|
Frustration–aggression Hypothesis
The frustration–aggression hypothesis, also known as the frustration–aggression–displacement theory, is a theory of aggression proposed by John Dollard, Neal Miller, Leonard Doob, Orval Mowrer, and Robert Sears in 1939, and further developed by Neal Miller in 1941 and Leonard Berkowitz in 1969. The theory says that aggression is the result of blocking, or frustrating, a person's efforts to attain a goal. When first formulated, the hypothesis stated that frustration always precedes aggression, and aggression is the sure consequence of frustration. Two years later, however, Miller and Sears re-formulated the hypothesis to suggest that while frustration creates a need to respond, some form of aggression is one possible outcome. Therefore, the re-formulated hypothesis stated that while frustration prompts a behavior that may or may not be aggressive, any aggressive behavior is the result of frustration, making frustration not sufficient, but a necessary condition for aggression. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In humans, aggression can be caused by various triggers, from frustration due to blocked goals to feeling disrespected. Human aggression can be classified into direct and indirect aggression; whilst the former is characterized by physical or verbal behavior intended to cause harm to someone, the latter is characterized by behavior intended to harm the social relations of an individual or group. In definitions commonly used in the social sciences and behavioral sciences, aggression is an action or response by an individual that delivers something unpleasant to another person. Some definitions include that the individual must intend to harm another person. In an interdisciplinary perspective, aggression is rega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Bateson
Gregory Bateson (9 May 1904 – 4 July 1980) was an English anthropologist, social scientist, linguist, visual anthropologist, semiotician, and cyberneticist whose work intersected that of many other fields. His writings include '' Steps to an Ecology of Mind'' (1972) and ''Mind and Nature'' (1979). In Palo Alto, California, Bateson and colleagues developed the double-bind theory of schizophrenia. Bateson's interest in systems theory forms a thread running through his work. He was one of the original members of the core group of the Macy conferences in Cybernetics (1941–1960), and the later set on Group Processes (1954–1960), where he represented the social and behavioral sciences. He was interested in the relationship of these fields to epistemology. His association with the editor and author Stewart Brand helped widen his influence. Early life and education Bateson was born in Grantchester in Cambridgeshire, England, on 9 May 1904. He was the third and youngest son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bowlby
Edward John Mostyn Bowlby, CBE, FBA, FRCP, FRCPsych (; 26 February 1907 – 2 September 1990) was a British psychologist, psychiatrist, and psychoanalyst, notable for his interest in child development and for his pioneering work in attachment theory. A ''Review of General Psychology'' survey, published in 2002, ranked Bowlby as the 49th most cited psychologist of the 20th century. Family background Bowlby was born in London to an upper-middle-income family. He was the fourth of six children and was brought up by a nanny in the British fashion of his class at that time: the family hired a nanny who was in charge of raising the children, in a separate nursery in the house.Van Dijken, S. (1998). John Bowlby: His Early Life: A Biographical Journey into the Roots of Attachment Theory. London: Free Association Books Nanny Friend took care of the infants and generally had two other nursemaids to help her. Bowlby was raised primarily by nursemaid Minnie who acted as a mother figur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evan Durbin
Evan Frank Mottram Durbin (1 March 1906 – 3 September 1948) was a British economist and Labour Party politician, whose writings combined a belief in central economic planning with a conviction that the price mechanism of markets was indispensable. Historian David Kynaston described Durbin as "the Labour Party's most interesting thinker of the 1940s and arguably of the twentieth century". Early life Durbin was born in 1906, the son of a Baptist minister. He was educated at Plympton and Exmouth Elementary Schools; Heles School, Exeter; Taunton School; and New College, Oxford. At Oxford he studied zoology, followed by PPE, and became one of what Ben Pimlott described as 'the "Cole group" of distinguished young socialists'.Pimlott, Ben "Harold Wilson" Harper Collins (1993). He befriended Hugh Gaitskell (later, leader of the Labour Party 1955–63) during the 1926 United Kingdom general strike, when he undertook public speaking tasks on behalf of the strikers in and around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded upon the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behaviorism
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understanding the behavior of humans and animals. It assumes that behavior is either a reflex evoked by the pairing of certain antecedent (behavioral psychology), antecedent stimuli in the environment, or a consequence of that individual's history, including especially reinforcement (psychology), reinforcement and punishment (psychology), punishment three-term contingency, contingencies, together with the individual's current motivating operation, motivational state and Stimulus control, controlling stimuli. Although behaviorists generally accept the important role of heredity in determining behavior, they focus primarily on environmental events. Behaviorism emerged in the early 1900s as a reaction to depth psychology and other traditional forms of psychology, which often had difficulty making predictions that could be tested experimentally, but derived from earlier research in the late nineteenth century, such as when Edward Thorndike p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event-related Potential
An event-related potential (ERP) is the measured brain response that is the direct result of a specific sense, sensory, cognition, cognitive, or motor system, motor event. More formally, it is any stereotyped electrophysiology, electrophysiological response to a stimulus. The study of the brain in this way provides a Invasiveness of surgical procedures, noninvasive means of evaluating brain functioning. ERPs are measured by means of electroencephalography (EEG). The magnetoencephalography (MEG) equivalent of ERP is the ERF, or event-related field. Evoked potentials and induced potentials are subtypes of ERPs. History With the discovery of the electroencephalogram (EEG) in 1924, Hans Berger revealed that one could measure the electrical activity of the human brain by placing electrodes on the scalp and amplifying the signal. Changes in voltage can then be plotted over a period of time. He observed that the voltages could be influenced by external events that stimulated the sens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeffrey Alan Gray
Jeffrey Alan Gray (26 May 1934 – 30 April 2004) was a British psychologist who is notable for his contributions to the theory of consciousness. Life and work He was born in the East End of London. His father was a tailor, but died when Jeffrey was only seven. His mother, who ran a haberdashery, brought him up alone. Following military service (1952–54), he took up a MacKinnon scholarship at Magdalen College, Oxford, with a place to study Law. In the event he negotiated a switch to Modern Languages, obtaining a first in French and Spanish. He stayed on to take a second BA, this time in Psychology and Philosophy, which he completed in 1959. In 1959–60 he trained as a clinical psychologist at the Institute of Psychiatry in London (now part of King's College London), after which he stayed on to study for a PhD in the department of psychology, headed by Hans Eysenck. His PhD was awarded in 1964 for a study of environmental, genetic and hormonal influences on emotional behavio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curiosity
Curiosity (from Latin '' cūriōsitās'', from ''cūriōsus'' "careful, diligent, curious", akin to ''cura'' "care") is a quality related to inquisitive thinking such as exploration, investigation, and learning, evident by observation in humans and other animals. Curiosity is heavily associated with all aspects of human development, in which derives the process of learning and desire to acquire knowledge and skill. The term ''curiosity'' can also be used to denote the behavior or emotion of being curious, in regard to the desire to gain knowledge or information. Curiosity as a behavior and emotion is attributed over millennia as the driving force behind not only human development, but developments in science, language, and industry. Causes Curiosity can be seen as an innate quality of many different species. It is common to human beings at all ages from infancy through adulthood, and is easy to observe in many other animal species; these include apes, cats, and rodents. Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fear
Fear is an intensely unpleasant emotion in response to perceiving or recognizing a danger or threat. Fear causes physiological changes that may produce behavioral reactions such as mounting an aggressive response or fleeing the threat. Fear in human beings may occur in response to a certain stimulus occurring in the present, or in anticipation or expectation of a future threat perceived as a risk to oneself. The fear response arises from the perception of danger leading to confrontation with or escape from/avoiding the threat (also known as the fight-or-flight response), which in extreme cases of fear (horror and terror) can be a freeze response or paralysis. In humans and other animals, fear is modulated by the process of cognition and learning. Thus, fear is judged as rational or appropriate and irrational or inappropriate. An irrational fear is called a phobia. Fear is closely related to the emotion anxiety, which occurs as the result of threats that are perceived to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Dissonance
In the field of psychology, cognitive dissonance is the perception of contradictory information, and the mental toll of it. Relevant items of information include a person's actions, feelings, ideas, beliefs, values, and things in the environment. Cognitive dissonance is typically experienced as psychological stress when persons participate in an action that goes against one or more of those things. According to this theory, when two actions or ideas are not psychologically consistent with each other, people do all in their power to change them until they become consistent. The discomfort is triggered by the person's belief clashing with new information perceived, wherein the individual tries to find a way to resolve the contradiction to reduce their discomfort.Festinger, L. (1957). ''A Theory of Cognitive Dissonance''. California: Stanford University Press. In '' When Prophecy Fails: A Social and Psychological Study of a Modern Group That Predicted the Destruction of the World'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
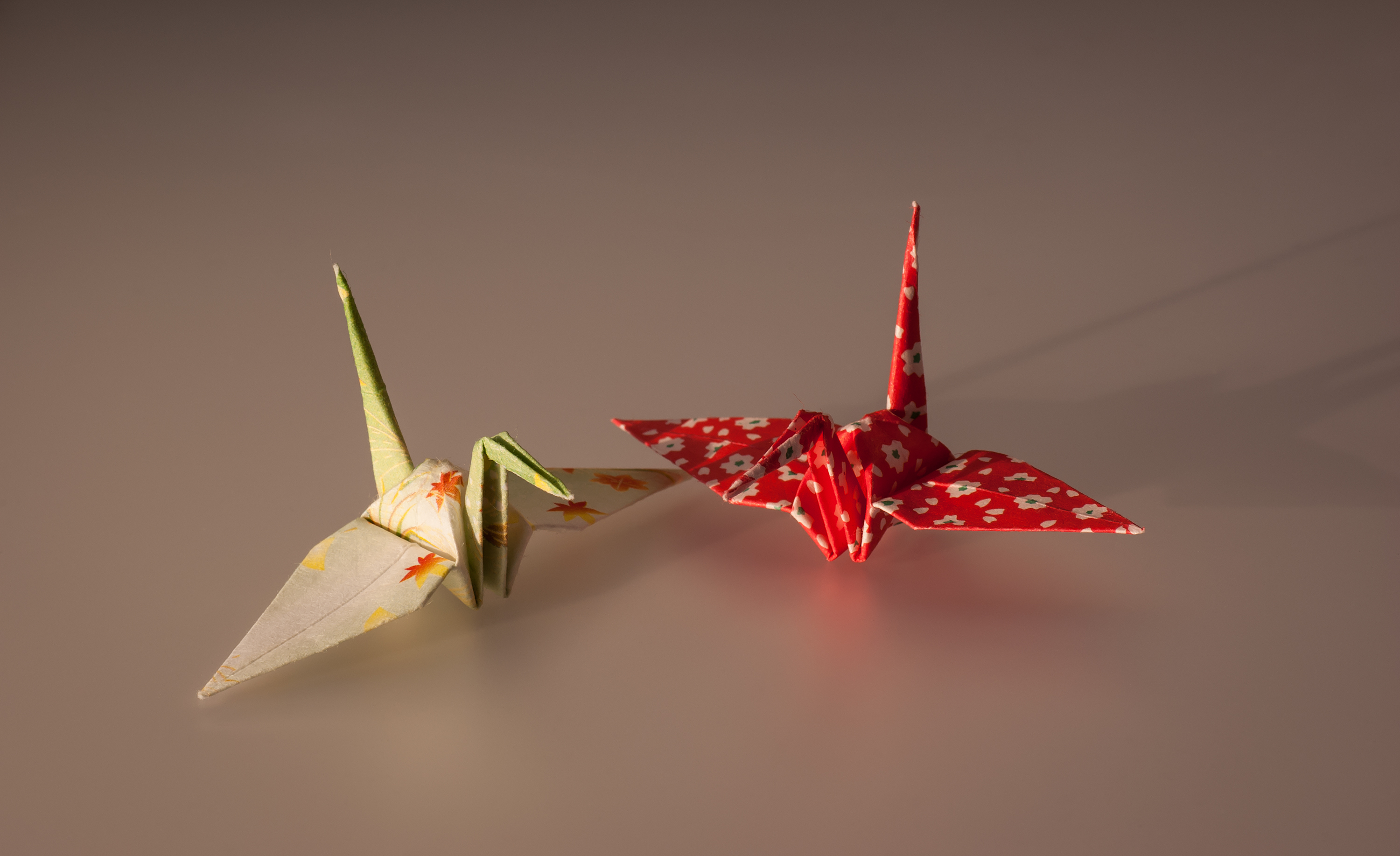
Origami
) is the Japanese paper art, art of paper folding. In modern usage, the word "origami" is often used as an inclusive term for all folding practices, regardless of their culture of origin. The goal is to transform a flat square sheet of paper into a finished sculpture through folding and sculpting techniques. Modern origami practitioners generally discourage the use of cuts, glue, or markings on the paper. Origami folders often use the Japanese word ' to refer to designs which use cuts. On the other hand, in the detailed Japanese classification, origami is divided into stylized ceremonial origami (儀礼折り紙, ''girei origami'') and recreational origami (遊戯折り紙, ''yūgi origami''), and only recreational origami is generally recognized as origami. In Japan, ceremonial origami is generally called "origata" (:ja:折形) to distinguish it from recreational origami. The term "origata" is one of the old terms for origami. The small number of basic Origami techniques, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_young_males_eyeballing.jpg)