|
Fast Reactor
A fast-neutron reactor (FNR) or fast-spectrum reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons (carrying energies above 1 MeV or greater, on average), as opposed to slow thermal neutrons used in thermal-neutron reactors. Such a fast reactor needs no neutron moderator, but requires fuel that is relatively rich in fissile material when compared to that required for a thermal-neutron reactor. Around 20 land based fast reactors have been built, accumulating over 400 reactor years of operation globally. The largest of this was the Superphénix Sodium cooled fast reactor in France that was designed to deliver 1,242 MWe. Fast reactors have been intensely studied since the 1950s, as they provide certain decisive advantages over the existing fleet of water cooled and water moderated reactors. These are: * More neutrons are produced when a fission occurs, resulting from the absorption of a fast neutron, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead-cooled Fast Reactor
The lead-cooled fast reactor is a nuclear reactor design that features a fast neutron spectrum and molten lead or lead-bismuth eutectic coolant. Molten lead or lead-bismuth eutectic can be used as the primary coolant because especially lead, and to a lesser degree bismuth have low neutron absorption and relatively low melting points. Neutrons are slowed less by interaction with these heavy nuclei (thus not being neutron moderators) and therefore, help make this type of reactor a fast-neutron reactor. In simple terms, if a neutron hits a particle with a similar mass (such as hydrogen in a Pressurized Water Reactor PWR), it tends to lose kinetic energy. In contrast, if it hits a much heavier atom such as lead, the neutron will "bounce off" without losing this energy. The coolant does, however, serve as a neutron reflector, returning some escaping neutrons to the core. Fuel designs being explored for this reactor scheme include fertile uranium as a metal, metal oxide or metal nitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shevchenko BN350
Shevchenko (alternative spellings Schevchenko, Ševčenko, Shevcenko, Szewczenko, Chevchenko; ua , Шевченко), a family name of Ukrainian origin. It is derived from the Ukrainian word ''shvets'' ( uk, швець), " cobbler/shoemaker", and the suffix ''-enko'', denoting descent. People Shevchenko * Alexander Shevchenko (other), multiple individuals * Alexandra Shevchenko (born 1988), Ukrainian feminist * Andrey Anatolyevich Shevchenko, Russian politician * Andriy Shevchenko (born 1976), Ukrainian football player and manager * Andriy Shevchenko (politician) (born 1976), Ukrainian journalist and politician * Anna Shevchenko (born 1993), Kazakhstani cross-country skier * Antonina Shevchenko (born 1984), Kyrgyzstani/Peruvian martial artist * Arkady Shevchenko (1930–1998), Ukrainian Soviet diplomat and defector * Artem Shevchenko (born 1977), Ukrainian TV journalist and manager * Christine Shevchenko (born 1988), Ukrainian-American ballet dancer * Daryna Shevchen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely more susceptible than fast neutrons to propagate a nuclear chain reaction of uranium-235 or other fissile isotope by colliding with their atomic nucleus. Water (sometimes called "light water" in this context) is the most commonly used moderator (roughly 75% of the world's reactors). Solid graphite (20% of reactors) and heavy water (5% of reactors) are the main alternatives. Beryllium has also been used in some experimental types, and hydrocarbons have been suggested as another possibility. Moderation Neutrons are normally bound into an atomic nucleus, and do not exist free for long in nature. The unbound neutron has a half-life of 10 minutes and 11 seconds. The release of neutrons from the nucleus requires exceeding the binding energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
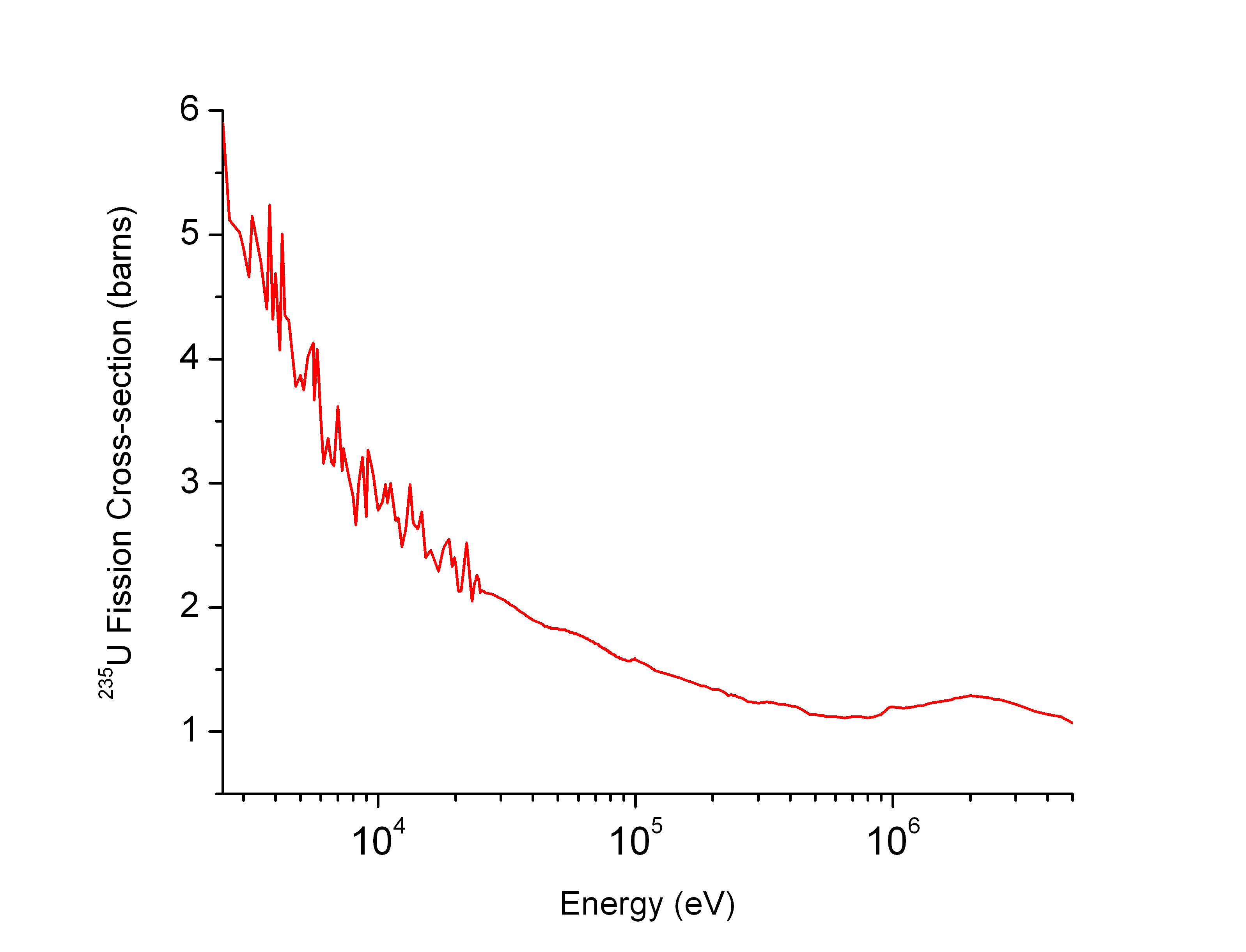
Neutron Cross Section
In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus. An isotope (or nuclide) can be classified according to its neutron cross section and how it reacts to an incident neutron. Nuclides that tend to absorb a neutron and either decay or keep the neutron in its nucleus are neutron absor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium-239
Plutonium-239 (239Pu or Pu-239) is an isotope of plutonium. Plutonium-239 is the primary fissile isotope used for the production of nuclear weapons, although uranium-235 is also used for that purpose. Plutonium-239 is also one of the three main isotopes demonstrated usable as fuel in thermal spectrum nuclear reactors, along with uranium-235 and uranium-233. Plutonium-239 has a half-life of 24,110 years. Nuclear properties The nuclear properties of plutonium-239, as well as the ability to produce large amounts of nearly pure 239Pu more cheaply than highly enriched weapons-grade uranium-235, led to its use in nuclear weapons and nuclear power plants. The fissioning of an atom of uranium-235 in the reactor of a nuclear power plant produces two to three neutrons, and these neutrons can be absorbed by uranium-238 to produce plutonium-239 and other isotopes. Plutonium-239 can also absorb neutrons and fission along with the uranium-235 in a reactor. Of all the common nuclear fuels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptunium-239
Neptunium (93Np) is usually considered an artificial element, although trace quantities are found in nature, so a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all trace or artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized and identified was 239Np in 1940, produced by bombarding with neutrons to produce , which then underwent beta decay to . Trace quantities are found in nature from neutron capture reactions by uranium atoms, a fact not discovered until 1951. Twenty-five neptunium radioisotopes have been characterized, with the most stable being with a half-life of 2.14 million years, with a half-life of 154,000 years, and with a half-life of 396.1 days. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lives that are less than 4.5 days, and the majority of these have half-lives that are less than 50 minutes. This element also has five meta states, with the most stable being (t1/2 22.5 hours). The isotopes of neptunium range from to , t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium-239
Uranium (92U) is a naturally occurring radioactive element that has no stable isotope. It has two primordial isotopes, uranium-238 and uranium-235, that have long half-lives and are found in appreciable quantity in the Earth's crust. The decay product uranium-234 is also found. Other isotopes such as uranium-233 have been produced in breeder reactors. In addition to isotopes found in nature or nuclear reactors, many isotopes with far shorter half-lives have been produced, ranging from 214U to 242U (with the exceptions of 220U and 241U). The standard atomic weight of natural uranium is . Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes, uranium-238 (99.2739–99.2752% natural abundance), uranium-235 (0.7198–0.7202%), and uranium-234 (0.0050–0.0059%). All three isotopes are radioactive (i.e., they are radioisotopes), and the most abundant and stable is uranium-238, with a half-life of (close to the age of the Earth). Uranium-238 is an alpha emitter, decaying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Graphite
Nuclear graphite is any grade of graphite, usually synthetic graphite, manufactured for use as a moderator or reflector within a nuclear reactor. Graphite is an important material for the construction of both historical and modern nuclear reactors, due to its extreme purity and ability to withstand extremely high temperature. Graphite has also recently been used in nuclear fusion reactors such as the Wendelstein 7-X. As of experiments published in 2019, graphite in elements of the stellarator's wall and a graphite island divertor have greatly improved plasma performance within the device, yielding better control over impurity and heat exhaust, and long high-density discharges. History Nuclear fission, the creation of a nuclear chain reaction in uranium, was discovered in 1939 following experiments by Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassman, and the interpretation of their results by physicists such as Lise Meitner and Otto Frisch. Shortly thereafter, word of the discovery spread thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form minerals. Notable gemstones high in beryllium include beryl ( aquamarine, emerald) and chrysoberyl. It is a relatively rare element in the universe, usually occurring as a product of the spallation of larger atomic nuclei that have collided with cosmic rays. Within the cores of stars, beryllium is depleted as it is fused into heavier elements. Beryllium constitutes about 0.0004 percent by mass of Earth's crust. The world's annual beryllium production of 220 tons is usually manufactured by extraction from the mineral beryl, a difficult process because beryllium bonds strongly to oxygen. In structural applications, the combination of high flexural rigidity, thermal stability, thermal conductivity and low density (1.85 times that of water) ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
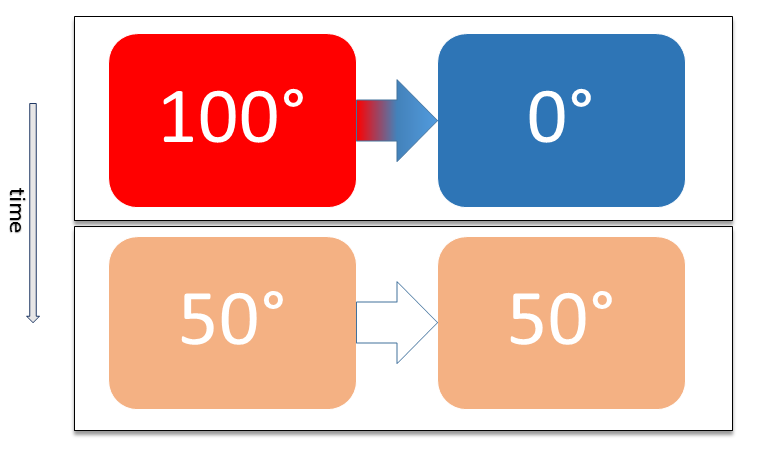
Thermal Equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in thermal equilibrium with itself if the temperature within the system is spatially uniform and temporally constant. Systems in thermodynamic equilibrium are always in thermal equilibrium, but the converse is not always true. If the connection between the systems allows transfer of energy as 'change in internal energy' but does not allow transfer of matter or transfer of energy as work, the two systems may reach thermal equilibrium without reaching thermodynamic equilibrium. Two varieties of thermal equilibrium Relation of thermal equilibrium between two thermally connected bodies The relation of thermal equilibrium is an instance of equilibrium between two bodies, which means that it refers to transfer through a selectively permeable p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elastic Scattering
Elastic scattering is a form of particle scattering in scattering theory, nuclear physics and particle physics. In this process, the kinetic energy of a particle is conserved in the center-of-mass frame, but its direction of propagation is modified (by interaction with other particles and/or potentials) meaning the two particles in the collision do not lose energy.“Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for materials characterization,” B.J. Inkson, “Materials Characterization Using Nondestructive Evaluation (NDE) Methods,” 2016. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/elastic-scattering Furthermore, while the particle's kinetic energy in the center-of-mass frame is constant, its energy in the lab frame is not. Generally, elastic scattering describes a process in which the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved. During elastic scattering of high-energy subatomic particles, linear energy transfer (LET) takes place un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |