|
Frontonasal Duct
The frontonasal duct is a communication between the frontal air sinuses and their corresponding nasal cavity. The duct is lined by mucous membrane. The duct empties into the nasal cavity middle nasal meatus through the infundibulum of the semilunar hiatus The semilunar hiatus or hiatus semilunaris, is a crescent-shaped groove in the lateral wall of the nasal cavity just inferior to the ethmoid bulla. It is the location of the openings of the maxillary sinuses. It is bounded inferiorly and anterio .... Bones of the head and neck {{Respiratory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
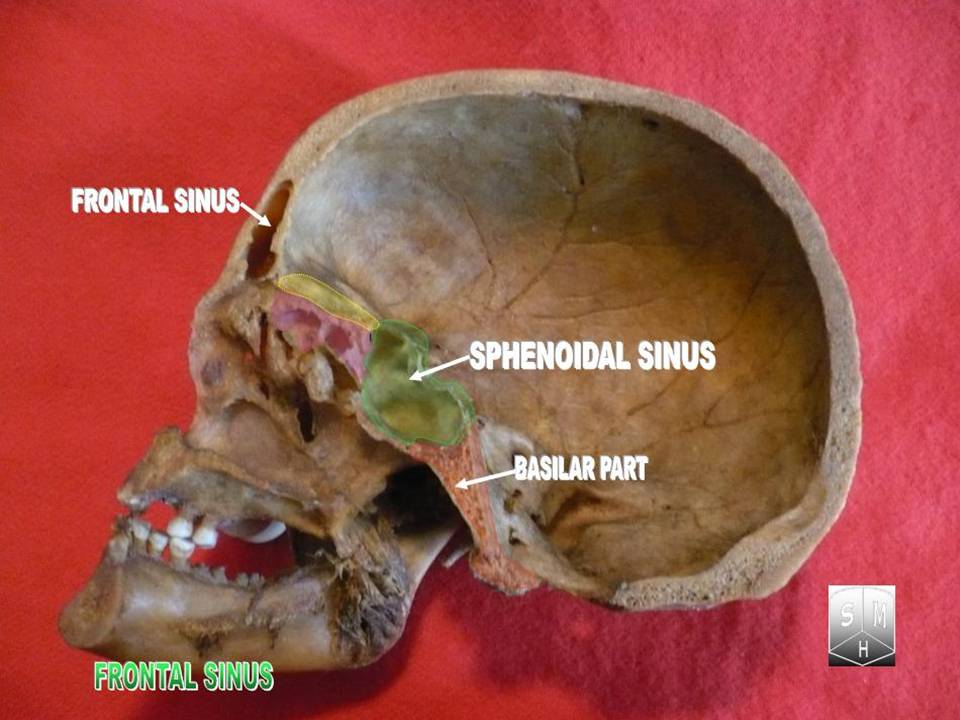
Frontal Air Sinus
The frontal sinuses are one of the four pairs of paranasal sinuses that are situated behind the brow ridges. Sinuses are mucosa-lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. Each opens into the anterior part of the corresponding middle nasal meatus of the nose through the frontonasal duct which traverses the anterior part of the labyrinth of the ethmoid. These structures then open into the semilunar hiatus in the middle meatus. Structure Each frontal sinus is situated between the external and internal plates of the frontal bone.Frontal sinuses are rarely symmetrical. Their average measurements are as follows: height 28 mm, breadth 24 mm, depth 20 mm, creating a space of 6-7 ml. Blood supply The mucous membrane of the frontal sinuses receives arterial supply via the supraorbital artery, and anterior ethmoidal artery. Innervation The mucous membrane in this sinus is innervated by the supraorbital nerve, which contains the postganglionic parasympat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
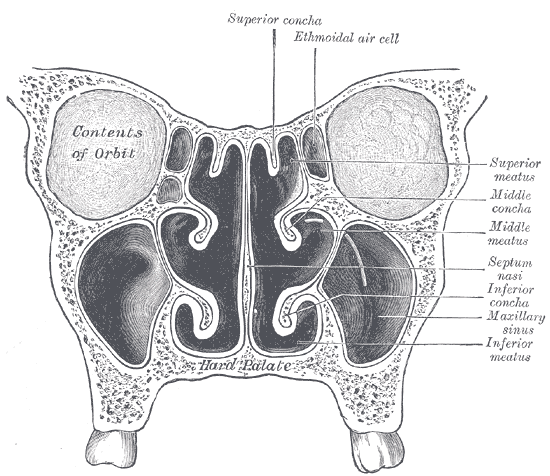
Middle Nasal Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are located beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semilunar Hiatus
The semilunar hiatus or hiatus semilunaris, is a crescent-shaped groove in the lateral wall of the nasal cavity just inferior to the ethmoid bulla. It is the location of the openings of the maxillary sinuses. It is bounded inferiorly and anteriorly by the sharp concave margin of the uncinate process of the ethmoid bone, superiorly by the ethmoid bulla, and posteriorly by the middle nasal concha. Sinus drainage Following the curve anteriorly leads into the infundibulum of the frontonasal duct, which drains the frontal sinus. The anterior ethmoidal cells of the ethmoidal sinus open into the front part of the infundibulum as well. In slightly over 50% of subjects, this is directly continuous with the frontonasal duct from the frontal air sinus. When the anterior end of the uncinate process fuses with the front part of the bulla, however, this continuity is interrupted and the frontonasal duct then drains directly into the anterior end of the middle meatus. The ostium for the maxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |