|
Fei Yi
Fei Yi (died 16 February 253), courtesy name Wenwei, was a regent and military general of the state of Shu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Born in the late Eastern Han dynasty, Fei Yi started his career as an attendant to Liu Shan, the eldest son and heir apparent of Liu Bei, a warlord who became the founding emperor of Shu. After Liu Shan became emperor in 223, Fei Yi gradually rose to prominence under the regency of Zhuge Liang, the Imperial Chancellor of Shu. During this time, he concurrently served as a military adviser under Zhuge Liang and as Shu's ambassador to its ally state Wu. He also played a significant role in the conflict between the Shu general Wei Yan and Zhuge Liang's chief clerk Yang Yi. After Zhuge Liang's death in 234, Fei Yi served as a deputy to the new regent Jiang Wan and progressively assumed greater responsibilities as Jiang Wan gradually relinquished his powers due to poor health. In 244, Fei Yi led Shu forces to victory at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu, is a Sub-provincial division, sub-provincial city which serves as the Capital city, capital of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a population of 20,937,757 inhabitants during the 2020 Chinese census, it is the fourth most populous city in China, and it is the only city apart from the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, direct-administered municipalities with a population of over 20 million (the other three are Chongqing, Shanghai and Beijing). It is traditionally the hub in Southwest China. Chengdu is located in central Sichuan. The surrounding Chengdu Plain is known as the "Country of Heaven" () and the "Land of Abundance". Its prehistoric settlers included the Sanxingdui culture. The site of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu (; pinyin: ''shŭ'' < : *''źjowk'' < : *''dźok''), was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). The state was based in the area around present-day , , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
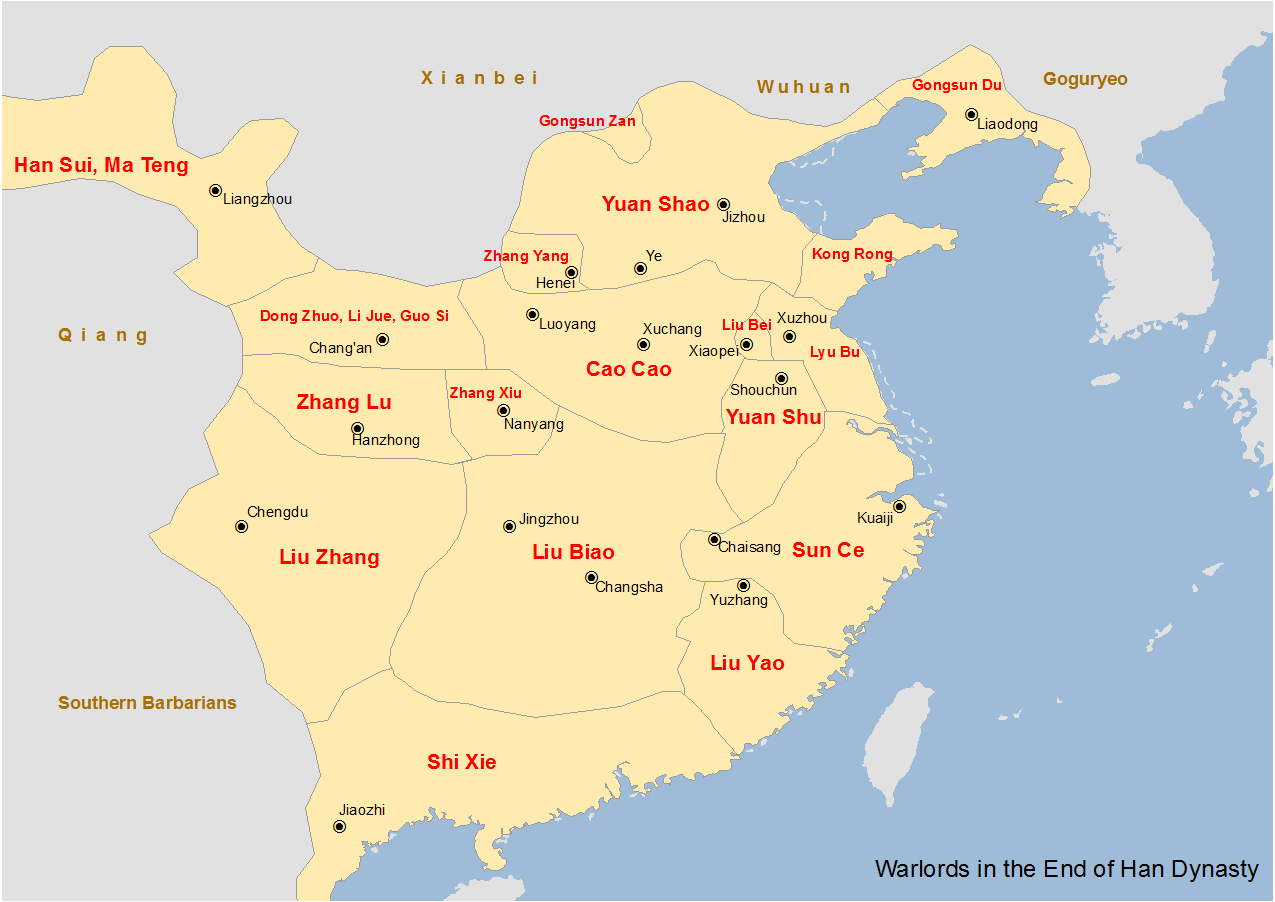
Liu Zhang (warlord)
Liu Zhang () ( 190s–210s), courtesy name Jiyu, was a Chinese politician and warlord who served as provincial governor who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He became the Governor of Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing), succeeding his father Liu Yan and ruled the region until 214, when he surrendered to Liu Bei. Six years later, Liu Zhang again surrendered to Eastern Wu, and died shortly afterwards. Liu Zhang is often considered an incapable leader but is noted to have been the original lord of some of Shu Han's most famous generals and officials such as Fa Zheng, Meng Da, Yan Yan, Liu Ba, Huang Quan, Wu Yi, Li Yan, Dong He and others. Early life Liu Zhang was a descendant of Liu Yu, who was Prince of Lu in the early Han dynasty. The youngest son of Liu Yan, Liu Zhang spent his early career at the Han imperial court as an assistant to his two eldest brothers, Liu Fan and Liu Dan. They served at the court when it was controlled by the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangxia Commandery
Jiangxia Commandery ( zh, 江夏郡) was a Chinese commandery that existed from Han dynasty to Tang dynasty. Its territories were located in present-day eastern Hubei province. History Jiangxia Commandery was established during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han. In the Western Han dynasty, the commandery consisted of 14 counties: Xiling (西陵), Jingling (竟陵), Xiyang (西陽), Xiang (襄), Zhu (邾), Dai (軑), E (鄂), Anlu (安陸), Shaxian (沙羨), Qichun (蘄春), Meng (鄳), Yundu (雲杜), Xiazhi (下雉) and Zhongwu (鍾武). The total population in 2 AD was 219,218 individuals, in 56,844 households. During the Eastern Han period, Xiang and Zhongwu counties were abolished, while Pingchun (平春) and Nanxinshi (南新市) were added. By 140 AD, the population had grown to 265,464, in 58,434 households. As the Han dynasty fell, Jiangxia was divided between Cao Wei and Eastern Wu. The seat was moved first to Shiyang (石陽, formerly part of Xiling County), and then to Anl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese New Year
Chinese New Year is the festival that celebrates the beginning of a New Year, new year on the traditional lunisolar calendar, lunisolar and solar Chinese calendar. In Sinophone, Chinese and other East Asian cultures, the festival is commonly referred to as the Spring Festival () as the Spring (season), spring season in the lunisolar calendar traditionally starts with lichun, the first of the twenty-four solar terms which the festival celebrates around the time of the Chinese New Year. Marking the end of winter and the beginning of the spring season, observances traditionally take place from Chinese New Year's Eve, New Year’s Eve, the evening preceding the first day of the year to the Lantern Festival, held on the 15th day of the year. The first day of Chinese New Year begins on the new moon that appears between 21 January and 20 February. Chinese New Year is one of the most important holidays in Chinese culture, and has strongly influenced Lunar New Year celebrations of its 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
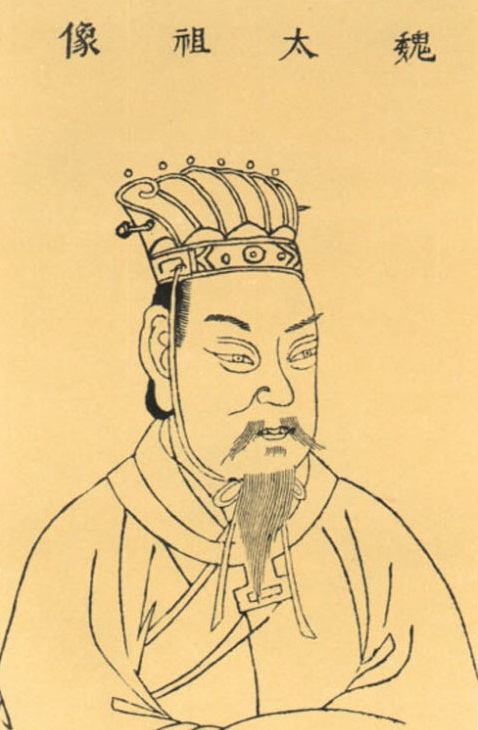
Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < : *''ŋuiC'') (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). With its capital initially located at , and thereafter |
Battle Of Xingshi
The Battle of Xingshi was fought between the states of Cao Wei and Shu Han in 244 during the Three Kingdoms period in China. The location was at Mount Xingshi (), which is situated north of present-day Yang County, Shaanxi, and is now part of the Changqing National Nature Reserve. The battle was an attempt by Cao Shuang, the regent of Wei, to conquer Wei's rival state, Shu. It ended in complete failure. Background Despite facing strong opposition in the Wei court, Cao Shuang believed that the campaign was viable, especially when the Shu commander, Jiang Wan, withdrew his main force from Hanzhong to Fu County () in October 243. Cao Shuang and his protégés concluded that with numerical superiority, their army could easily conquer Hanzhong before Shu reinforcements arrive. Even if they failed to eliminate Shu, the fall of Hanzhong would be sufficient to increase Cao Shuang's fame and influence in the Wei court. Geography The three traditional passages from Hanzhong to Guanzhon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yang Yi (Shu Han)
Yang Yi (died March or April 235), courtesy name Weigong, was an official of the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period of China. Early life and career Yang Yi was from Xiangyang Commandery in Jing Province, which is around present-day Xiangyang, Hubei. He was born sometime in the late Eastern Han dynasty and initially served as a Registrar () under Fu Qun (), the Inspector () of Jing Province. However, later, he defected to Guan Yu, a general under the warlord Liu Bei. Guan Yu appointed Yang Yi as an Officer of Merit () and sent him to Chengdu – the capital of Yi Province, which covered present-day Sichuan and Chongqing – to meet Liu Bei. Liu Bei had a discussion with Yang Yi on military strategy and politics and was so pleased with his replies that he appointed Yang Yi as a Senior Clerk () in his administrative office. He promoted Yang Yi to a Master of Writing () in 219 after declaring himself "King of Hanzhong" () following his victory in the Hanzhong Campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wei Yan
Wei Yan () (died October 234), courtesy name Wenchang, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Originally a subordinate of the warlord Liu Bei in the late Eastern Han dynasty, Wei Yan rose through the ranks and became a general when Liu Bei seized control of Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing) in 214. His performance in battle helped him to become a prominent figure in the Shu military in a short period of time. He was later appointed as the Administrator of Hanzhong Commandery and as an Area Commander in 219. Between 228 and 234, he participated actively in the Northern Expeditions led by the Shu regent Zhuge Liang against Shu's rival state, Cao Wei. After Zhuge Liang's death in September 234, Wei Yan was killed by another Shu general, Ma Dai, for alleged treason. Early life Wei Yan was from Yiyang Commandery (), which covered parts of present-day Nanyang in southern Henan and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Wu
Wu ( Chinese: 吳; pinyin: ''Wú''; Middle Chinese *''ŋuo'' < : ''*ŋuɑ''), known in historiography as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over in the period (220–280). It previously existed from 220–222 as a kingdom nominally under , its rival state, but declared independence from Wei and became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor (China)
The grand chancellor (''zaixiang, tsai-hsiang''), also translated as counselor-in-chief, chancellor, chief councillor, chief minister, imperial chancellor, lieutenant chancellor and prime minister, was the highest-ranking executive official in the imperial Chinese government. The term was known by many different names throughout Chinese history, and the exact extent of the powers associated with the position fluctuated greatly, even during a particular dynasty. During the Six Dynasties period, the term denoted a number of power-holders serving as chief administrators, including ''zhongshun jian'' (Inspector General of the Secretariat), ''zhongshu ling'' (President of the Secretariat), ''shizhong'' (Palace Attendant), ''shangshu ling'' and ''puye'' (president and vice-president of the Department of State Affairs). History In the Spring and Autumn period, Guan Zhong was the first chancellor in China, who became chancellor under the state of Qi in 685 BC. In Qin, during the Warring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
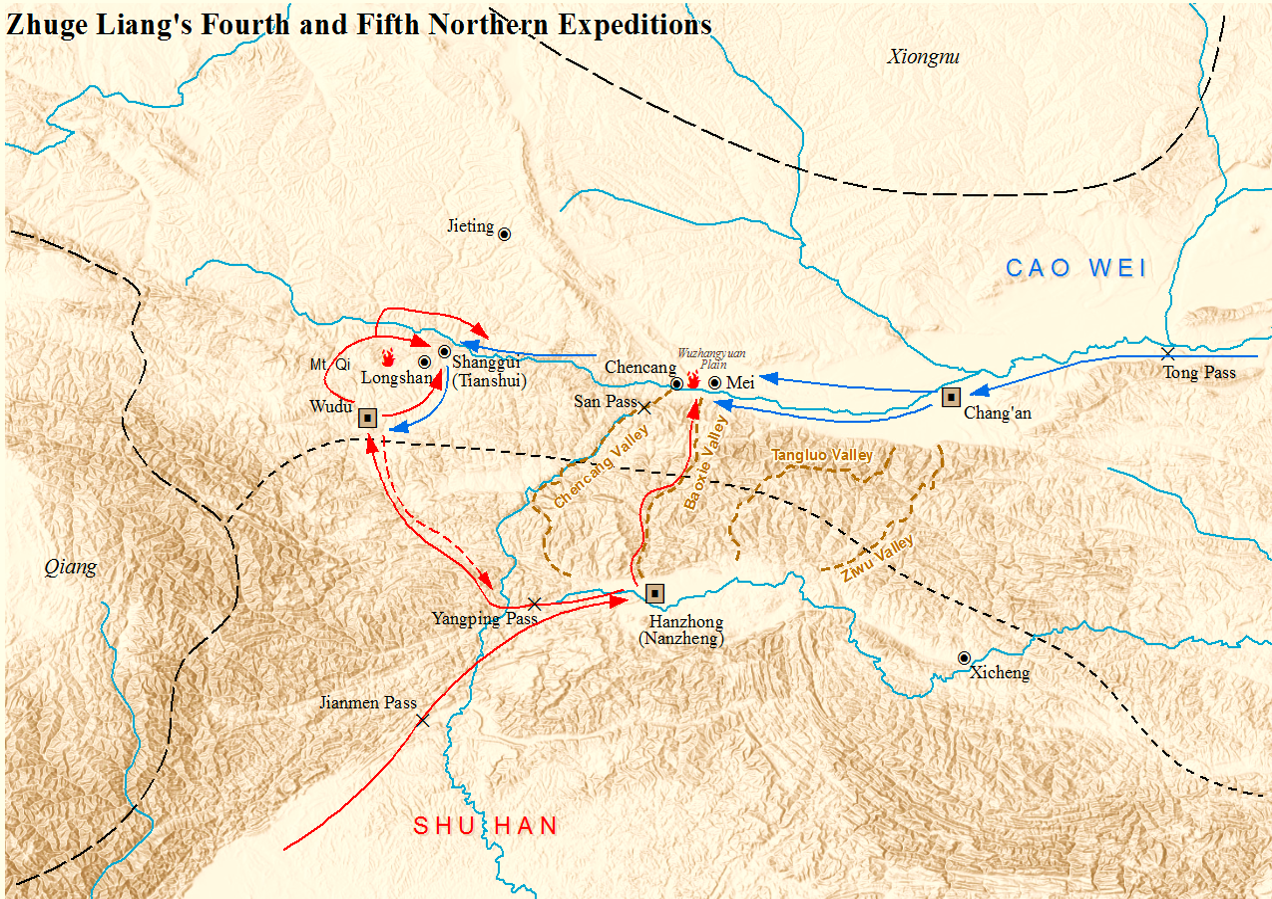
Zhuge Liang
Zhuge Liang ( zh, t=諸葛亮 / 诸葛亮) (181 – September 234), courtesy name Kongming, was a Chinese statesman and military strategist. He was chancellor and later regent of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. He is recognised as the most accomplished strategist of his era, and has been compared to Sun Tzu, the author of ''The Art of War''. His reputation as an intelligent and learned scholar grew even while he was living in relative seclusion, earning him the nickname "Wolong" or "Fulong", meaning "Crouching Dragon" or "Sleeping Dragon". Zhuge Liang is often depicted wearing a Taoist robe and holding a hand fan made of crane feathers. Zhuge Liang was a Confucian-oriented "Legalist". He liked to compare himself to the sage minister Guan Zhong and Yue Yi developing Shu's agriculture and industry to become a regional power, and attached great importance to the works of Shen Buhai and Han Fei, refusing to indulge local elites and adopting strict, but fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


.jpg)