|
Frank D. Gilroy
Frank Daniel Gilroy (October 13, 1925 – September 12, 2015) was an American playwright, screenwriter, and film producer and director. He received the Tony Award for Best Play and the Pulitzer Prize for Drama for his play ''The Subject Was Roses'' in 1965. Early life Gilroy was born on October 13, 1925 in New York City, the son of Bettina (née Vasti) and Frank B. Gilroy, a coffee broker. His father was Irish American and his mother was of Italian and German descent. Gilroy lived in the Bronx for most of his childhood and attended DeWitt Clinton High School. He then enlisted in the U.S. Army after graduation. He served two and a half years in the 89th Division, of which eighteen months were in the European Theater. After the war, Gilroy attended Dartmouth College, where he edited ''The Dartmouth'', the campus newspaper, and wrote for ''Jack-o-Lantern'', the college humor magazine. He graduated magna cum laude with a Bachelor of Arts in 1950. In 1966, he received an honorary Doct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monroe, New York
Monroe is a town in Orange County, New York, United States. The population was 21,387 at the 2020 census, compared to 39,912 at the 2010 census; the significant fall in census population was due to the secession of the town of Palm Tree in 2019. The town is named after President James Monroe. History The first settlers to this land were American Indians from the Leni-Lenape Indian nation. The Leni-Lenape nation consisted of three tribes: the Unulactus, the turkeys; Minsis, the wolf tribe; and the Unamis, the turtle tribe. As white settlers started to move north, the Leni-Lenape were forced to move west, out of New York and New Jersey into Pennsylvania and later into central North America, under the treaty of Easton, a colonial agreement signed in October, 1758. The British colonial government of the province of Pennsylvania and the Native American tribes in the Ohio country signed this document stating they would be allies in the French and Indian War. In the early 1700s the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Age Of Television
The first Golden Age of Television is an era of television in the Television in the United States, United States marked by its large number of live productions. The period is generally recognized as beginning in 1947 with the first episode of the drama anthology ''Kraft Television Theater''Anthony Slide, ed., ''The Television Industry: A Historical Dictionary'', Greenwood Press, 1991, p. 121. and ending in 1960 with the final episode of ''Playhouse 90'' (although a few Golden Age shows and stars continued into the 1960s). The Golden Age was followed by the network era, wherein television audiences and programming had channel drift, shifted to less critically acclaimed fare, almost all of it taped or filmed. Limitations of early television Prior to 1928, there had been some attempts at television programming using the mechanical television process. One of the first series made specifically for television to have a sustained run was CBS's 1931–1933 murder-mystery series ''The Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
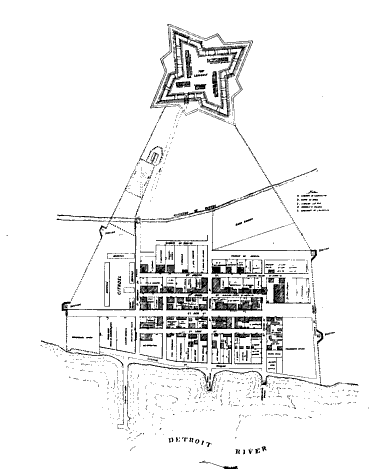
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at the 2020 census, making it the 27th-most populous city in the United States. The metropolitan area, known as Metro Detroit, is home to 4.3 million people, making it the second-largest in the Midwest after the Chicago metropolitan area, and the 14th-largest in the United States. Regarded as a major cultural center, Detroit is known for its contributions to music, art, architecture and design, in addition to its historical automotive background. ''Time'' named Detroit as one of the fifty World's Greatest Places of 2022 to explore. Detroit is a major port on the Detroit River, one of the four major straits that connect the Great Lakes system to the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The City of Detroit anchors the second-largest regional economy in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Kerr
Walter Francis Kerr (July 8, 1913 – October 9, 1996) was an American writer and Broadway theatre critic. He also was the writer, lyricist, and/or director of several Broadway plays and musicals as well as the author of several books, generally on the subject of theater and cinema. Biography Kerr was born in Evanston, Illinois, and earned both a B.A. and M.A. from Northwestern University., after graduation from St. George H.S. also in Evanston. He was a regular film critic for the St. George High School newspaper while a student there, and was also a critic for the Evanston News Index. He was the editor of the high school newspaper and yearbook. He taught speech and drama at The Catholic University of America. After writing criticism for ''Commonweal'' he became a theater critic for the ''New York Herald Tribune'' in 1951. When that paper folded, he then began writing theater reviews for ''The New York Times'' in 1966, writing for the next seventeen years. He married Jean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene O'Neill
Eugene Gladstone O'Neill (October 16, 1888 – November 27, 1953) was an American playwright and Nobel laureate in literature. His poetically titled plays were among the first to introduce into the U.S. the drama techniques of realism, earlier associated with Russian playwright Anton Chekhov, Norwegian playwright Henrik Ibsen, and Swedish playwright August Strindberg. The tragedy '' Long Day's Journey into Night'' is often included on lists of the finest U.S. plays in the 20th century, alongside Tennessee Williams's ''A Streetcar Named Desire'' and Arthur Miller's ''Death of a Salesman''. O'Neill's plays were among the first to include speeches in American English vernacular and involve characters on the fringes of society. They struggle to maintain their hopes and aspirations, but ultimately slide into disillusion and despair. Of his very few comedies, only one is well-known (''Ah, Wilderness!'').The Eugene O'Neill Foundation newsletter: "''Now I Ask You'', along with ''The M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obie Award
The Obie Awards or Off-Broadway Theater Awards are annual awards originally given by ''The Village Voice'' newspaper to theatre artists and groups in New York City. In September 2014, the awards were jointly presented and administered with the American Theatre Wing. As the Tony Awards cover Broadway productions, the Obie Awards cover off-Broadway and off-off-Broadway productions. Background The Obie Awards were initiated by Edwin (Ed) Fancher, publisher of ''The Village Voice,'' who handled the financing and business side of the project. They were first given in 1956 under the direction of theater critic Jerry Tallmer. Initially, only off-Broadway productions were eligible; in 1964, off-off-Broadway productions were made eligible. The first Obie Awards ceremony was held at Helen Gee's cafe.Aletti, Vince"Helen Gee 1919–2004" ''Village Voice'' (New York City), 12 October 2004, accessed on 21 November 2013 With the exception of the Lifetime Achievement and Best New American Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix Theatre (New York)
The Phoenix Theatre was a pioneering off-Broadway theatre in New York City, extant from 1953 to 1982. The Phoenix was founded by impresario Norris Houghton and T. Edward Hambleton. The project was a pioneering effort in the establishment of off-Broadway theatre. Houghton and Hambleton wanted a theatre away from Times Square, that would host a permanent company, abjure the star system (players would be listed alphabetically), produce four or five plays a season for limited engagements (contributors would be asked to sponsor an entire season rather than individual productions), and with ticket prices much lower than on Broadway. The Phoenix Theatre was established in a building at East 12th Street and Second Avenue in the East Village, far from Broadway. The building, opened in 1926, had formerly housed the Yiddish Art Theatre and is now the Village East Cinema. The Phoenix opened on December 1, 1953, with a production of ''Madam Will You Walk?'', Sidney Howard's last play, starri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Off-Broadway
An off-Broadway theatre is any professional theatre venue in New York City with a seating capacity between 100 and 499, inclusive. These theatres are smaller than Broadway theatres, but larger than off-off-Broadway theatres, which seat fewer than 100. An "off-Broadway production" is a production of a play, musical, or revue that appears in such a venue and adheres to related trade union and other contracts. Some shows that premiere off-Broadway are subsequently produced on Broadway. History The term originally referred to any venue, and its productions, on a street intersecting Broadway in Midtown Manhattan's Theater District, the hub of the American theatre industry. It later became defined by the League of Off-Broadway Theatres and Producers as a professional venue in Manhattan with a seating capacity of at least 100, but not more than 499, or a production that appears in such a venue and adheres to related trade union and other contracts. Previously, regardless of the size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lux Video Theatre
''Lux Video Theatre'' is an American television anthology series that was produced from 1950 until 1957. The series presented both comedy and drama in original teleplays, as well as abridged adaptations of films and plays. Overview The ''Lux Video Theatre'' was a spin-off from the successful ''Lux Radio Theater'' series broadcast on the NBC Blue Network (1934–1935) and CBS (1935–1955). ''Lux Video Theatre'' began as a live 30-minute Monday evening CBS series on October 2, 1950, switching to Thursday nights during August, 1951. In September 1953, the show relocated from New York to Hollywood. On August 26, 1954, it debuted on NBC as an hour-long show on Thursday nights, telecast until September 12, 1957. With the introduction of the one-hour format and the move to Hollywood, abridged versions of popular films were often used as the basis for shows. To introduce each act and interview the stars at the conclusion, NBC added a series of regular hosts: James Mason (1954–55), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraft Television Theatre
''Kraft Television Theatre'' is an American anthology drama television series running from 1947 to 1958. It began May 7, 1947 on NBC, airing at 7:30pm on Wednesday evenings until December of that year. It first promoted MacLaren's Imperial Cheese, which was advertised nowhere else. In January 1948, it moved to 9pm on Wednesdays, continuing in that timeslot until 1958. Initially produced by the J. Walter Thompson advertising agency, the live hour-long series offered television plays with new stories and new characters each week, in addition to adaptations of such classics as '' A Christmas Carol'' and '' Alice in Wonderland''. The program was broadcast live from Studio 8-H at 30 Rockefeller Plaza, currently the home of ''Saturday Night Live''. Beginning October 1953, ABC added a separate series (also titled ''Kraft Television Theatre''), created to promote Kraft's new Cheez Whiz product. This series ran for sixteen months, telecast on Thursday evenings at 9:30pm, until January 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnibus (U
Omnibus may refer to: Film and television * ''Omnibus'' (film) * Omnibus (broadcast), a compilation of Radio or TV episodes * ''Omnibus'' (UK TV series), an arts-based documentary programme * ''Omnibus'' (U.S. TV series), an educational program * ''Omnibus'' (talk show), an Italian series Literature * Omnibus edition, a collection of literary works * Omnibus Press, a book publisher * Omnibus, a Marvel Comics character associated with the Leader Music Albums * ''Omnibus'' (album), a 2006 album by Tarkio * ''Omnibus'', a 2008 album by Blue Mountain * ''Omnibus'', a 2001 album by Ruby Braff * ''Omnibus: The 60s Singles As and Bs'', a 1999 album by The Move Songs * "Omnibus", a song by the Move on the B-side of " Wild Tiger Woman" * "Omnibus", a song by XTC from '' Nonsuch'' Transport * Horse-drawn omnibus or horsebus, a large, enclosed and sprung horse-drawn vehicle used for passenger transport * Motor omnibus or autobus, a road vehicle designed to carry passengers O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
