|
French Ship Soleil-Royal (1749)
The ''Soleil-Royal'' was a ship in the French Navy, the third ship of that name. She was the first 80-gun two-decker to use the 24-pounder long gun on her second battery, giving her considerable firepower for the time and allowing her to challenge three-deckers. Her name ''Soleil-Royal'', honouring the French crown and usually reserved for the largest units of the Navy, testifies to the change of focus from large three-deckers to strong two-deckers. She was Brienne's flagship at the battle of Quiberon Bay, where she ran aground and was burnt to prevent her capture. Her cannons were recovered by the Royal Navy and transported to Plymouth Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth ... for reuse in British vessels. Citations References * External links * Ships of the lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
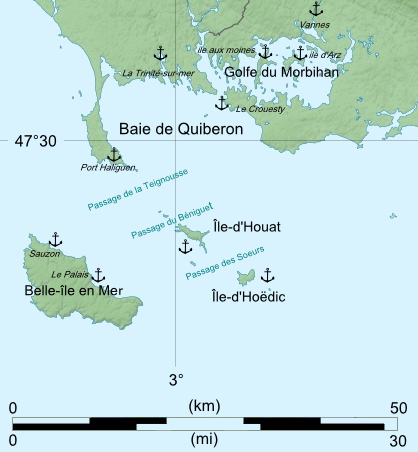
Battle Of Quiberon Bay
The Battle of Quiberon Bay (known as ''Bataille des Cardinaux'' in French) was a decisive naval engagement during the Seven Years' War. It was fought on 20 November 1759 between the Royal Navy and the French Navy in Quiberon Bay, off the coast of France near St. Nazaire. The battle was the culmination of British efforts to eliminate French naval superiority, which could have given the French the ability to carry out their planned invasion of Great Britain. A British fleet of 24 ships of the line under Sir Edward Hawke tracked down and engaged a French fleet of 21 ships of the line under Marshal de Conflans. After hard fighting, the British fleet sank or ran aground six French ships, captured one and scattered the rest, giving the Royal Navy one of its greatest victories, and ending the threat of French invasion for good. The battle signalled the rise of the Royal Navy in becoming the world's foremost naval power, and, for the British, was part of the Annus Mirabilis of 1759 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The Kingdom Of France (1814-1830)
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as "vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
36-pounder Long Gun
The 36-pounder long gun was the largest piece of artillery mounted on French warships of the Age of Sail. They were also used for Coastal defense and fortification. They largely exceeded the heaviest guns fielded by the Army, which were 24-pounder long guns. The nominal weight of shot was 36 French ''livres'', . Usage Installed on the lower deck of the larger warships, the 36-pounder long gun was the largest caliber used in the Navy of the Age of the Sail. Attempts to use 48-pounders were made, for instance on ''Royal Louis'', but these proved impractical to use on ships, partly because their weight allowed for only a few pieces, and because the heavy balls were unwieldy to load by hand. However, some coastal batteries fielded 48-pounders and even 64-pounders. In the Royal Navy, a similar role was fulfilled by 32-pounder long guns. History French warships began to carry 36-pounders under Louis XIV, with the reform of the Navy undertaken by Richelieu. At this time, only fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
24-pounder Long Gun
The 24-pounder long gun was a heavy calibre piece of artillery mounted on warships of the Age of Sail. 24-pounders were in service in the navies of France, Spain, Great Britain, the Netherlands, Sweden, and the United States. They were comparable to the Canon de 24 Gribeauval used by the French Army as its largest piece of siege artillery. 24-pounders were used as main guns on the heaviest frigates of the early 19th century and on fourth-rate ships of the line, on the second deck of first-rate ships of the line, and on the second deck of a few large third-rates. Usage The 24-pounder calibre was consistent with both the French and the British calibre systems, and was a widespread gun amongst nations between the 17th and the 19th century. From the late 18th century, the French Navy used the 24-pounder in two capacities: as main gun on frigates and 64-guns, or as secondary artillery on three-deckers and even enlarged versions two-deckers. Under Louis XV, a typical heavy frigate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-pounder Long Gun
The 8-pounder long gun was a light calibre piece of artillery mounted on French warships of the Age of sail. It fired a projectile of eight ''livres'' in weight, equivalent to 8.633 English pounds, or 8 lb 10 oz (the French ''livre'' was 7.916% heavier than the English pound weight). They were used as chase guns or main guns on light ships of the early 19th century, and on the quarterdeck and forecastle of ships of the line. They were similar in design to the Canon de 8 Gribeauval. Usage The 8-pounder was the heaviest of the light guns. Its light weight allowed it to be mounted on the upper gun posts of ships of the line, where the timber of the deck was too light to support larger guns; furthermore, it could be mounted relatively high without jeopardy to the stability of the ship, and could be installed at will at different positions. This made it useful as a chase gun A chase gun (or chaser), usually distinguished as bow chaser and stern chaser, was a cannon mounted in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in the world, ranking seventh in combined fleet tonnage and fifth in number of naval vessels. The French Navy is one of eight naval forces currently operating fixed-wing aircraft carriers,Along with the U.S., U.K., China, Russia, Italy, India and Spain with its flagship being the only nuclear-powered aircraft carrier outside the United States Navy, and one of two non-American vessels to use catapults to launch aircraft. Founded in the 17th century, the French Navy is one of the oldest navies still in continual service, with precursors dating back to the Middle Ages. It has taken part in key events in French history, including the Napoleonic Wars and both world wars, and played a critical role in establishing and securing the French colonial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Soleil-Royal
Three French ships of the line of the Ancien Régime have borne the name ''Soleil Royal'' ("''Royal Sun''"), honouring the personal emblem of Louis XIV , house = Bourbon , father = Louis XIII , mother = Anne of Austria , birth_date = , birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France , death_date = , death_place = Palace of Vers ...: * , present at the Battle of Barfleur * * Furthermore, was briefly named ''Soleil Royal'' before taking her final name. Sources Les « Soleil Royal » de la marine de l’Ancien Régime Nicolas Mioque {{DEFAULTSORT:Soleil Royal, French Ship French Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubert De Brienne, Comte De Conflans
Hubert de Brienne, Comte de Conflans (1690, in Paris – 27 January 1777, in Paris) was a French naval commander. Early life The son of Henri Jacob marquis de Conflans and Marie du Bouchet, at 15 he was made a knight of the Order of Saint Lazarus and the following year entered the Gardes de la Marine school at Brest. He then served in the War of the Spanish Succession under Duquesne-Guitton (from 1708 to 1709) and Duguay-Trouin (1710), in which he received his baptism of fire, taking part in the capture of two merchant ships. In 1712, he was made ensign and participated in several anti-pirate operations in the Caribbean and on the Moroccan coast. In 1721, he was sent on a mission to Constantinople, and then in 1723 cruised along the coast of Saint-Domingue and took part in the repression of the troubles there. First commands and governor-general of Saint-Dominique He was made lieutenant in 1727 and carried out two campaigns in the Mediterranean. Then, in 1731, he s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of The Line Of The French Navy
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1749 Ships
Events January–March * January 3 ** Benning Wentworth issues the first of the New Hampshire Grants, leading to the establishment of Vermont. ** The first issue of ''Berlingske'', Denmark's oldest continually operating newspaper, is published. * January 21 – The Teatro Filarmonico, the main opera theater in Verona, Italy, is destroyed by fire. It is rebuilt in 1754. * February – The second part of John Cleland's erotic novel ''Fanny Hill'' (''Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure'') is published in London. The author is released from debtors' prison in March. * February 28 – Henry Fielding's comic novel ''The History of Tom Jones, a Foundling'' is published in London. Also this year, Fielding becomes magistrate at Bow Street, and first enlists the help of the Bow Street Runners, an early police force (eight men at first). * March 6 – A "corpse riot" breaks out in Glasgow after a body disappears from a churchyard in the Gorbals district. Suspicion fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |