cosmological model for a flat matter-only Friedmann–Lemaître–Robertson–Walker metric (FLRW) universe. Lars Bergström & Ariel Goobar: "''Cosmology and Particle Astrophysics''", 2nd ed. Springer (2004), p. 70+77. . In the model, Einstein and de Sitter derived a simple relation between the average density of matter in the universe and its expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
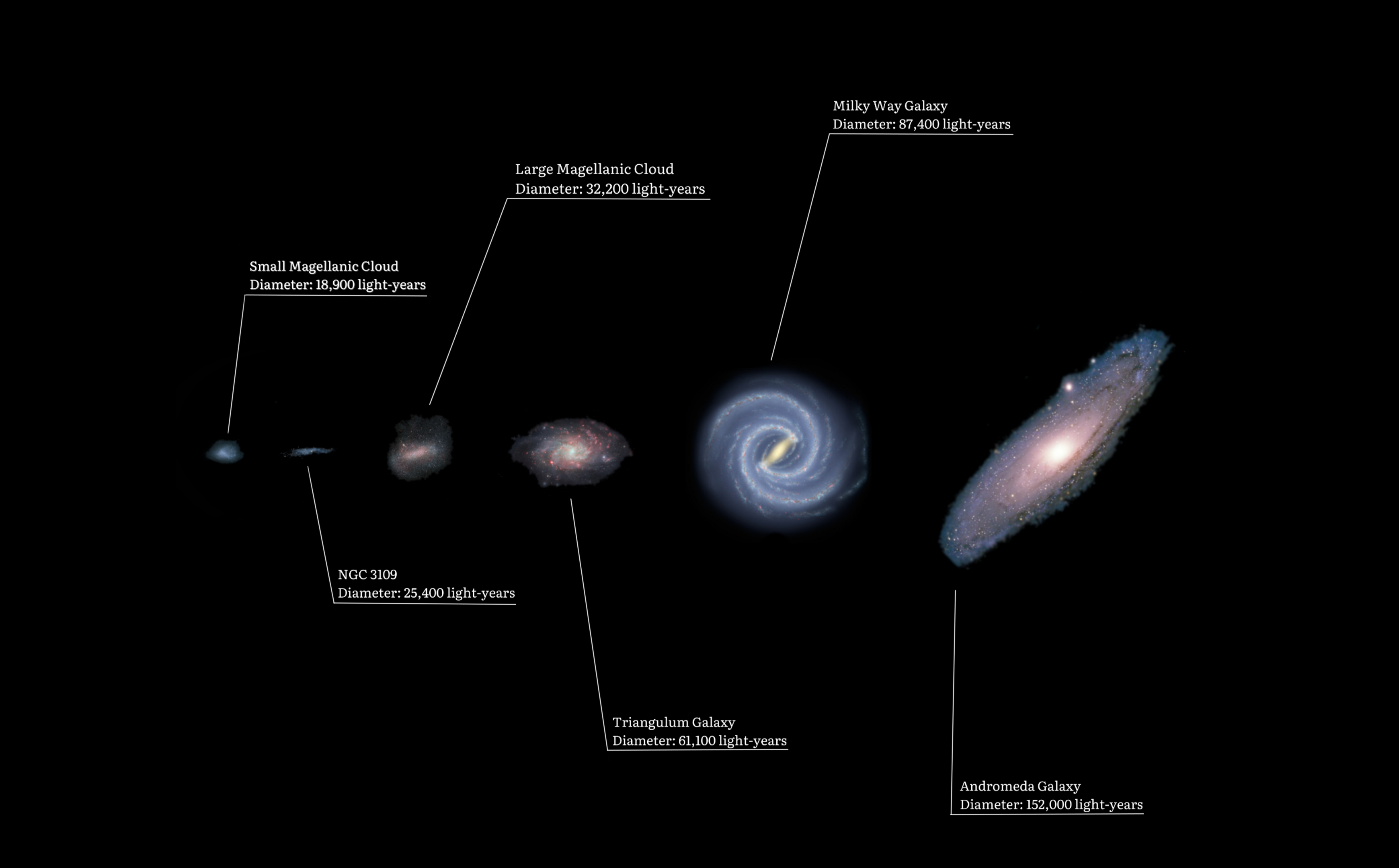
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, NGC 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original object, called the ''progenitor'', either collapses to a neutron star or black hole, or is completely destroyed. The peak optical luminosity of a supernova can be comparable to that of an entire galaxy before fading over several weeks or months. Supernovae are more energetic than novae. In Latin, ''nova'' means "new", referring astronomically to what appears to be a temporary new bright star. Adding the prefix "super-" distinguishes supernovae from ordinary novae, which are far less luminous. The word ''supernova'' was coined by Walter Baade and Fritz Zwicky in 1929. The last supernova to be directly observed in the Milky Way was Kepler's Supernova in 1604, ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramatic appearance of a nova vary, depending on the circumstances of the two progenitor stars. All observed novae involve white dwarfs in close binary systems. The main sub-classes of novae are classical novae, recurrent novae (RNe), and dwarf novae. They are all considered to be cataclysmic variable stars. Classical nova eruptions are the most common type. They are likely created in a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf and either a main sequence, subgiant, or red giant star. When the orbital period falls in the range of several days to one day, the white dwarf is close enough to its companion star to start drawing accreted matter onto the surface of the white dwarf, which creates a dense but shallow atmosphere. This atmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
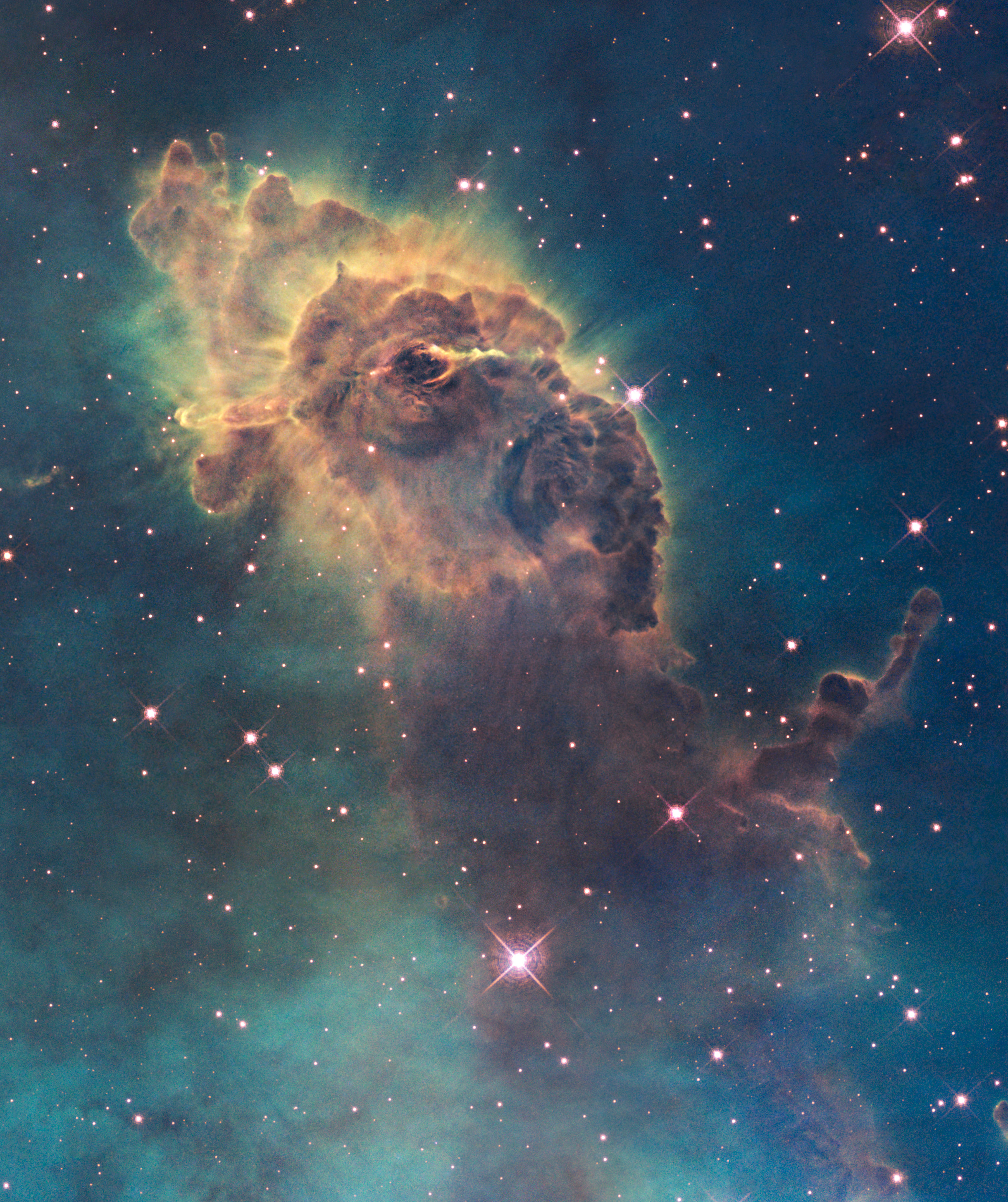
Nebula
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the " Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter, and eventually will become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Corona
The terms galactic corona and gaseous corona have been used in the first decade of the 21st century to describe a hot, ionised, gaseous component in the galactic halo of the Milky Way. A similar body of very hot and tenuous gas in the halo of any spiral galaxy may also be described by these terms. Current hypothetical scenario The hypothetical source of the galactic halo of ''coronal gas'' may be the cumulative output of many “galactic fountains” in the galactic disc ejecting hot gas. The hypothesis is that a single supernova and then its supernova remnant both produce hot ionized gas that supplies an individual “galactic fountain”. The expelled material forms a giant bubble of high-pressure, low density, hot gas in the denser, cooler gas and dust of the galactic disc. At least some of those bubbles extend high or low enough, vertically, to pierce through the denser disk, and form “chimneys” which exhaust the hot gas into the halo, analogous to a terrestrial g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spherically symmetric. Different types of stars have different types of stellar winds. Post-main-sequence stars nearing the ends of their lives often eject large quantities of mass in massive ( \scriptstyle \dot > 10^ solar masses per year), slow (v = 10 km/s) winds. These include red giants and supergiants, and asymptotic giant branch stars. These winds are understood to be driven by radiation pressure on dust condensing in the upper atmosphere of the stars. Young T Tauri stars often have very powerful stellar winds. Massive stars of types O and B have stellar winds with lower mass loss rates (\scriptstyle \dot 1–2000 km/s). Such winds are driven by radiation pressure on the resonance absorption lines of heavy elements such as carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in The "medium" is present further soon.-->interstellar space, sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "-forming regions", and form s. As a branch of , star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |