|
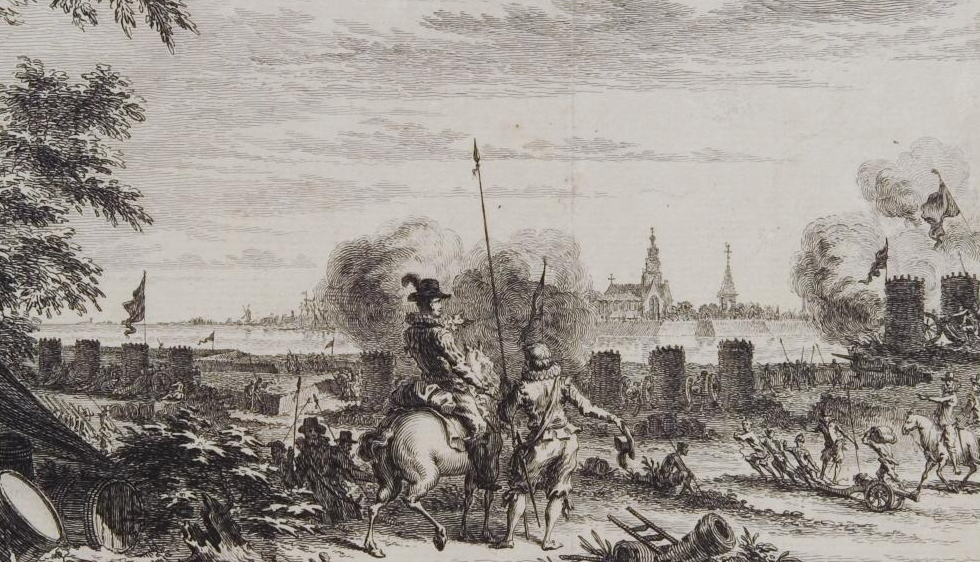
Fort Crèvecoeur (Netherlands)
Fort Crèvecoeur was a Dutch fortress near 's-Hertogenbosch. It is now used as a military exercise terrain. First Fort Crèvecoeur Eighty Years War Fort Crèvecoeur was founded during the Eighty Years' War. In 1587 the main campaign was centered around the Siege of Sluis in Zeeland. A smaller part of the States' army under Philip of Hohenlohe came in action near 's-Hertogenbosch. Hohenlohe first took the Loon op Zand Castle, and plundered some villages. He then made a ship bridge over the Meuse and started to besiege the Sconce of Engelen. The Spanish Netherlands therefore sent Claude de Berlaymont lord of Haultpenne to the area with 42 companies of foot and 25 squadrons of cavalry. He attacked Hohenlohe in order to lift the siege, but was defeated. Haultpenne himself was wounded, and on 14 July he died from his wounds in 's-Hertogenbosch. Hohenlohe then conquered the Sconce of Engelen, and razed it. On the place 'where the battle was fought' Hohenlohe somewhat later con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a total length of . History From 1301 the upper Meuse roughly marked the western border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of France, after Count Henry III of Bar had to receive the western part of the County of Bar (''Barrois mouvant'') as a French fief from the hands of King Philip IV. In 1408, a Burgundian army led by John the Fearless went to the aid of John III against the citizens of Liège, who were in open revolt. After the battle which saw the men from Liège defeated, John ordered the drowning in the Meuse of suspicious burghers and noblemen in Liège. The border remained stable until the annexation of the Three Bishoprics Metz, Toul and Verdun by King Henry II in 1552 and the occupation of the Duchy of Lorraine by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walloons
Walloons (; french: Wallons ; wa, Walons) are a Gallo-Romance ethnic group living native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of France. Walloons primarily speak '' langues d'oïl'' such as Belgian French, Picard and Walloon. Walloons are historically and primarily Roman Catholic. In modern Belgium, Walloons are, by law, termed a "distinctive linguistic and ethnic community" within the country, as are the neighbouring Flemish, a Germanic group. When understood as a regional identification, the ethnonym is also extended to refer to the inhabitants of the Walloon region in general, regardless of ethnicity or ancestry. Etymology The term ''Walloon'' is derived from ''*walha'', a Proto-Germanic term used to refer to Celtic and Latin speakers. ''Walloon'' originated in Romance languages alongside other related terms, but it supplanted them. Its oldest written trace is found in Jean de Haynin's ''Mémoires de Jean, sire de Haynin et de Louvignies'' in 1465, where it r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
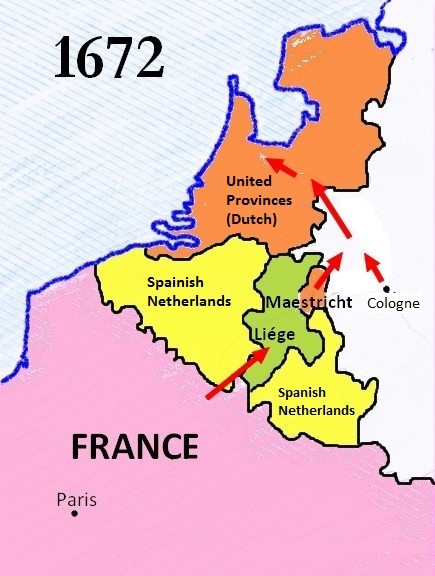
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, also known as the Dutch War (french: Guerre de Hollande; nl, Hollandse Oorlog), was fought between France and the Dutch Republic, supported by its allies the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, Brandenburg-Prussia and Denmark-Norway. In its early stages, France was allied with Münster and Cologne, as well as England. The 1672 to 1674 Third Anglo-Dutch War and 1675 to 1679 Scanian War are considered related conflicts. The war began in May 1672 when France nearly overran the Dutch Republic, an event still known as the ''Rampjaar'' or "Disaster Year". Their advance was halted by the Dutch Water Line in June and by late July the Dutch position had stabilised. Concern over French gains led to a formal alliance in August 1673 between the Dutch, Emperor Leopold I, Spain and Brandenburg-Prussia. They were joined by Lorraine and Denmark, while England made peace in February 1674. Now facing a war on multiple fronts, the French withdrew from the Dutch Republic, retaining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of 's-Hertogenbosch
The siege of 's-Hertogenbosch also known as the ''siege of Bois-Le-Duc''Markham pp. 435-38 was an action in 1629, during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War in which a Dutch and English army captured the city of 's-Hertogenbosch. The city had been loyal to the King of Spain since 1579 and was part of the Spanish Netherlands. Background The Twelve Years' Truce ended in 1621. Stadtholder Maurice of Orange had in the meantime played a part in instigating the Thirty Years' War in Germany. The Habsburgs tried to punish the rebellious Dutch Republic by cutting it off from its hinterland by a land blockade. 's-Hertogenbosch was the main fortress in this perimeter and enormous sums of money were poured into the improvement of its defences. As the ground surrounding the city was a marsh, the city was generally deemed to be impregnable, as the water-saturated soil seemed to make an application of current siege methods impossible; trench-digging and undermining were appare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Groenlo (1627)
The siege of Grol in 1627 was a battle between the Army of the Dutch Republic, commanded by Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange, and the Spanish-controlled fortified city of Grol (now known as Groenlo), during the Eighty Years War and the Anglo–Spanish War in 1627. The Spanish Army, led by Hendrik van den Bergh, came to relieve Grol but too late. The siege lasted from 20 July until 19 August 1627, resulting in the surrender of the city to the Dutch army.Jaques p. 411 During the siege, a 16 km circumvallation line was made around Grol to prevent the enemy from leaving and to prevent the liberation of the city from outside. Ambrosio Spinola had used a similar technique during the Siege of Breda (1624), and after the successful siege of Grol Frederic-Henry would later use it in other sieges in the Netherlands, such as at the Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch. The success at Grol provided the first serious victory on land for the Republic after the Twelve Years' Truce. About Grol Even tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Oldenzaal (1626)
The siege of Oldenzaal took place in the Spanish held town of Oldenzaal in the Twente region from July 23 to August 1, 1626 during the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War. After an eight-day siege led by Ernest Casimir the city surrendered.Poot p. 60Duffy p.101 Events Background Ambrogio Spinola had captured Oldenzaal in 1605 and Groenlo a year later – with this the region was under Spanish occupation and they undertook raids. In May 1626, the Dutch decided to eliminate the Spanish from the area once and for all. They brought two armies under the command of Frederick Henry, Prince of Orange and with them a detachment of the English army which had been raised as result of their war with Spain. Oldenzaal's garrison which had been continuously strengthened since it capture and twenty years later the city had around 800 troops along with cannon under the command of Spanish Governor Guillermo Verdugo. Siege On July 23 the Dutch and English besieged the town and had a go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Breda (1624)
The siege of Breda of 1624–25 occurred during the Eighty Years' War. The siege resulted in Breda, a Dutch fortified city, falling into the control of the Army of Flanders. Following the orders of Ambrogio Spinola, Philip IV's army laid siege to Breda in August 1624. The siege was contrary to the wishes of Philip IV's government because of the already excessive burdens of the concurrent Eighty and Thirty Years' wars. The strategically located city was heavily fortified and strongly defended by a large and well prepared garrison of 7,000 men, that the Dutch were confident would hold out long enough to wear down besiegers while awaiting a relief force to disrupt the siege. Yet despite the Spanish government's opposition to major sieges in the Low Countries and the obstacles confronting any attack on such a strongly fortified and defended city, Spinola launched his Breda campaign, rapidly blocking the city's defences and driving off a Dutch relief army under the leadership ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
's Hertogenbosch 1649 Blaeu'''
{{DEFAULTSORT:s ...
's may refer to: * 's, an ending used to form the possessive of English nouns and noun phrases * 's, a contraction of the English words ''is'' and ''has'' * 's, a form of the English plural ending, written after single letters and in some other instances (see also Greengrocers' apostrophes) * 's, a contraction of the old Dutch genitive article ''des'', appearing in names such as 's-Hertogenbosch See also * All pages beginning with 's * All pages beginning with 'S * Apostrophe * -s (other) * S (other) S is the nineteenth letter of the English alphabet. S may also refer to: History * an Anglo-Saxon charter's number in Peter Sawyer's, catalogue Language and linguistics * Long s (ſ), a form of the lower-case letter s formerly used where "s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries held in personal union by the Spanish Crown (also called Habsburg Spain). This region comprised most of the modern states of Belgium and Luxembourg, as well as parts of northern France, the southern Netherlands, and western Germany with the capital being Brussels. The Army of Flanders was given the task of defending the territory. The Imperial fiefs of the former Burgundian Netherlands had been inherited by the Austrian House of Habsburg from the extinct House of Valois-Burgundy upon the death of Mary of Burgundy in 1482. The Seventeen Provinces formed the core of the Habsburg N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Years' Truce
The Twelve Years' Truce was a ceasefire during the Eighty Years' War between Spain and the Dutch Republic, agreed in Antwerp on 9 April 1609 and ended on 9 April 1621. While European powers like France began treating the Republic as a sovereign nation, the Spanish viewed it as a temporary measure forced on them by financial exhaustion and domestic issues and did not formally recognise Dutch independence until the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648.Goodman p. 15Anderson p. 4 The Truce allowed Philip III of Spain to focus his resources elsewhere, while Archdukes Archduke Albert and Isabella used it to consolidate Habsburg rule and implement the Counter-Reformation in the Southern Netherlands. Context The war in the Low Countries reached a stalemate in the 1590s. After the fall of Antwerp in 1585, Spain's Philip II ordered Alexander Farnese to direct his military actions first towards the failed campaign of the Spanish Armada, then against France to prevent the succession of Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Grave (1602)
The siege of Grave was a siege that took place between 18 July to 20 September 1602, as part of the Eighty Years' War and the Anglo–Spanish War. The Spanish-held city of Grave was besieged by a Dutch and English army led by Maurice of Orange and Francis Vere respectively.Markham pp. 338–339 After a siege of nearly two months the city surrendered when a Spanish relief army under Francisco de Mendoza was defeated just outside the city by the besiegers.Wernham pp. 411–412Dalton pp. 93–97 The defeat was severe enough to cause a major mutiny in the Spanish army.Duerloo p. 130 Background Prince Maurice of Orange had been actively campaigning against the Spanish armies in the Southern Netherlands and had successfully made sure that Ostend then under siege by Albert of Austria would be a key distraction while he took the rest of the Spanish garrisons that were still in the Republic.Borman pp. 230–232 Maurice in his first objective successfully besieged and took Rheinberg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Provinces Of The Netherlands
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a federal republic that existed from 1579, during the Dutch Revolt, to 1795 (the Batavian Revolution). It was a predecessor state of the Netherlands and the first fully independent Dutch nation state. The republic was established after seven Dutch provinces in the Spanish Netherlands revolted against rule by Spain. The provinces formed a mutual alliance against Spain in 1579 (the Union of Utrecht) and declared their independence in 1581 (the Act of Abjuration). It comprised Groningen, Frisia, Overijssel, Guelders, Utrecht, Holland and Zeeland. Although the state was small and contained only around 1.5 million inhabitants, it controlled a worldwide network of seafaring trade routes. Through its trading com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)



