|
Féchín Of Fore
Saint Féchín or Féichín (died 665), also known as Mo-Ecca, was a 7th-century Irish saint, chiefly remembered as the founder of the monastery at Fore (''Fobar''), County Westmeath. Sources for his life and legend include Irish annals, martyrologies, genealogies and hagiographical works. Of the two surviving medieval ''Lives'', one was written in Latin, the other in Irish. The Latin ''Life'' was written ''c''. 1400 by Augustine mac Graidín, who belonged to the Saints' Island on the southeastern shore of Lough Ree, south of the present-day village of Newtowncashel. His main source appears to have been a ''Life'' originating in Féchín's monastery on Omey Island. The Irish ''Life'' (''Betha Féchín Fabair'' "The Life of St Féchín of Fore") was written down by Nicol Óg, son of the abbot of Cong, in 1328 and it seems that parts of it go back to even earlier (Latin) sources. The text may be seen as a combination of two texts. The first part is primarily concerned with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
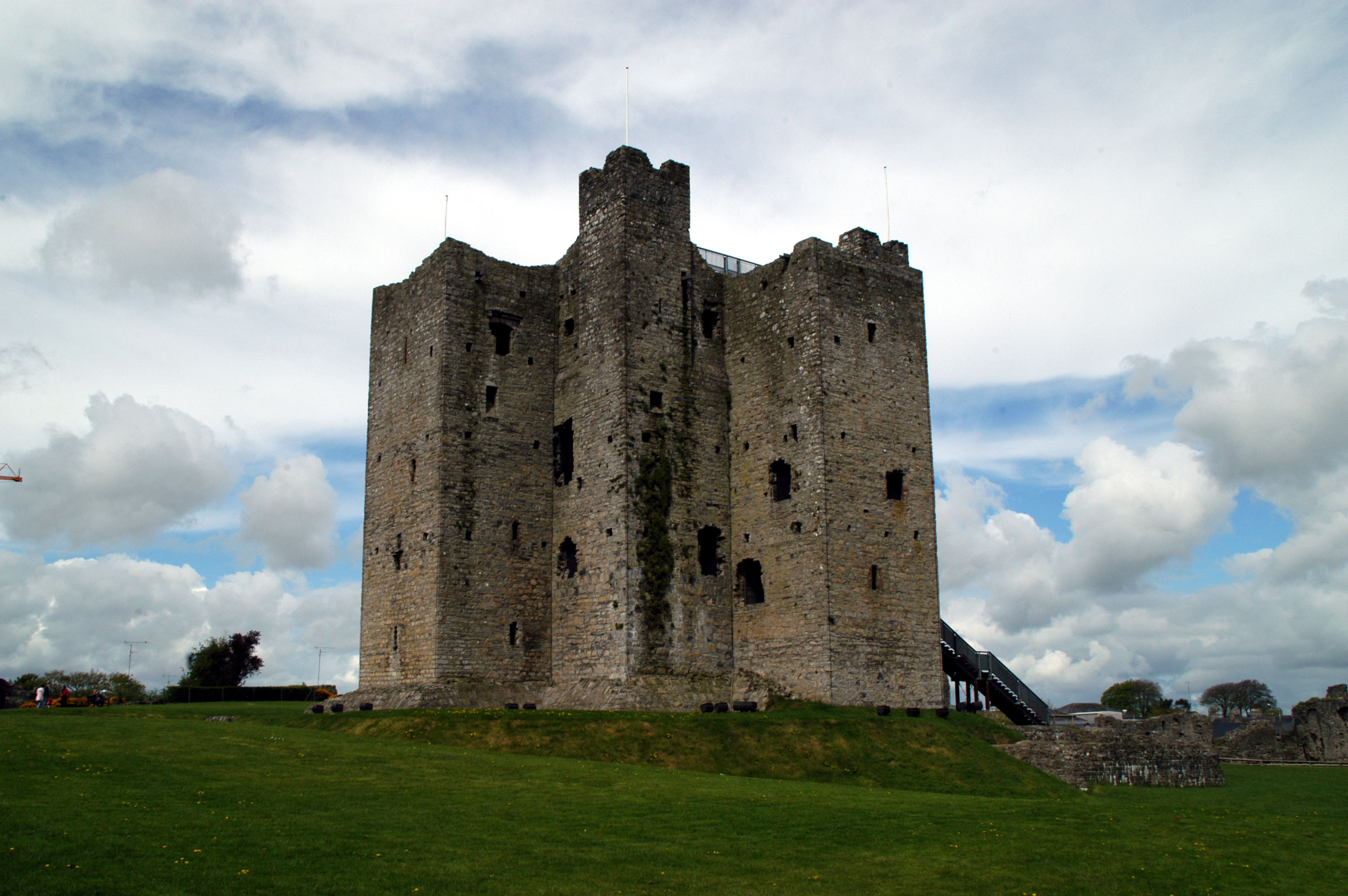
Fore Abbey
Fore Abbey () is the ruin of a Benedictine Abbey, situated to the north of Lough Lene in County Westmeath, near Fore village. The abbey was founded by Saint Feichin in 630 CE and functioned for over 900 years. By 665 CE (the time of the yellow plague), the abbey is believed to have housed up to 300 Benedictine monks from Normandy and 2000 students. Architectural additions and damage by fire have altered the site's appearance and layout over the centuries. Fore is the anglicised version of the Irish "Fobhar", meaning "water-springs". The name is derived from St. Feichin's spring or well which is next to the old church, a short distance from the ruined monastery. The site is referenced in the Annals of Inisfallen (AI) as "Repose of Fechtnach of Fobar". The Ó Cibhleacháin clan were recorded as the coarbs of the Monastery at Fore. A Benedictine Priory In the 13th century Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath the Norman and landlord built a Benedictine priory in the valley nearby. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nath Í Of Achonry
Saint Nath Í, or Crumnathy, (''fl''. 6th century) was an early Irish saint who was remembered as the founder of Achonry. He is said to have been born in the barony of Leyney, in present-day Co. Sligo. In the 17th century, John Colgan compiled a Latin ''Life'' of St Cormac, published in the ''Acta Sanctorum Hiberniae'' series, which relates that Cormac left his native Munster for Connacht and arrived in the area of Leyney. When Niall, the brother of the local chieftain Diarmait, begged the saint for a blessing, Cormac revealed that he was to have a son by the name of ''Conamel'', whose descendants would include a number of illustrious saints, such as Náth Í "the priest". In the ''Martyrology of Donegal'' (9 August), he is described as the priest (''cruimthir'') Nath Í of Achad Cain Conairi. He is said to have studied under St Finnián of Clonard. On the instructions of his mentor, he founded a monastery in Achad Cain or Achad Conaire (Achonry) in the district of the Luig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of The Four Masters
The ''Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland'' ( ga, Annála Ríoghachta Éireann) or the ''Annals of the Four Masters'' (''Annála na gCeithre Máistrí'') are chronicles of medieval Irish history. The entries span from the Deluge, dated as 2,242 years after creation to AD 1616. Publication delay Due to the criticisms by 17th century Irish historian Tuileagna Ó Maol Chonaire, the text was not published in the lifetimes of any of the participants. Text The annals are mainly a compilation of earlier annals, although there is some original work. They were compiled between 1632 and 1636, allegedly in a cottage beside the ruins of Donegal Abbey, just outside Donegal Town. At this time, however, the Franciscans had a house of refuge by the River Drowes in County Leitrim, just outside Ballyshannon, and it was here, according to others, that the ''Annals'' were compiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh De Lacy, Lord Of Meath
Hugh de Lacy, Lord of Meath, 4th Baron Lacy (; before 1135 – 25 July 1186), was an Anglo-Norman landowner and royal office-holder. He had substantial land holdings in Herefordshire and Shropshire. Following his participation in the Norman Invasion of Ireland, he was granted, in 1172, the lands of the Kingdom of Meath by the Anglo-Norman King Henry II, but he had to gain control of them. The Lordship of Meath was then the most extensive liberty in Ireland. Early life Hugh de Lacy was the son of Gilbert de Lacy (died after 1163) of Ewyas Lacy, Weobley, and Ludlow. He is said to have had a dispute with Joscelin de Dinan as to certain lands in Herefordshire in 1154. He was in possession of his father's lands before 1163, and in 1165–66 held fifty-eight and three-quarters knights' fees, and had nine tenants without knight service. Career in Ireland In October 1171 Lacy went over with Henry II as part of an Anglo-Norman force to invade Ireland, and early in 1172 he was sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Meath
County Meath (; gle, Contae na Mí or simply ) is a county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. It is bordered by Dublin to the southeast, Louth to the northeast, Kildare to the south, Offaly to the southwest, Westmeath to the west, Cavan to the northwest, and Monaghan to the north. To the east, Meath also borders the Irish Sea along a narrow strip between the rivers Boyne and Delvin, giving it the second shortest coastline of any county. Meath County Council is the local authority for the county. Meath is the 14th-largest of Ireland's 32 traditional counties by land area, and the 8th-most populous, with a total population of 220,296 according to the 2022 census. The county town and largest settlement in Meath is Navan, located in the centre of the county along the River Boyne. Other towns in the county include Trim, Kells, Laytown, Ashbourne, Dunboyne, Slane and Bettystown. Colloquially known as "The Royal County", the historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Of Wales
Gerald of Wales ( la, Giraldus Cambrensis; cy, Gerallt Gymro; french: Gerald de Barri; ) was a Cambro-Norman priest and English historians in the Middle Ages, historian. As a royal clerk to the king and two archbishops, he travelled widely and wrote extensively. He studied and taught in France and visited Rome several times, meeting the Pope. He was nominated for several bishoprics but turned them down in the hope of becoming Bishop of St Davids, but was unsuccessful despite considerable support. His final post was as Archdeacon of Brecon, from which he retired to academic study for the remainder of his life. Much of his writing survives. Life Early life Born at Manorbier Castle in Pembrokeshire, Wales, Gerald was of mixed Normans, Norman and Welsh people, Welsh descent. Gerald was the youngest son of William Fitz Odo de Barry (or Barri), the common ancestor of the De Barry family of Ireland, a retainer of Arnulf de Montgomery and Gerald de Windsor, and one of the most powerfu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaire Aidne Mac Colmáin
Guaire Aidne mac Colmáin (died 663) was a king of Connacht. A member of the Ui Fiachrach Aidhne and son of king Colmán mac Cobthaig (died 622). Guaire ruled at the height of Ui Fiachrach Aidne power in south Connacht. Early reign Guaire appears to have succeeded his father as king of the Ui Fiachrach Aidhne in 622. In 629 was fought the Battle of Carn Feradaig (Carhernarry, County Limerick), where he suffered a defeat at the hands of the Munster king Faílbe Flann mac Áedo Duib (died 639). His ally Conall mac Máele Dúib of the Ui Maine was slain. According to Keating, Guaire's reason for this campaign was to recover the Thomond region from Munster. Prof. Byrne believes that this defeat marked the true expansion of the Déisi Tuisceart into Thomond. He also states that this defeat may have paved the way for Rogallach mac Uatach (died 649) in acquiring the overlordship of Connacht. Carn Conaill The next event recorded of Guaire in the annals is the Battle of Carn Conaill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Ruins On Omey Island - Geograph
Church may refer to: Religion * Church (building), a building for Christian religious activities * Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination * Church service, a formalized period of Christian communal worship * Christian denomination, a Christian organization with distinct doctrine and practice * Christian Church, either the collective body of all Christian believers, or early Christianity Places United Kingdom * Church (Liverpool ward), a Liverpool City Council ward * Church (Reading ward), a Reading Borough Council ward * Church (Sefton ward), a Metropolitan Borough of Sefton ward * Church, Lancashire, England United States * Church, Iowa, an unincorporated community * Church Lake, a lake in Minnesota Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Church magazine'', a pastoral theology magazine published by the National Pastoral Life Center Fictional entities * Church (''Red vs. Blue''), a fictional character in the video web series ''Red vs. Blue'' * Churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sligo
Sligo ( ; ga, Sligeach , meaning 'abounding in shells') is a coastal seaport and the county town of County Sligo, Ireland, within the western province of Connacht. With a population of approximately 20,000 in 2016, it is the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland by population, largest urban centre in the county, with Sligo Municipal district (Ireland), Borough District constituting 61% (38,581) of the county's population of 63,000. Sligo is a commercial and cultural centre situated on the west coast of Ireland. Its surrounding coast and countryside, as well as its connections to the poet W. B. Yeats, have made it a tourist destination. History Etymology Sligo is the anglicisation of the Irish name ''Sligeach'', meaning "abounding in shells" or "shelly place". It refers to the abundance of shellfish found in the river and its estuary, and from the extensive shell middens in the vicinity. The river now known as the River Garavogue, Garavogue ( ga, An Ghairbhe-og), per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galway
Galway ( ; ga, Gaillimh, ) is a City status in Ireland, city in the West Region, Ireland, West of Ireland, in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Connacht, which is the county town of County Galway. It lies on the River Corrib between Lough Corrib and Galway Bay, and is the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, sixth most populous city on the island of Ireland and the List of urban areas in the Republic of Ireland by population, fourth most populous in the Republic of Ireland, with a population at the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census of 83,456. Located near an earlier settlement, Galway grew around a fortification built by the Kings of Connacht, King of Connacht in 1124. A municipal charter in 1484 allowed citizens of the by then walled city to form a Galway City Council, council and mayoralty. Controlled largely by a group of merchant families, the Tribes of Galway, the city grew into a trading port. Following a period of decline, as of the 21st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connemara
Connemara (; )( ga, Conamara ) is a region on the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of western County Galway, in the west of Ireland. The area has a strong association with traditional Irish culture and contains much of the Connacht Irish-speaking Gaeltacht, which is a key part of the identity of the region and is the largest Gaeltacht in the country. Historically, Connemara was part of the territory of Iar Connacht (West Connacht). Geographically, it has many mountains (notably the Twelve Bens), peninsulas, coves, islands and small lakes. Connemara National Park is in the northwest. It is mostly rural and its largest settlement is Clifden. Etymology "Connemara" derives from the tribal name , which designated a branch of the , an early tribal grouping that had a number of branches located in different parts of . Since this particular branch of the lived by the sea, they became known as the (sea in Irish is , genitive case, genitive , hence "of the sea"). Definition One common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |