|
Friedrich Wilhelm Conrad Eduard Bornhardt
Friedrich Wilhelm Conrad Eduard Bornhardt (20 April 1864 Braunschweig - 2 December 1946 Goslar) was a German geologist, engineer and explorer, and was Director of the Berlin College of Mines (Bergakademie) from 1907 to 1916. He explored and set out the groundwork of the geology of German East Africa. His published work consisted of two parts – an account of his travels and his geological findings. In 1896 he set out from Lindi to Lake Malawi where he stayed for ten months undertaking eight exploratory trips of the region. Afterwards he returned to the coast to write up his geology journals. In 1897 he explored the protectorate of Dar es Salaam as far as the Ruvuma Region, the Zanzibar Archipelago and the Usambara Mountains, carrying out some thirteen journeys. In all he covered about and prepared maps of the geology and vegetation of the regions he traversed. Bornhardt documented the existence of coal reserves in present-day Tanzania in 1896 when he explored the Songwe Kiwira are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braunschweig
Braunschweig () or Brunswick ( , from Low German ''Brunswiek'' , Braunschweig dialect: ''Bronswiek'') is a city in Lower Saxony, Germany, north of the Harz Mountains at the farthest navigable point of the river Oker, which connects it to the North Sea via the rivers Aller and Weser. In 2016, it had a population of 250,704. A powerful and influential centre of commerce in medieval Germany, Brunswick was a member of the Hanseatic League from the 13th until the 17th century. It was the capital city of three successive states: the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (1269–1432, 1754–1807, and 1813–1814), the Duchy of Brunswick (1814–1918), and the Free State of Brunswick (1918–1946). Today, Brunswick is the second-largest city in Lower Saxony and a major centre of scientific research and development. History Foundation and early history The date and circumstances of the town's foundation are unknown. Tradition maintains that Brunswick was created through the merge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
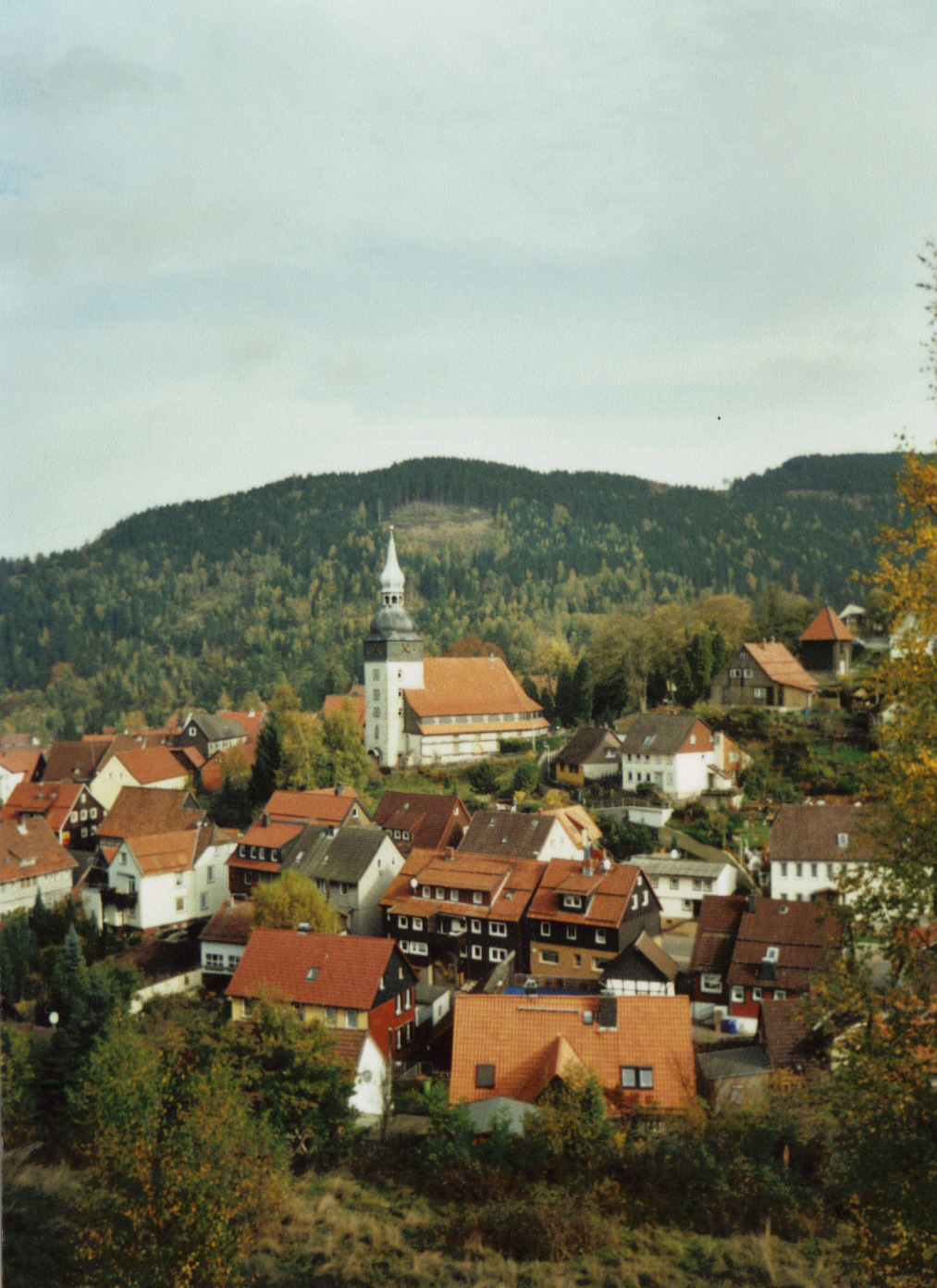
Lautenthal
The formerly free mining town ('' Bergstadt'') of Lautenthal in Germany is a state-recognised, climatic spa with around 1,570 inhabitants and has been part of the borough of Langelsheim since 1972. Geography Lautenthal lies in the Innerste valley between Clausthal-Zellerfeld and Langelsheim in the northwestern Upper Harz. The town is located at a height of about in a valley bowl, the surrounding mountains being up to . The two rivers of the Innerste and the Laute flow through the town. Towards Langelsheim the Innerste is impounded by the Innerste Dam. History Mining of copper, lead and silver in the area around Lautenthal started about 1225. In the middle of the 14th century, however, the Harz was depopulated because of plague and mining came to an end. Mining in the Harz was started again in 1524. Lautenthal was founded in 1538 as a mining settlement on the river Laute, a small tributary of the Innerste, and had already been given the status of a town by 1580. Sixte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From The Duchy Of Brunswick
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientists From Braunschweig
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales (circa 624-545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. In modern times, many scientists have advanced degrees in an area of science and pursue careers in various sectors of the economy such as academia, industry, government, and nonprofit environments.'''' History The roles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1946 Deaths
Events January * January 6 - The first general election ever in Vietnam is held. * January 7 – The Allies recognize the Austrian republic with its 1937 borders, and divide the country into four occupation zones. * January 10 ** The first meeting of the United Nations is held, at Methodist Central Hall Westminster in London. ** ''Project Diana'' bounces radar waves off the Moon, measuring the exact distance between the Earth and the Moon, and proves that communication is possible between Earth and outer space, effectively opening the Space Age. * January 11 - Enver Hoxha declares the People's Republic of Albania, with himself as prime minister. * January 16 – Charles de Gaulle resigns as head of the French provisional government. * January 17 - The United Nations Security Council holds its first session, at Church House, Westminster in London. * January 19 ** The Bell XS-1 is test flown for the first time (unpowered), with Bell's chief test pilot Jack Woolams at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1864 Births
Events January–March * January 13 – American songwriter Stephen Foster ("Oh! Susanna", "Old Folks at Home") dies aged 37 in New York City, leaving a scrap of paper reading "Dear friends and gentle hearts". His parlor song " Beautiful Dreamer" is published in March. * January 16 – Denmark rejects an Austrian-Prussian ultimatum to repeal the Danish Constitution, which says that Schleswig-Holstein is part of Denmark. * January 21 – New Zealand Wars: The Tauranga campaign begins. * February – John Wisden publishes '' The Cricketer's Almanack for the year 1864'' in England; it will go on to become the major annual cricket reference publication. * February 1 – Danish-Prussian War (Second Schleswig War): 57,000 Austrian and Prussian troops cross the Eider River into Denmark. * February 15 – Heineken brewery founded in Netherlands. * February 17 – American Civil War: The tiny Confederate hand-propelled submarine ''H. L. Hunl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Bornhardt00 , the Dutch national anthem
{{Disambiguation ...
Wilhelm may refer to: People and fictional characters * William Charles John Pitcher, costume designer known professionally as "Wilhelm" * Wilhelm (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or surname Other uses * Mount Wilhelm, the highest mountain in Papua New Guinea * Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica * Wilhelm (crater), a lunar crater See also * Wilhelm scream, a stock sound effect * SS ''Kaiser Wilhelm II'', or USS ''Agamemnon'', a German steam ship * Wilhelmus "Wilhelmus van Nassouwe", usually known just as "Wilhelmus" ( nl, Het Wilhelmus, italic=no; ; English translation: "The William"), is the national anthem of both the Netherlands and the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It dates back to at least 1572 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bornhardt
A bornhardt () is a dome-shaped, steep-sided, bald rock outcropping at least in height and several hundred metres in width. They are named after Wilhelm Bornhardt (1864–1946), a German geologist and explorer of German East Africa, who first described the feature. While ''bornhardt'' was originally used to sometimes denote a type of inselberg (literally island mountain—an isolated dome in an otherwise flat landscape), the term ''bornhardt'' is used in modern literature to refer to domed hills and mountains regardless of isolation; thus, not all bornhardts are inselbergs and not all inselbergs are bornhardts. Bornhardts are commonly composed of igneous rocks, often granites, but examples of gneiss, quartzite and arkose bornhardts exists. The Sugarloaf Mountain of Rio de Janeiro is a typical example of this landform and is the origin of the common bornhardt nickname "sugar loaf". Bornhardts are most easily seen in arid and semi-arid regions, but occur over a wide range of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inselberg
An inselberg or monadnock () is an isolated rock hill, knob, ridge, or small mountain that rises abruptly from a gently sloping or virtually level surrounding plain. In Southern Africa a similar formation of granite is known as a koppie, an Afrikaans word ("little head") from the Dutch diminutive word ''kopje''. If the inselberg is dome-shaped and formed from granite or gneiss, it can also be called a bornhardt, though not all bornhardts are inselbergs. An inselberg results when a body of rock resistant to erosion, such as granite, occurring within a body of softer rocks, is exposed by differential erosion and lowering of the surrounding landscape. Etymology Inselberg The word ''inselberg'' is a loan word from German, and means "island mountain". The term was coined in 1900 by geologist Wilhelm Bornhardt (1864–1946) to describe the abundance of such features found in eastern Africa. At that time, the term applied only to arid landscape features. However, it has sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' federated as the Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian are still spoken, albeit in declining numbers. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-enclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Lüneburg, Osnabrück, Oldenburg, Hildesheim, Salzgitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harz
The Harz () is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German word ''Hardt'' or ''Hart'' (hill forest). The name ''Hercynia'' derives from a Celtic name and could refer to other mountain forests, but has also been applied to the geology of the Harz. The Brocken is the highest summit in the Harz with an elevation of above sea level. The Wurmberg () is the highest peak located entirely within the state of Lower Saxony. Geography Location and extent The Harz has a length of , stretching from the town of Seesen in the northwest to Eisleben in the east, and a width of . It occupies an area of , and is divided into the Upper Harz (''Oberharz'') in the northwest, which is up to 800 m high, apart from the 1,100 m high Brocken massif, and the Lower Harz (''Unterharz'') in the east which is up to aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)


.jpg)

