|
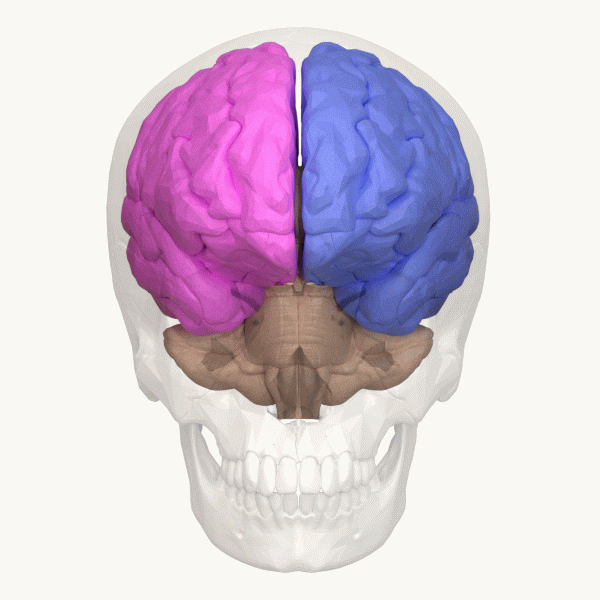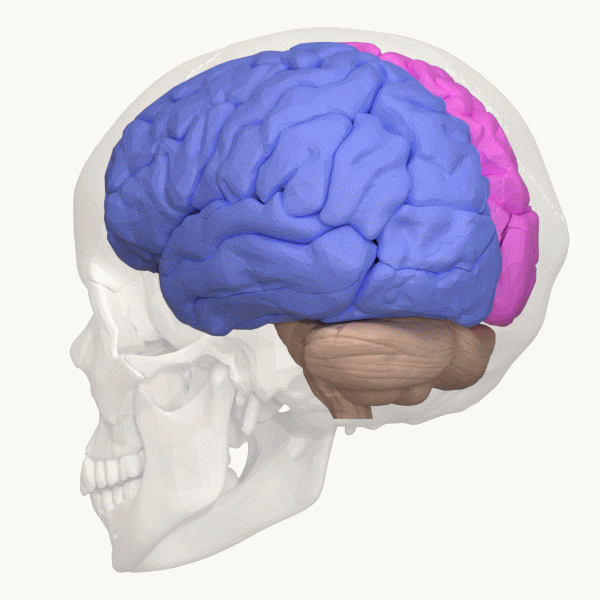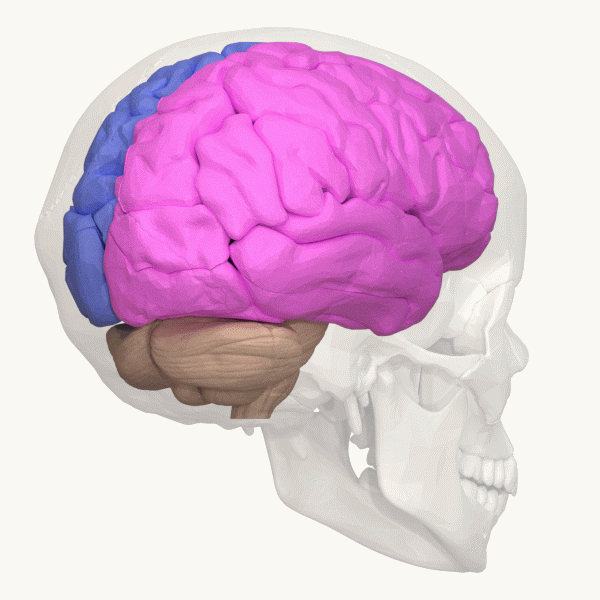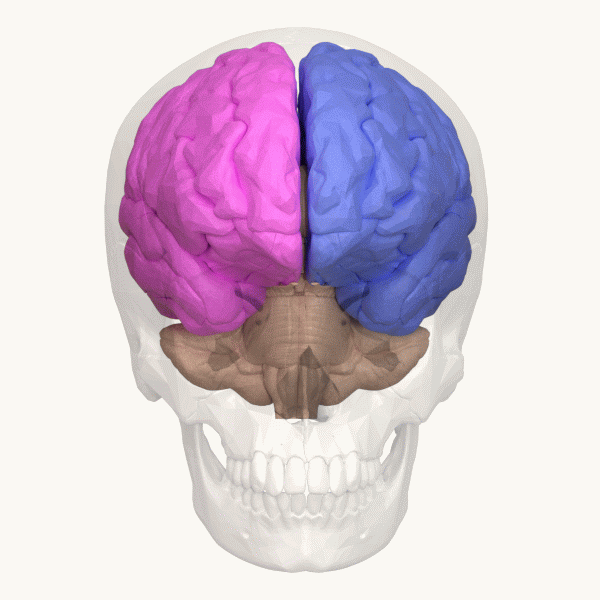
Fusiform Body Area
The Fusiform body area (FBA) is a part of the extrastriate visual cortex, an object representation system involved in the visual processing of human bodies in contrast to body parts. Its function is similar to but distinct from the extrastriate body area (EBA), which perceives bodies in relation body parts, and the fusiform face area (FFA), which is involved in the perception of faces. Marius Peelen and Paul Downing identified this brain region in 2004 through an fMRI study.; in 2005 Rebecca Schwarzlose and a team of cognitive researchers named this brain region the fusiform body area. Location The FBA shares overlapping structures with the FFA, both are located in Brodmann area 37, specifically a part of the occipital lobe and temporal lobe known as the fusiform gyrus. The FBA is located on the ventral surface of the brain, on the lateral posterior surface of the fusiform gyrus. Typically activation in the right hemisphere is larger, which suggests a degree of lateralization. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphere's V1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrastriate Body Area
The extrastriate body area (EBA) is a subpart of the extrastriate visual cortex involved in the visual perception of human body and body parts, akin in its respective domain to the fusiform face area, involved in the perception of human faces. The EBA was identified in 2001 by the team of Nancy Kanwisher using fMRI. Function The extrastriate body area is a category-selective region for the visual processing of static and moving images of the human body and parts of it. It is also modulated even in the absence of visual feedback from the limb movement. It is insensitive to faces and stimulus categories unrelated to the human body. The extrastriate cortex responds not only during the perception of other people's body parts but also during goal-directed movement of the participant's body parts. The extrastriate cortex represents the human body in a more integrative and dynamic manner, being able to detect an incongruence of internal body or action representations and external visual s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusiform Face Area
The fusiform face area (FFA, meaning spindle-shaped face area) is a part of the human visual system (while also activated in people blind from birth) that is specialized for facial recognition. It is located in the inferior temporal cortex (IT), in the fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37). Structure The FFA is located in the ventral stream on the ventral surface of the temporal lobe on the lateral side of the fusiform gyrus. It is lateral to the parahippocampal place area. It displays some lateralization, usually being larger in the right hemisphere. The FFA was discovered and continues to be investigated in humans using positron emission tomography (PET) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies. Usually, a participant views images of faces, objects, places, bodies, scrambled faces, scrambled objects, scrambled places, and scrambled bodies. This is called a functional localizer. Comparing the neural response between faces and scrambled faces will reveal areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brodmann Area 37
Brodmann area 37, or BA37, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. It contains the fusiform gyrus which in turn contains the fusiform face area, an area important for the recognition of faces. This area is also known as occipitotemporal area 37 (H). It is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined temporal region of cerebral cortex. It is located primarily in the caudal portions of the fusiform gyrus and inferior temporal gyrus on the mediobasal and lateral surfaces at the caudal extreme of the temporal lobe. Cytoarchitecturally, it is bounded caudally by the peristriate Brodmann area 19, rostrally by the inferior temporal area 20 and middle temporal area 21, and dorsally on the lateral aspect of the hemisphere by the angular area 39 (H) (Brodmann-1909). See also * Fusiform face area * Brodmann area A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head". The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex. The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the occipital pole. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception. Bilateral lesions of the occipital lobe can lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four Lobes of the brain, major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's Temple (anatomy), temples. Structure The Temple (anatomy)#Etymology, temporal Lobe (anatomy), lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative memory, Declarative (denotative) or Explicit memory, explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). Medial temporal lobe structures that are critical for long-term memory include the hippocampus, along with the surrounding Hippocampal formation, hippocampal region consisting of the Perirhinal cortex, perirhinal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusiform Gyrus
The fusiform gyrus, also known as the ''lateral occipitotemporal gyrus'','' ''is part of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe in Brodmann area 37. The fusiform gyrus is located between the lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus above, and the inferior temporal gyrus below. Though the functionality of the fusiform gyrus is not fully understood, it has been linked with various neural pathways related to recognition. Additionally, it has been linked to various neurological phenomena such as synesthesia, dyslexia, and prosopagnosia. Anatomy Anatomically, the fusiform gyrus is the largest macro-anatomical structure within the ventral temporal cortex, which mainly includes structures involved in high-level vision. The term fusiform gyrus (lit. "spindle-shaped convolution") refers to the fact that the shape of the gyrus is wider at its centre than at its ends. This term is based on the description of the gyrus by Emil Huschke in 1854. (see also section on history). The fusiform gyrus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Hemisphere
The lateralization of brain function is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. Although the macrostructure of the two hemispheres appears to be almost identical, different composition of neuronal networks allows for specialized function that is different in each hemisphere. Lateralization of brain structures is based on general trends expressed in healthy patients; however, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization. Each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger anthropological history. The best examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateralization
The lateralization of brain function is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres, connected by the corpus callosum. Although the macrostructure of the two hemispheres appears to be almost identical, different composition of neuronal networks allows for specialized function that is different in each hemisphere. Lateralization of brain structures is based on general trends expressed in healthy patients; however, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization. Each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger anthropological history. The best examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episodic Memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred at particular times and places; for example, the party on one's 7th birthday. Along with semantic memory, it comprises the category of explicit memory, one of the two major divisions of long-term memory (the other being implicit memory). The term "episodic memory" was coined by Endel Tulving in 1972, referring to the distinction between knowing and remembering: ''knowing'' is factual recollection (semantic) whereas ''remembering'' is a feeling that is located in the past (episodic). One of the main components of episodic memory is the process of recollection, which elicits the retrieval of contextual information pertaining to a specific event or experience that has occurred. Tulving seminally defined three key properties of episodic memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. This technique relies on the fact that cerebral blood flow and neuronal activation are coupled. When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases. The primary form of fMRI uses the blood-oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) contrast, discovered by Seiji Ogawa in 1990. This is a type of specialized brain and body scan used to map neuron, neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals by imaging the change in blood flow (hemodynamic response) related to energy use by brain cells. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has come to dominate brain mapping research because it does not involve the use of injections, surgery, the ingestion of substances, or exposure to ionizing radiation. This measure is frequently corrupted by noise from various sources; hence, statistical procedures are used to extract the underlying si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nancy Kanwisher
Nancy Gail Kanwisher FBA (born 1958) is the Ellen Swallow Richards Professor in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and an investigator at the McGovern Institute for Brain Research. She studies the neural and cognitive mechanisms underlying human visual perception and cognition. Academic background Nancy Kanwisher received her SB in biology from MIT in 1980 and her PhD in Brain and Cognitive Sciences from MIT in 1986. After obtaining her PhD working with Mary C. Potter, she then did her post-doctoral work with Anne Treisman at UC-Berkeley. Before returning to MIT as a faculty member in 1997 in the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Kanwisher served as a faculty member at both UCLA and Harvard University. Kanwisher is a member and associate editor for journals in areas of cognitive science, including Cognition, Current Opinion in Neurobiology, Journal of Neuroscience, Trends in Cognitive Sciences, and Cognitive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |