|
Five Hegemons (Spring And Autumn Period)
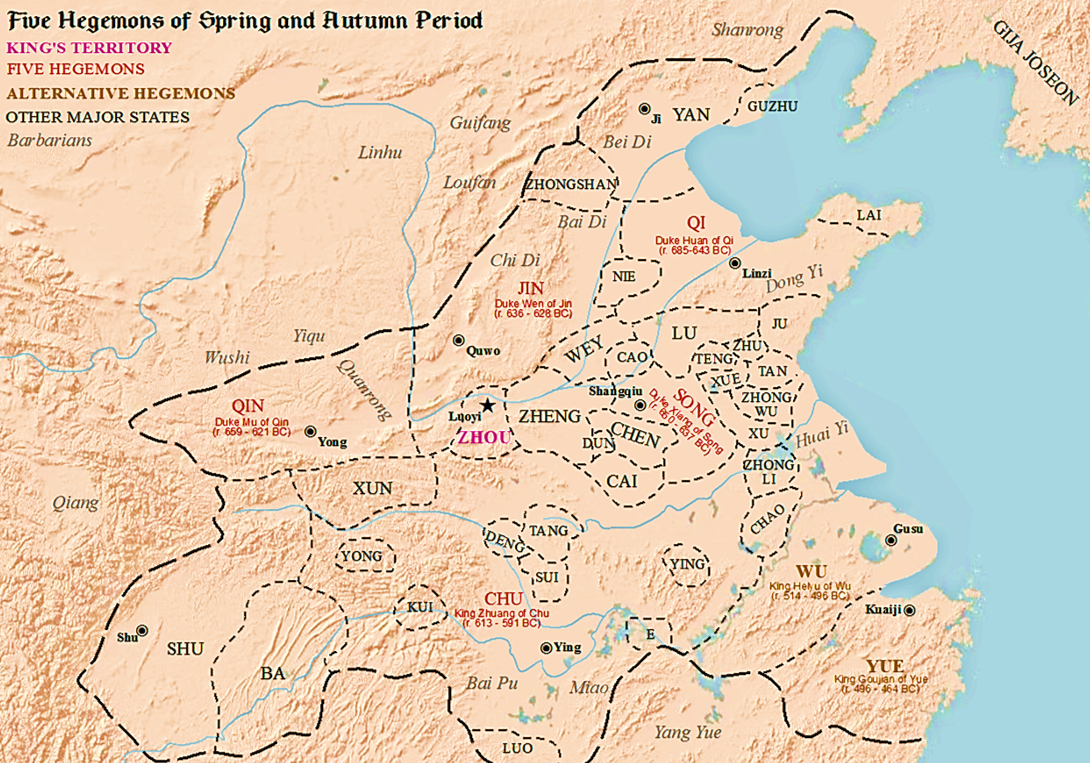
The Five Hegemons () refers to several especially powerful rulers of Chinese states of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history (770 to 476 BCE), sometimes alternatively referred to as the "Age of Hegemons". There are various lists of five rulers of those certain states which rose to power over the other states of this time period, states which were also formed during the period of dissolution of a once real and strong central state, namely the empire of the Zhou dynasty. The Hegemons mobilized the remnants of the Zhou empire, according to shared mutual political and martial interests. An especially prominent Hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi. Pronunciation and meaning In ancient Chinese, (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ) '' has a similar meaning and pronunciation to (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ), which means 'the eldest son in a family', or 'senator'. Both and can be translated as the 'Five Hegemons'. () literally means 'five', but in the context of ancient Chinese also has a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Hegemons
The Five Hegemons () refers to several especially powerful rulers of Chinese states of the Spring and Autumn period of Chinese history (770 to 476 BCE), sometimes alternatively referred to as the "Age of Hegemons". There are various lists of five rulers of those certain states which rose to power over the other states of this time period, states which were also formed during the period of dissolution of a once real and strong central state, namely the empire of the Zhou dynasty. The Hegemons mobilized the remnants of the Zhou empire, according to shared mutual political and martial interests. An especially prominent Hegemon was Duke Huan of Qi. Pronunciation and meaning In ancient Chinese, (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ) '' has a similar meaning and pronunciation to (Old Chinese: ; Pinyin: ), which means 'the eldest son in a family', or 'senator'. Both and can be translated as the 'Five Hegemons'. () literally means 'five', but in the context of ancient Chinese also has a more ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Zhou Dynasty
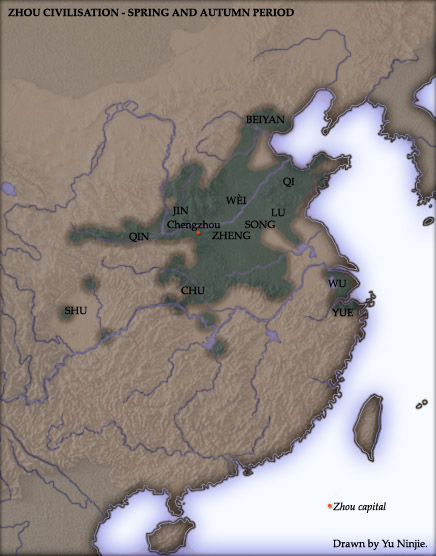
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bai Hu Tong
''Bai Hu Tong'' (, also , ) is a Confucian text based on the held in 79 CE. History The traditional view of this text is that it was compiled by Ban Gu (32–92 CE) on the orders of the Emperor Zhang of Han (57-88 CE). The name is derived from the White Tiger Hall () in the of Luoyang (the capital) where a series of discussions took place in 79 CE, on the subject of the true meanings of the classics. The discussions covered a broad range of topics including rites Rail India Technical and Economic Service Limited, abbreviated as RITES Ltd, is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways, Government of India. It is an engineering consultancy corporation, specializing in the field ..., politics, cosmology, and philosophy. Ban Gu is said to have edited the records of these discussions, and from them to have produced the book we have today. Some scholars have suggested that the book may in fact be made up of material produced as late as the 3rd centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ci Tong (book)
CI or Ci may refer to: Business terminology * Customer intelligence, a discipline in marketing * Competitive intelligence * Corporate identity * Continual improvement * Confidential information Businesses and organisations Academia and education * California State University, Channel Islands * Channel Islands High School * Collegium Invisibile * Confucius Institute Religion * Josephites of Belgium, a Catholic congregation * Christian Identity * Christian Institute, a British charity which promotes Christian values Other businesses and organizations * Charity Intelligence Canada * China Airlines (IATA code) * Cigna health services (NYSE symbol) * Consumers International * Cycling Ireland * CI Records, a music record label * Cambria and Indiana Railroad * CANZUK International, organisation which promotes cooperation between Canada, Australia, New Zealand and the United Kingdom * Conservation International, an international environmental non-governmental organization * Communicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weihui
Weihui (), formerly Jixian or Ji County (), is a county-level city in the north of Henan province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Xinxiang. The city has an area of and a population of Administrative divisions As 2012, this city is divided to 7 towns and 6 townships. ;Towns ;Townships Climate References External links Cities in Henan County-level divisions of Henan Xinxiang {{Henan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiji
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Xiang Of Zhou
King Xiang of Zhou (died 619BC), personal name Ji Zheng (), was the eighteenth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the sixth of the Eastern Zhou. He was a successor of his father King Hui of Zhou. He married Lady of the Dí, but later dismissed her. In 635 he was driven from the capital by his brother Dai and was restored by Duke Wen of Jin. After his death, his son King Qing of Zhou succeeded him.''Trình Doãn Thắng, Ngô Trâu Cương, Thái Thành (1998), Cố sự Quỳnh Lâm, NXB Thanh Hoá'' Family Spouse: * Zhai Hou, of the Kui clan of Di (), deposed Sons: * Prince Renchen (; d. 613 BC), ruled as King Qing of Zhou from 618–613 BC * Youngest son, the father of Prince Man (), who rebuffed King Zhuang of Chu regarding the weight of the Nine Tripod Cauldrons The Nine Tripod Cauldrons () were a collection of ding cast by the legendary Yu the Great of the Xia dynasty of ancient China. They were viewed as symbols of the authority given to the ruler by the mandate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Xi Of Zhou
King Xi of Zhou (died 677 BC) (), personal name Jī Húqí, was the sixteenth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the fourth of the Eastern Zhou. He was a successor of his father King Zhuang of Zhou, and was succeeded by his son, King Hui of Zhou. By his time China had dissolved into a multitude of states, only nominally subject to the king, who was no longer even the most powerful figure in China (that was Duke Huán of the State of Qí). (Warring States Period) Family Sons: * Prince Lang (; d. 652 BC), ruled as from 676–652 BC * Prince Hu (; d. 624 BC), ruled as Duke Wen of Wangshu () until 624 BCAncestry See also |
Xunzi (book)
The ''Xunzi'' () is an ancient Chinese collection of philosophical writings attributed to and named after Xun Kuang, a 3rd-century BCE philosopher usually associated with the Confucian tradition. The ''Xunzi'' is perhaps most famous for the emphasis it places on education and propriety, as well as its striking assertion that "human nature is detestable". The text is furthermore an important source of early theories of ritual, cosmology, and governance. The ideas within the ''Xunzi'' are thought to have exerted a strong influence on Legalist thinkers, such as Han Fei, and laid the groundwork for much of Han Dynasty political ideology. The text criticizes a wide range of other prominent early Chinese thinkers, including Laozi, Zhuangzi, Mozi, and Mencius. Some ''Xunzi'' chapters are especially significant. The "Discussion of Heaven ( ''Tiān lùn'')" rejects the notion that heaven has a moral will. Instead, Xunzi asserts that heaven operates according to constant principles; thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Grand Historian
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese historian Sima Qian, whose father Sima Tan had begun it several decades earlier. The work covers a 2,500-year period from the age of the legendary Yellow Emperor to the reign of Emperor Wu of Han in the author's own time, and describes the world as it was known to the Chinese of the Western Han dynasty. The ''Records'' has been called a "foundational text in Chinese civilization". After Confucius and the First Emperor of Qin, "Sima Qian was one of the creators of Imperial China, not least because by providing definitive biographies, he virtually created the two earlier figures." The ''Records'' set the model for all subsequent dynastic histories of China. In contrast to Western historical works, the ''Records'' do not treat history as "a cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interstate Relations During The Spring And Autumn Period
Certain patterns emerged to govern the conduct of relations among the states of the Spring and Autumn period of ancient China. These patterns constituted a rudimentary system of interstate or international law based on the model of feudalism established under the Western Zhou dynasty. The norms of interstate relations during the Spring and Autumn period was one of the earliest systems of interstate relations and international law in the world. It was of importance in the early cultural and political development of China, allowing greater ease in maintaining relations, and facilitating the flow of trade and information. There was a growing body of customary international law which developed as contacts and commerce increased, a number of treaties were signed, and the appeal was frequently made to rules set up within the leagues of states. A great many of the canons of interstate law concerned diplomacy among the states. Interstate relations originated in the feudal system of the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
