|
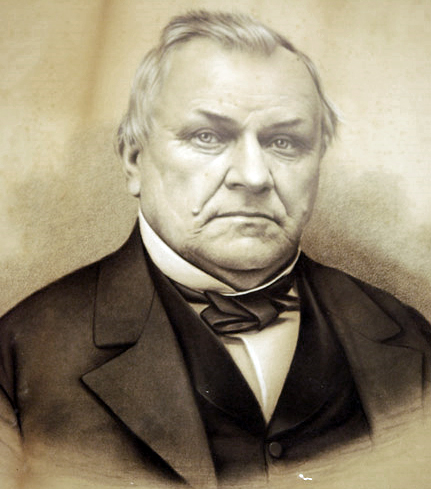
Frank Olson
Frank Rudolph Emmanuel Olson (July 17, 1910 – November 28, 1953) was an American bacteriologist, biological warfare scientist, and an employee of the United States Army Biological Warfare Laboratories (USBWL) who worked at Camp Detrick (now Fort Detrick) in Maryland. At a meeting in rural Maryland, he was covertly dosed with LSD by his colleague Sidney Gottlieb (head of the CIA's MKUltra program) and, nine days later, plunged to his death from the window of the Hotel Statler in New York. The U.S. government first described his death as a suicide, and then as misadventure, while others allege murder. The Rockefeller Commission report on the CIA in 1975 acknowledged their having conducted covert drug studies on fellow agents. Olson's death is one of the most mysterious outcomes of the CIA mind control project MKUltra. Biography Youth and education Olson was born to Swedish immigrant parents in Hurley, Iron County, Wisconsin. Olson graduated from Hurley High School in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurley, Wisconsin
Hurley is a city in and the county seat of Iron County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 1,547 at the 2010 census. It is located directly across the Montreal River from Ironwood, Michigan. History Hurley is located on the Montreal River, the border between Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. The city is on U.S. Highway 2 (US 2), and is the northern terminus of US 51, and is about south of Lake Superior. Hurley had its origins in the iron mining and lumbering booms of the 1880s. The city is located, along with adjacent Ironwood, Michigan, at the center of the Gogebic Range. The economy of Hurley, together with the city of Montreal in Wisconsin, and the cities of Ironwood, Bessemer and Wakefield in Michigan, was dependent upon the extraction of iron ore from the Gogebic (a/k/a Penokee) Range during the 19th and 20th centuries. Hurley took its name from Canadian-born M. A. Hurley, a prominent attorney of Wausau who won a lawsuit for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purdue University
Purdue University is a public land-grant research university in West Lafayette, Indiana, and the flagship campus of the Purdue University system. The university was founded in 1869 after Lafayette businessman John Purdue donated land and money to establish a college of science, technology, and agriculture in his name. The first classes were held on September 16, 1874, with six instructors and 39 students. It has been ranked as among the best public universities in the United States by major institutional rankings, and is renowned for its engineering program. The main campus in West Lafayette offers more than 200 majors for undergraduates, over 70 masters and doctoral programs, and professional degrees in pharmacy, veterinary medicine, and doctor of nursing practice. In addition, Purdue has 18 intercollegiate sports teams and more than 900 student organizations. Purdue is the founding member of the Big Ten Conference and enrolls the largest student body of any individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al Jazeera
Al Jazeera ( ar, الجزيرة, translit-std=DIN, translit=al-jazīrah, , "The Island") is a state-owned Arabic-language international radio and TV broadcaster of Qatar. It is based in Doha and operated by the media conglomerate Al Jazeera Media Network. The flagship of the network, its station identification, is ''Al Jazeera.'' The patent holding is a "private foundation for public benefit" under Qatari law. Under this organizational structure, the parent receives funding from the government of Qatar but maintains its editorial independence. In June 2017, the Saudi, Emirati, Bahraini, and Egyptian governments insisted on the closure of the entire conglomerate as one of thirteen demands made to the Government of Qatar during the Qatar diplomatic crisis. The channel has been criticised by some organisations as well as nations such as Saudi Arabia for being "Qatari propaganda". Etymology In Arabic, ' literally means "the island". However, it refers here to the Arabia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bud Mahurin
Colonel Walker Melville "Bud" Mahurin (December 5, 1918 – May 11, 2010) was a United States Air Force officer and aviator. During World War II, while serving in the United States Army Air Forces, he was a flying ace. Mahurin was the first American pilot to become a double ace in the European Theater. He was the only United States Air Force pilot to shoot down enemy planes in both the European and Pacific Theaters and the Korean War. During World War II he was credited with 20.75 aerial victories, making him the sixth-highest American P-47 ace. He was credited with shooting down 3.5 MiG-15s in Korea, giving him a total of 24.25 aircraft destroyed in aerial combat. Early life Born in Benton Harbor, Michigan, Mahurin joined the United States Army Air Forces as an aviation cadet on September 29, 1941 after several years as an engineering student at Purdue University. He graduated from pilot training on April 29, 1942. World War II Mahurin was assigned to the 63d Fighter Squa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Schwable
Brigadier General Frank Hawse Schwable (July 18, 1908 – October 28, 1988) was a decorated U.S. Marine pilot whose prosecution for collaborating with his Korean captors while a prisoner of war was dismissed in 1954. Biography Schwable, the son of a marine colonel who served thirty years, graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in 1929. He was awarded the Cross of Valor by the Nicaraguan government in 1932. In September 1933, he was among 19 aviators representing the Marine Corps at the International Air Races in Chicago. He received the Legion of Merit for his service in World War II. Colonel While chief of staff of the First Marine Air Wing, Colonel Schwable and his co-pilot were reported missing on a combat mission in Korea in July 1952. On February 23, 1953, the Chinese broadcast charges that two officers, Schwable and his co-pilot, had said that the U.S. was conducting germ warfare. Schwable was quoted saying the purpose was "to test under field conditions various elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Artichoke
Project ARTICHOKE (also referred to as Operation ARTICHOKE) was a Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) project that researched interrogation methods. Preceded by Project BLUEBIRD, ARTICHOKE officially arose on August 20, 1951 and was operated by the CIA's Office of Scientific Intelligence. The primary goal of Project ARTICHOKE was to determine whether a person could be involuntarily made to perform an act of attempted assassination. The project also studied hypnosis, forced morphine addiction (and subsequent forced withdrawal) and the use of other chemicals including LSD, to produce amnesia and other vulnerable states in subjects. Project ARTICHOKE led to Project MKUltra, which began in 1953. The project ARTICHOKE was a mind control program that gathered information together with the intelligence divisions of the Army, Navy, Air Force and FBI. In addition, the scope of the project was outlined in a memo dated January 1952 that asked, "Can we get control of an individual to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Sea-Spray
Operation Sea-Spray was a 1950 U.S. Navy secret biological warfare experiment in which ''Serratia marcescens'' and '' Bacillus globigii'' bacteria were sprayed over the San Francisco Bay Area in California, in order to determine how vulnerable a city like San Francisco may be to a bioweapon attack. Military test Starting on September 20, 1950 and continuing until September 27, the U.S. Navy released the two types of bacteria from a ship off the shore of San Francisco, believing them to be harmless to humans. Based on results from monitoring equipment at 43 locations around the city, the Army determined that San Francisco had received enough of a dose for nearly all of the city's 800,000 residents to inhale at least 5,000 of the particles. Illnesses On October 11, 1950, eleven residents checked into Stanford Hospital in San Francisco with very rare, serious urinary tract infections. Although ten recovered, Edward J. Nevin, who had had recent prostate surgery, died three weeks l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Harness
Operation Harness was a series of three-month secret biological warfare trials carried out by the government of the United Kingdom in the Caribbean, off the Bahamas, in December 1948 - February 1949.Brian Balmer''Britain and Biological Warfare: Expert Advice and Science Policy, 1930-65'' London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2001 Animals were exposed to anthrax, tularemia, and brucella bacteria on inflatable dinghies offshore but the results were found meaningless. History The operation did not go well, for several reasons. The sea was rougher than expected, making it impossible for the dinghies with animal crates to be picked up by craft converted for the operation. This meant the tests were carried out just off the shore of an island, endangering inhabitants. Protective suits were found to be so heavy that those using them had to undergo a lengthy acclimatisation process to avoid heat exhaustion. Sampling equipment was accidentally activated by local radio signals and conditions at sea ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
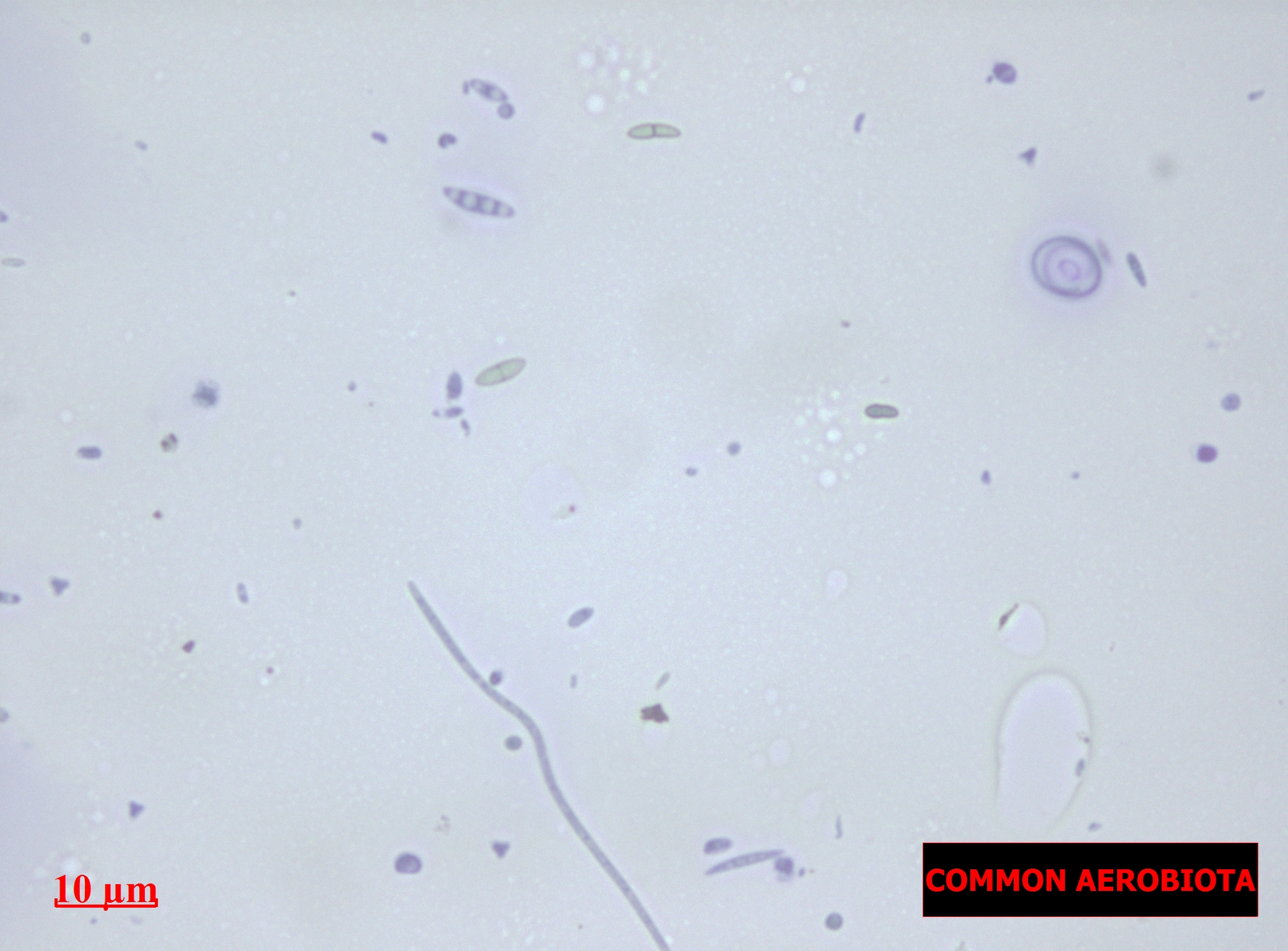
Aerobiology
Aerobiology (from Greek ἀήρ, ''aēr'', "air"; βίος, ''bios'', "life"; and -λογία, ''-logia'') is a branch of biology that studies organic particles, such as bacteria, fungal spores, very small insects, pollen grains and viruses, which are passively transported by the air. Aerobiologists have traditionally been involved in the measurement and reporting of airborne pollen and fungal spores as a service to those with allergies. The first finding of airborne algae took place in Germany in 1910. See also *Aeroplankton Aeroplankton (or aerial plankton) are tiny lifeforms that float and drift in the air, carried by wind. Most of the living things that make up aeroplankton are very small to microscopic in size, and many can be difficult to identify because of ... References External linksInternational Society of Aerobiology *https://www.knowmold.com/know-your-mold.html {{Authority control Mycology Microbiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Anthracis
''Bacillus anthracis'' is a gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium that causes anthrax, a deadly disease to livestock and, occasionally, to humans. It is the only permanent ( obligate) pathogen within the genus '' Bacillus''. Its infection is a type of zoonosis, as it is transmitted from animals to humans. It was discovered by a German physician Robert Koch in 1876, and became the first bacterium to be experimentally shown as a pathogen. The discovery was also the first scientific evidence for the germ theory of diseases. ''B. anthracis'' measures about 3 to 5 μm long and 1 to 1.2 μm wide. The reference genome consists of a 5,227,419 bp circular chromosome and two extrachromosomal DNA plasmids, pXO1 and pXO2, of 181,677 and 94,830 bp respectively, which are responsible for the pathogenicity. It forms a protective layer called endospore by which it can remain inactive for many years and suddenly becomes infective under suitable environmental conditions. Because of the resil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Paperclip
Operation Paperclip was a secret United States intelligence program in which more than 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians were taken from the former Nazi Germany to the U.S. for government employment after the end of World War II in Europe, between 1945 and 1959. Conducted by the Joint Intelligence Objectives Agency (JIOA), it was largely carried out by special agents of the U.S. Army's Counterintelligence Corps (CIC). Many of these personnel were former members and some were former leaders of the Nazi Party. In February 1945, Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force (SHAEF) set up T-Force, or Special Sections Subdivision, which grew to over 2,000 personnel by June. T-Force examined 5,000 German targets with a high priority on synthetic rubber and oil catalysts, new designs in armored equipment, V-2 (rocket) weapons, jet and rocket propelled aircraft, naval equipment, field radios, secret writing chemicals, aero medicine research, gliders, and "scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.png)