|
Full-disk Encryption
Disk encryption is a technology which protects information by converting it into unreadable code that cannot be deciphered easily by unauthorized people. Disk encryption uses disk encryption software or hardware to encrypt every bit of data that goes on a disk or disk volume. It is used to prevent unauthorized access to data storage. The expression ''full disk encryption (FDE)'' (or ''whole disk encryption'') signifies that everything on the disk is encrypted, but the master boot record (MBR), or similar area of a bootable disk, with code that starts the operating system loading sequence, is not encrypted. Some hardware-based full disk encryption systems can truly encrypt an entire boot disk, including the MBR. Transparent encryption Transparent encryption, also known as real-time encryption and on-the-fly encryption (OTFE), is a method used by some disk encryption software. "Transparent" refers to the fact that data is automatically encrypted or decrypted as it is loaded o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disk Encryption Software
Disk encryption software is computer security software that protects the confidentiality of data stored on computer media (e.g., a hard disk, floppy disk, or USB device) by using disk encryption. Compared to access controls commonly enforced by an operating system (OS), encryption passively protects data confidentiality even when the OS is not active, for example, if data is read directly from the hardware or by a different OS. In addition crypto-shredding suppresses the need to erase the data at the end of the disk's lifecycle. Disk encryption generally refers to wholesale encryption that operates on an entire volume mostly transparently to the user, the system, and applications. This is generally distinguished from file-level encryption that operates by user invocation on a single file or group of files, and which requires the user to decide which specific files should be encrypted. Disk encryption usually includes all aspects of the disk, including directories, so that an ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transparency (human-computer Interaction)
Transparency, transparence or transparent most often refer to: * Transparency (optics), the physical property of allowing the transmission of light through a material They may also refer to: Literal uses * Transparency (photography), a still, positive image created on a transparent base using photochemical means * Transparency (projection), a thin sheet of transparent material for use with an overhead projector * Electromagnetically induced transparency, an effect in which a medium that is normally opaque is caused to become temporarily transparent * Pentimento, an alteration in a painting, often revealed with growing transparency in paints with age Animals and plants * Transparent goby, a fish species of the family Gobiidae * White Transparent, a cultivar of apple which is usually used for cooking due to its sharp taste Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels * Transparency (record label), a North American music publisher * Transparent (band), a rock band fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardware-based Full Disk Encryption
Hardware-based full disk encryption (FDE) is available from many hard disk drive (HDD/SSD) vendors, including: ClevX, Hitachi, Integral Memory, iStorage Limited, Micron, Seagate Technology, Samsung, Toshiba, Viasat UK, Western Digital. The symmetric encryption key is maintained independently from the computer's CPU, thus allowing the complete data store to be encrypted and removing computer memory as a potential attack vector. Hardware-FDE has two major components: the hardware encryptor and the data store. There are currently four varieties of hardware-FDE in common use: #Hard disk drive (HDD) FDE (self-encrypting drive) #Enclosed hard disk drive FDE #Removable hard disk drive FDE #Bridge and Chipset (BC) FDE Hardware designed for a particular purpose can often achieve better performance than disk encryption software, and disk encryption hardware can be made more transparent to software than encryption done in software. As soon as the key has been initialised, the hardware ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host Bus Adaptor
In computer hardware, a host controller, host adapter, or host bus adapter (HBA), connects a computer system bus, which acts as the host system, to other network and storage devices. The terms are primarily used to refer to devices for connecting SCSI, Fibre Channel and SATA devices. Devices for connecting to IDE, Ethernet, FireWire, USB and other systems may also be called host adapters. Host adapters can be integrated in the motherboard or be on a separate expansion card. The term network interface controller (NIC) is more often used for devices connecting to computer networks, while the term converged network adapter can be applied when protocols such as iSCSI or Fibre Channel over Ethernet allow storage and network functionality over the same physical connection. SCSI A SCSI host adapter connects a host system and a peripheral SCSI device or storage system. These adapters manage service and task communication between the host and target. Typically a device driver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
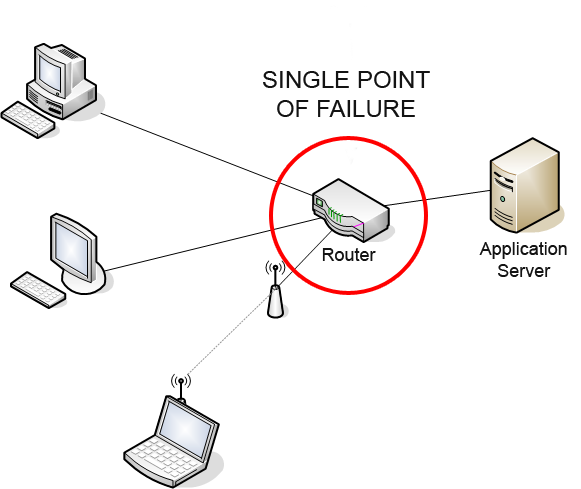
Single Point Of Failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that, if it fails, will stop the entire system from working. SPOFs are undesirable in any system with a goal of high availability or reliability, be it a business practice, software application, or other industrial system. Overview Systems can be made robust by adding redundancy in all potential SPOFs. Redundancy can be achieved at various levels. The assessment of a potential SPOF involves identifying the critical components of a complex system that would provoke a total systems failure in case of malfunction. Highly reliable systems should not rely on any such individual component. For instance, the owner of a small tree care company may only own one woodchipper. If the chipper breaks, he may be unable to complete his current job and may have to cancel future jobs until he can obtain a replacement. The owner of the tree care company may have spare parts ready for the repair of the wood chipper, in case it fails. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Token
A security token is a peripheral device used to gain access to an electronically restricted resource. The token is used in addition to or in place of a password. It acts like an electronic key to access something. Examples of security tokens include wireless keycards used to open locked doors, or in the case of a customer trying to access their bank account online, bank-provided tokens can prove that the customer is who they claim to be. Some security tokens may store cryptographic keys that may be used to generate a digital signature, or biometric data, such as fingerprint details. Some may also store passwords. Some designs incorporate tamper resistant packaging, while others may include small keypads to allow entry of a PIN or a simple button to start a generating routine with some display capability to show a generated key number. Connected tokens utilize a variety of interfaces including USB, near-field communication (NFC), radio-frequency identification (RFID), or Bluet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. It might involve validating personal identity documents, verifying the authenticity of a website with a digital certificate, determining the age of an artifact by carbon dating, or ensuring that a product or document is not counterfeit. Methods Authentication is relevant to multiple fields. In art, antiques, and anthropology, a common problem is verifying that a given artifact was produced by a certain person or in a certain place or period of history. In computer science, verifying a user's identity is often required to allow access to confidential data or systems. Authentication can be considered to be of three types: The first type of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motherboard
A motherboard (also called mainboard, main circuit board, mb, mboard, backplane board, base board, system board, logic board (only in Apple computers) or mobo) is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use. ''Motherboard'' means specifically a PCB with expansion capabilities. As the name suggests, this board is often referred to as the "mother" of all components attached to it, which often include peripherals, interface cards, and daughterboards: sound cards, video cards, network cards, host bus adapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Cryptoprocessor
A secure cryptoprocessor is a dedicated computer-on-a-chip or microprocessor for carrying out cryptographic operations, embedded in a packaging with multiple physical security measures, which give it a degree of tamper resistance. Unlike cryptographic processors that output decrypted data onto a bus in a secure environment, a secure cryptoprocessor does not output decrypted data or decrypted program instructions in an environment where security cannot always be maintained. The purpose of a secure cryptoprocessor is to act as the keystone of a security subsystem, eliminating the need to protect the rest of the subsystem with physical security measures. Examples A hardware security module (HSM) contains one or more secure cryptoprocessor chips. These devices are high grade secure cryptoprocessors used with enterprise servers. A hardware security module can have multiple levels of physical security with a single-chip cryptoprocessor as its most secure component. The cryptoprocess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trusted Platform Module
Trusted Platform Module (TPM, also known as ISO/IEC 11889) is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard. TPM is used for digital rights management (DRM), Windows Defender, Windows Domain logon, protection and enforcement of software licenses, and prevention of cheating in online games. One of Windows 11's system requirements is TPM 2.0. Microsoft has stated that this is to help increase security against firmware and ransomware attacks. History Trusted Platform Module (TPM) was conceived by a computer industry consortium called Trusted Computing Group (TCG). It evolved into ''TPM Main Specification Version 1.2'' which was standardized by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 2009 as ISO/IEC 11889:2009. ''TPM Main Specification Version 1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timestamp
A timestamp is a sequence of characters or encoded information identifying when a certain event occurred, usually giving date and time of day, sometimes accurate to a small fraction of a second. Timestamps do not have to be based on some absolute notion of time, however. They can have any epoch, can be relative to any arbitrary time, such as the power-on time of a system, or to some arbitrary time in the past. The term "timestamp" derives from rubber stamps used in offices to stamp the current date, and sometimes time, in ink on paper documents, to record when the document was received. Common examples of this type of timestamp are a postmark on a letter or the "in" and "out" times on a time card. In modern times usage of the term has expanded to refer to digital date and time information attached to digital data. For example, computer files contain timestamps that tell when the file was last modified, and digital cameras add timestamps to the pictures they take, recording ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |