|
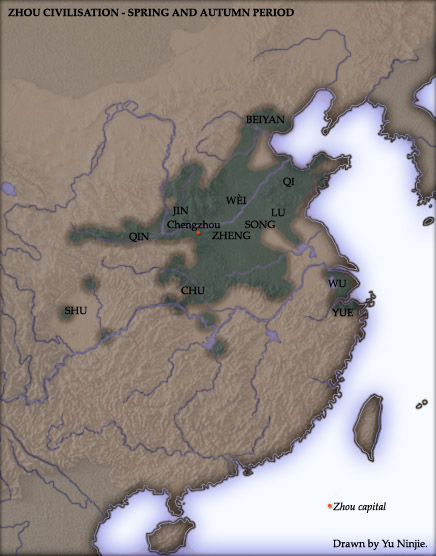
Eastern Zhou Dynasty
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China 2b
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land, the List of countries and territories by land borders, most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces of China, provinces, five autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, four direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and two special administrative regions of China, Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the List of cities in China by population, most populous cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World History Encyclopedia
World History Encyclopedia (formerly Ancient History Encyclopedia) is a nonprofit educational company created in 2009 by Jan van der Crabben. The organization publishes and maintains articles, images, videos, podcasts, and interactive educational tools related to history. All users may contribute content to the site, although submissions are reviewed by an editorial team before publication. In 2021, the organization was renamed from the Ancient History Encyclopedia to World History Encyclopedia to reflect its broadened scope, covering world history from all time periods, as opposed to just ancient history. Original articles are written in English and later translated into other languages, mainly French and Spanish. Organization history The Ancient History Encyclopedia was founded in 2009 by van der Crabben with the stated goal of improving history education worldwide by creating a freely accessible and reliable history source. The nonprofit organization is based in Godalming, Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Qing Of Zhou
King Qing of Zhou (), personal name Jī Rénchén, was the nineteenth king of the Chinese Zhou Dynasty and the seventh of the Eastern Zhou. The son of King Xiang of Zhou, he became king in 618 BC after his father died. King Qing had three sons, Princes Ban, Yu and Jizi. After King Qing died in 613 BC, Bān become King Kuang.''Trình Doãn Thắng, Ngô Trâu Cương, Thái Thành (1998), Cố sự Quỳnh Lâm, NXB Thanh Hoá'' Family Sons: * Prince Ban (; d. 607 BC), ruled as King Kuang of Zhou from 612 to 607 BC * Prince Yu (; d. 586 BC), ruled as King Ding of Zhou from 606 to 586 BC * Prince Jizi (; d. 544 BC), ruled the State of Liu (劉國) as Duke Kang of Liu (劉康公) from 592 to 544 BC Ancestry See also Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs covering the period of the Five Emperors up through the end of the Spring and Autumn period. Five Emperors The legendary Five Emperors were traditionally regarded as the founder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Xiang Of Zhou
King Xiang of Zhou (died 619BC), personal name Ji Zheng (), was the eighteenth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the sixth of the Eastern Zhou. He was a successor of his father King Hui of Zhou. He married Lady of the Dí, but later dismissed her. In 635 he was driven from the capital by his brother Dai and was restored by Duke Wen of Jin. After his death, his son King Qing of Zhou succeeded him.''Trình Doãn Thắng, Ngô Trâu Cương, Thái Thành (1998), Cố sự Quỳnh Lâm, NXB Thanh Hoá'' Family Spouse: * Zhai Hou, of the Kui clan of Di (), deposed Sons: * Prince Renchen (; d. 613 BC), ruled as King Qing of Zhou from 618–613 BC * Youngest son, the father of Prince Man (), who rebuffed King Zhuang of Chu regarding the weight of the Nine Tripod Cauldrons The Nine Tripod Cauldrons () were a collection of ding cast by the legendary Yu the Great of the Xia dynasty of ancient China. They were viewed as symbols of the authority given to the ruler by the mandate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Hui Of Zhou
King Hui of Zhou (), personal name Ji Lang, was the seventeenth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the fifth of Eastern Zhou.''Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Qian Family Queens: * Queen Chen () * Queen Hui of Zhou, of the Gui clan of Chen (), known as Chen Gui (); possibly a daughter of Duke Xuan of Chen; married in 676 BC; the mother of Crown Prince Zheng and Prince Dai Sons: * Crown Prince Zheng (; d. 619 BC), ruled as King Xiang of Zhou from 651–619 BC * Prince Dai (; 672–635 BC), ruled as Duke Zhao of Gan () until 635 BC Daughters: * Wang Ji () ** Married Duke Xiang of Song (d. 637 BC) Ancestry See also Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors This is a family tree of Chinese monarchs covering the period of the Five Emperors up through the end of the Spring and Autumn period. Five Emperors The legendary Five Emperors were traditionally regarded as the founders of the Chinese state. ... References 652 BC deaths Zhou dynasty kings 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Xi Of Zhou
King Xi of Zhou (died 677 BC) (), personal name Jī Húqí, was the sixteenth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the fourth of the Eastern Zhou. He was a successor of his father King Zhuang of Zhou, and was succeeded by his son, King Hui of Zhou. By his time China had dissolved into a multitude of states, only nominally subject to the king, who was no longer even the most powerful figure in China (that was Duke Huán of the State of Qí). (Warring States Period) Family Sons: * Prince Lang (; d. 652 BC), ruled as from 676–652 BC * Prince Hu (; d. 624 BC), ruled as Duke Wen of Wangshu () until 624 BCAncestry See also |
King Zhuang Of Zhou
King Zhuang of Zhou (died 682 BC) (), personal name Ji Tuo, was the fifteenth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the third of the Eastern Zhou. He ruled 696–682 BC as a successor of his father, King Huan of Zhou. He was later succeeded by his son, King Xi of Zhou, in 682 BC. Rulers of the Zhou states – with links to their occurrences in pre-Qin and Han texts. His younger son was Prince Tui. Family Concubines: * Yao Ji, of the Yao clan (), the mother of Prince Tui Sons: * First son, Prince Huqi (; d. 677 BC), ruled as from 681–677 BC * Prince Tui (; 696–673 BC), claimed the throne of Zhou from 675–673 BCAncestry See ...
|
King Huan Of Zhou
King Huan of Zhou (; died 697 BC), personal name Jī Lín (姬林), was the fourteenth king of the Chinese Zhou dynasty and the second of the Eastern Zhou Dynasty (770–256 BC). King Huan’s father was King Ping's son, Crown Prince Xiefu. Huan succeeded his grandfather in 719 BC. The son and successor of Huan was King Zhuang of Zhou. In 707 BC, the royal forces were defeated in the Battle of Xuge (𦈡葛之战) by Duke Zhuang of Zheng (r. 743–701). The king himself was wounded by an arrow in the shoulder, and the defeat destroyed the prestige of the Zhou house. Family Queens: * Ji Ji Jiang, of the Jiang clan of Ji (), a princess of Ji by birth; married in 703 BC Sons: * Prince Tuo (; d. 682 BC), ruled as King Zhuang of Zhou from 696–682 BC * Prince Ke (), fled to Southern Yan () in 694 BC Daughters: * Zhou Wang Ji () ** Married Duke Xiang of Qi (729–686 BC) in 695 BC Ancestry See also Family tree of ancient Chinese emperors This is a family tree of Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Xie Of Zhou
King Xie of Zhou (died 750 BCE) claimed sovereignty during the final stages of the Chinese Western Zhou Dynasty (1046–771 BCE). After King You of Zhou replaced the then Queen Shen with his concubine Bao Si, whilst at the same time substituting Yijiu as crown prince with Bao Si's son Bofu, Queen Shen's father, the Marquess of Shen became irate. Along with the State of Zeng and a band of Quanrong nomads he attacked the Zhou capital at Haojing. You was killed in the assault whereupon the Marquesses of Shēn and Zēng, together with Duke Wen of Xu () enthroned Yijiu as King Ping of Zhou in the State of Shēn. At the same time, Jī Hàn (), Duke of Guó (), conspired with the Quanrong to elevate Yúchén to the throne as ''King Xie of Zhou''. Thus began a period when there existed two parallel Zhou kings, a stalemate brought to an end in 750 BCE when Marquis Wen of Jin killed King Xie of Zhou. Documented sources According to the '' Zuo Zhuan'': :''As far as King You was concerned, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold Sword Hilt Eastern Zhou BM
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Huang
Ray Huang (; 25 June 19188 January 2000) was a Chinese-American historian and philosopher who was an officer in the National Revolutionary Army and fought in the Burma Campaign. In 1964, Huang earned a Ph.D. in history from the University of Michigan. He worked with Joseph Needham and was a contributor to Needham's ''Science and Civilisation in China''. Huang taught history at universities in the US and the UK, and he is best known in his later years for the idea of macro-history. Early life Ray Huang was born in Ningxiang, Hunan Province, in 1918. He was the oldest of three children. His father, Huang Zhenbai (), was an early member of the revolutionary group Tongmenghui but became less active in the group over the years. Ray Huang grew up in Hunan and went on to study electrical engineering at Nankai University, Tianjin, in 1936. At the outbreak of the Second Sino-Japanese War in 1938, he returned to Changsha and wrote for the ''Anti-Japanese War Report'' (). Soon after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |