|
Fundamenta Botanica
''Fundamenta Botanica'' (“Foundations of botany”) (Amsterdam, Salomon Schouten, ed. 1, 1736) was one of the major works of the Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and issued both as a separate work and part of the ''Bibliotheca Botanica''. This book states, for the first time, Linnaeus's ideas for the reformation of botanical taxonomy. The first edition is dated 1736 but it was released on 14 September 1735 (Linnaeus wrote in his personal copy “Typus absolutus 1735, Sept. 3”). The full title was ''Fundamenta Botanica, quae Majorum Operum Prodromi instar Theoriam Scientiae Botanices by breves Aphorismos tradunt''. The first edition was dedicated to Olof Rudbeck, Lorenz Heister, Adriaan van Royen, Johann Jacob Dillen, Antoine de Jussieu, Giulio Pontedera, Johann Amman, Johannes Burman, Pierre Magnol and Giuseppe Monti. A second edition was published in Stockholm in 1740 and a third in Amsterdam in 1741. The publication of this work as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
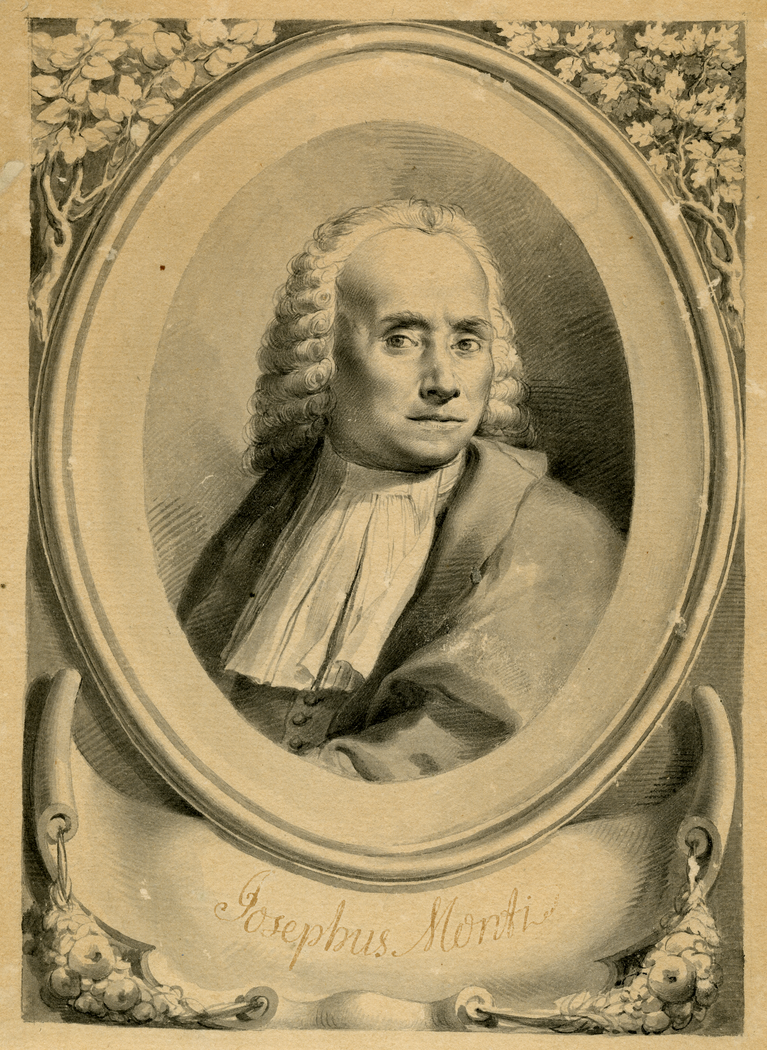
Giuseppe Monti
Giuseppe Monti (27 November 1682 – 29 February 1760) was an Italian chemist and botanist. He was a professor of botany and from 1722 to 1760 director of the Bologna Botanical Garden. His son Gaetano Lorenzo Monti (1712–1797) was also a botanist who continued work at the same botanical garden. His herbarium consisted of 10000 specimens representing more than 2500 species. His collection also included specimens from Aldrovandi. Monti discovered a fossil jawbone in the Alps and used it as support for the Biblical flood and both he and his son were among the last defenders of diluvialism among the naturalists of the period. Monti's botanical works were a source for Carl Linnaeus. Several plant genera have been named in his honour, including in 1753, Carl Linnaeus published ''Montia'' from the family Montiaceae, Then in 1898, botanist Otto Kuntze published ''Montiopsis'', a genus of flowering plants from South America belonging to the family Montiaceae Montiaceae are a family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1736 In Science
The year 1736 in science and technology involved some significant events. Botany * Charles Marie de La Condamine, with François Fresneau Gataudière, makes the first scientific observations of rubber, in Ecuador. Earth sciences * June 19 – French Academy of Sciences expedition led by Pierre Louis Maupertuis, with Anders Celsius, begins work on measuring a meridian arc in the Torne Valley of Finland. Mathematics * June 8 – Leonhard Euler writes to James Stirling describing the Euler–Maclaurin formula, providing a connection between integrals and calculus. * Euler produces the first ''published'' proof of Fermat's "little theorem". * Sir Isaac Newton's ''Method of Fluxions'' (1671), describing his method of differential calculus, is first published (posthumously) and Thomas Bayes publishes a defense of its logical foundations against the criticism of George Berkeley (anonymously). Medicine * Early 1736 – The “Publick Workhouse and House of Correction” that is to bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany Books
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek word (''botanē'') meaning "pasture", " herbs" "grass", or " fodder"; is in turn derived from (), "to feed" or "to graze". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of land plants of which some 391,000 species are vascular plants (including approximately 369,000 species of flowering plants), and approximately 20,000 are bryophytes. Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florae (publication)
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''. Etymology The word "flora" comes from the Latin name of Flora, the goddess of plants, flowers, and fertility in Roman mythology. The technical term "flora" is then derived from a metonymy of this goddess at the end of the sixteenth century. It was first used in poetry to denote the natural vegetation of an area, but soon also assumed the meaning of a work cataloguing such vegetation. Moreover, "Flora" was used to refer to the flowers of an artificial garden in the seventeenth century. The distinction between vegetation (the general appearance of a community) and flora (the taxonomic composition of a community) was first made by Jules Thurmann (1849). Prior to this, the two terms were used indiscriminately.Thurmann, J. (1849). ''Essai de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Nomenclature
Botanical nomenclature is the formal, scientific naming of plants. It is related to, but distinct from Alpha taxonomy, taxonomy. Plant taxonomy is concerned with grouping and classifying plants; botanical nomenclature then provides names for the results of this process. The starting point for modern botanical nomenclature is Carl Linnaeus, Linnaeus' ''Species Plantarum'' of 1753. Botanical nomenclature is governed by the ''International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants'' (''ICN''), which replaces the ''International Code of Botanical Nomenclature'' (''ICBN''). Fossil plants are also covered by the code of nomenclature. Within the limits set by that code there is another set of rules, the ''International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants, International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP)'' which applies to plant cultivars that have been deliberately altered or selected by humans (see cultigen). History and scope Botanical nomenclature has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1736 Books
Events January–March * January 12 – George Hamilton, 1st Earl of Orkney, becomes the first Field Marshal of Great Britain. * January 23 – The Civil Code of 1734 is passed in Sweden. * January 26 – Stanislaus I of Poland abdicates his throne. * February 12 – Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor marries Maria Theresa of Austria, ruler of the Habsburg Empire. * March 8 – Nader Shah, founder of the Afsharid dynasty, is crowned Shah of Iran on a date selected by court astrologers. * March 31 – Bellevue Hospital is founded in New York. April–June * April 14 – The Porteous Riots erupt in Edinburgh (Scotland), after the execution of smuggler Andrew Wilson, when town guard Captain John Porteous orders his men to fire at the crowd. Porteous is arrested later. * April 14 – German adventurer Theodor Stephan Freiherr von Neuhoff is crowned King Theodore of Corsica, 25 days after his arrival on Corsica on March 20. His reign ends on Nove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophia Botanica
''Philosophia Botanica'' ("Botanical Philosophy", ed. 1, Stockholm & Amsterdam, 1751.) was published by the Swedish naturalist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) who greatly influenced the development of botanical taxonomy and systematics in the 18th and 19th centuries. It is "''the first textbook of descriptive systematic botany and botanical Latin''". It also contains Linnaeus's first published description of his binomial nomenclature. ''Philosophia Botanica'' represents a maturing of Linnaeus's thinking on botany and its theoretical foundations, being an elaboration of ideas first published in his ''Fundamenta Botanica'' (1736) and '' Critica Botanica'' (1737), and set out in a similar way as a series of stark and uncompromising principles (aphorismen). The book also establishes a basic botanical terminology. The following principle §79 demonstrates the style of presentation and Linnaeus's method of introducing his ideas. A detailed analysis of the work is given i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are given a taxonomic rank; groups of a given rank can be aggregated to form a more inclusive group of higher rank, thus creating a taxonomic hierarchy. The principal ranks in modern use are domain, kingdom, phylum (''division'' is sometimes used in botany in place of ''phylum''), class, order, family, genus, and species. The Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus is regarded as the founder of the current system of taxonomy, as he developed a ranked system known as Linnaean taxonomy for categorizing organisms and binomial nomenclature for naming organisms. With advances in the theory, data and analytical technology of biological systematics, the Linnaean system has transformed into a system of modern biological classification intended to reflect the evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal naming conventions, conventions of everyday speech to the internationally agreed principles, rules and recommendations that govern the formation and use of the specialist terms used in scientific and any other disciplines. Naming "things" is a part of general human communication using words and language: it is an aspect of everyday Taxonomy (general), taxonomy as people distinguish the objects of their experience, together with their similarities and differences, which observers Identification (information), identify, name and wikt:classification, classify. The use of names, as the many different kinds of nouns embedded in different languages, connects nomenclature to theoretical linguistics, while the way humans mentally structure the world in relation to semantics, word meanings and Experience ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critica Botanica
''Critica Botanica'' ("Critique of botany", Leiden, July 1737) was written by Swedish botanist, physician, zoologist and naturalist Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778). The book was published in Germany when Linnaeus was 29 with a discursus by the botanist Johannes Browallius (1707–1755), bishop of Åbo. The first edition was published in July 1737 under the full title ''Critica botanica in qua nomina plantarum generica, specifica & variantia examini subjiciuntur, selectoria confirmantur, indigna rejiciuntur; simulque doctrina circa denominationem plantarum traditur. Seu Fundamentorum botanicorum pars IV Accedit Johannis Browallii De necessitate historiae naturalis discursus''. Linnaeus's principles of botanical nomenclature were first expounded in ''Fundamenta Botanica'' ("Foundations of botany") of 1736 chapters VII to X which contained the aphorisms (principles) 210 to 324 that outlined the rules for the acceptance and formation of names. These were later elaborated, with numerous e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Boerhaave
Herman Boerhaave (, 31 December 1668 – 23 September 1738Underwood, E. Ashworth. "Boerhaave After Three Hundred Years." ''The British Medical Journal'' 4, no. 5634 (1968): 820–25. https://www.jstor.org/stable/20395297.) was a Dutch botanist, chemist, Christian humanist, and physician of European fame. He is regarded as the founder of clinical teaching and of the modern academic hospital and is sometimes referred to as "the father of physiology," along with Venetian physician Santorio Santorio (1561–1636). Boerhaave introduced the quantitative approach into medicine, along with his pupil Albrecht von Haller (1708–1777) and is best known for demonstrating the relation of symptoms to lesions. He was the first to isolate the chemical urea from urine. He was the first physician to put thermometer measurements to clinical practice. His motto was ''Simplex sigillum veri'': 'Simplicity is the sign of the truth'. He is often hailed as the "Dutch Hippocrates". Biography Boerhaave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |