|
Freedom Of Religion In Bulgaria
The constitution provides for freedom of religion, and other laws and policies contributed to the generally free practice of religion. However, the constitution designates Eastern Orthodox Christianity as the "traditional" religion, exempting it from having to register in court as required for all other religious groups. The government generally respected the religious freedom of registered religious groups. There were some concerns that the government did not proactively intervene to prevent societal abuses. There also were continuing reports of intolerance from police and local authorities during the reporting period. There were continued reports of societal abuses or discrimination based on religious affiliation, belief, or practice. Discrimination, harassment, and general public intolerance of some religious groups remained an intermittent problem. There was an increasing number of anti-Semitic incidents and vandalism against mosques. Religious demography The country ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Bulgaria
The Constitution of the Republic of Bulgaria ( bg, Конституция на Република България, ''Konstitutsia na Republika Bǎlgariya'') is the supreme and basic law of the Republic of Bulgaria. The current constitution was adopted on 12 July 1991 by the 7th Grand National Assembly of Bulgaria, and defines the country as a unitary parliamentary republic. It has been amended five times (in 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, and 2015). Chronologically, it is the fourth constitution of Bulgaria, the first being the Tarnovo Constitution of 1879. It was immediately preceded by the two Socialist-era constitutions–the Dimitrov Constitution (named after Georgi Dimitrov), in force between 1947 and 1971, and the Zhivkov Constitution (named after Todor Zhivkov), in force between 1971 and 1991. Content Political System Distribution of powers The constitution sets about a parliamentary form of government, in which executive power is rested upon the Government of Bulgaria, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and has many mineral springs, such as the Sofia Central Mineral Baths. It has a humid continental climate. Being in the centre of the Balkans, it is midway between the Black Sea and the Adriatic Sea, and closest to the Aegean Sea. Known as Serdica in Antiquity and Sredets in the Middle Ages, Sofia has been an area of human habitation since at least 7000 BC. The recorded history of the city begins with the attestation of the conquest of Serdica by the Roman Republic in 29 BC from the Celtic tribe Serdi. During the decline of the Roman Empire, the city was raided by Huns, Visigoths, Avars and Slavs. In 809, Serdica was incorporated into the Bulgarian Empire by Khan Krum and became known as Sredets. In 1018, the Byzantines ended Bulgarian rule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work A creative work is a manifestation of creative effort including fine artwork (sculpture, paintings, drawing, sketching, performance art), dance, writing (literature), filmmaking, and composition. Legal definitions Creative works require a cre ... to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission. As examples, the works of William Shakespeare, Ludwig van Beethoven, Leonardo da Vinci and Georges Méliès are in the public domain either by virtue of their having been created before copyright existed, or by their copyright term having expired. Some works are not covered by a country's copyright laws, and are therefore in the public domain; for example, in the United States, items excluded from copyright include the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights In Bulgaria
Bulgaria joined the European Union in 2007, its compliance with human rights norms, however, is far from perfect. Although the media have a record of unbiased reporting,Text used in this cited section originally came fromBulgaria (June 2005) profilefrom the Library of Congress Country Studies project. Bulgaria’s lack of specific legislation protecting the media from state interference is a theoretical weakness. Conditions in Bulgaria’s twelve aging and overcrowded prisons generally are poor. A probate reform in mid-2005 was expected to relieve prison overcrowding. The police have been accused of abusing prisoners and using illegal investigative methods, and institutional incentives discourage full reporting and investigation of many crimes. The constitution guarantees freedom of religion, but local governments have attempted to enforce special registration requirements on some groups not designated as historically entitled to full protection. Besides the Bulgarian Orthodox Chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Bulgaria
Religion in Bulgaria has been dominated by Christianity since its adoption as the state religion in 864. The dominant form of the religion is Eastern Orthodox Christianity within the fold of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. During the Ottoman rule of the Balkans, Islam spread to the territories of Bulgaria, and it remains a significant minority today. The Catholic Church has roots in the country since the Middle Ages, and Protestantism arrived in the 19th century; both of them remain very small minorities. Today, a significant part of the Bulgarians are not religious, or believers who do not identify with any specific religion, and Bulgaria has been the cradle of some new religions, notably the Neo-Theosophical movement of Dunovism. Since the early 21st century, there has been a decline of both the historic religions of Bulgaria—Eastern Orthodox Christianity and Islam—, which have shrunken, respectively, the former from 7.3m or 87% of the population in the 1992 census to 4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Alternative Synod
Bulgarian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria * Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group * Bulgarian language, a Slavic language * Bulgarian alphabet * A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria * Bulgarian culture * Bulgarian cuisine, a representative of the cuisine of Southeastern Europe See also * * List of Bulgarians, include * Bulgarian name, names of Bulgarians * Bulgarian umbrella, an umbrella with a hidden pneumatic mechanism * Bulgar (other) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (other) The term Bulgarian-Serbian War or Serbian-Bulgarian War may refer to: * Bulgarian-Serbian War (839-842) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (853) * Bulgarian-Serbian wars (917-924) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (1330) * Bulgarian-Serbian War (1885) * Bulgarian-Serbi ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Academy Of Sciences
The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (abbreviated BAS; bg, Българска академия на науките, ''Balgarska akademiya na naukite'', abbreviated ''БАН'') is the National Academy of Bulgaria, established in 1869. The Academy, with headquarters in Sofia, is autonomous and consists of a Society of Academicians, Correspondent Members and Foreign Members. It publishes and circulates different scientific works, encyclopaedias, dictionaries and journals, and runs its own publishing house. The activities are distributed in three main branches: ''Natural, mathematical and engineering sciences''; ''Biological, medical and agrarian sciences'' and ''Social sciences, humanities and art''. They are structured in 42 independent scientific institutes, and a dozen of laboratories and other sections. Julian Revalski has been the president of the BAS since 2016. As of 2021, its budget was 117,8 million leva (€60,2 million). History As Bulgaria was part of the Ottoman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rousse
Ruse (also transliterated as Rousse, Russe; bg, Русе ) is the fifth largest city in Bulgaria. Ruse is in the northeastern part of the country, on the right bank of the Danube, opposite the Romanian city of Giurgiu, approximately south of Bucharest, Romania's capital, from the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast and from the capital Sofia. Thanks to its location and its railway and road bridge over the Danube (Danube Bridge), it is the most significant Bulgarian river port, serving an important part of the international trade of the country. Ruse is known for its 19th- and 20th-century Neo-Baroque and Neo-Rococo architecture, which attracts many tourists. It is often called the Little Vienna. The Ruse-Giurgiu Friendship Bridge, until 14 June 2013 the only one in the shared Bulgarian-Romanian section of the Danube, crosses the river here. Ruse is the birthplace of the Nobel laureate in Literature Elias Canetti and the writer Michael Arlen. Ruse is on the right bank of the rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomaks
Pomaks ( bg, Помаци, Pomatsi; el, Πομάκοι, Pomáki; tr, Pomaklar) are Bulgarian-speaking Muslims inhabiting northwestern Turkey, Bulgaria and northeastern Greece. The c. 220,000 strong ethno-confessional minority in Bulgaria is recognized officially as Bulgarian Muslims by the government. The term has also been used as a wider designation, including also the Slavic Muslim populations of North Macedonia and Albania. Most Pomaks today live in Turkey where they have settled as muhacirs as a result of escaping previous ethnic cleansing in Bulgaria. Bulgaria recognizes their language as a Bulgarian dialect whereas in Greece and Turkey they self-declare their language as the Pomak language. The community in Greece is commonly fluent in Greek, and in Turkey, Turkish, while the communities in these two countries, especially in Turkey, are increasingly adopting Turkish as their first language as a result of education and family links with the Turkish people. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Christianity
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") Eastern Orthodox Church is organised into autocephalous churches independent from each other. In the 21st century, the number of mainstream autocephalous churches is seventeen; there also exist autocephalous churches unrecognized by those mainstream ones. Autocephalous churches choose their own primate. Autocephalous churches can have jurisdiction (authority) over other churches, some of which have the status of "autonomous" which means they have more autonomy than simple eparchies. Many of these jurisdictions correspond to the territories of one or more modern states; the Patriarchate of Moscow, for example, corresponds to Russia and some of the other post-Soviet states. They can also include metropolises, bishoprics, parishes, monas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romani People
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with significant concentrations in the Americas. In the English language, the Romani people are widely known by the exonym Gypsies (or Gipsies), which is considered pejorative by many Romani people due to its connotations of illegality and irregularity as well as its historical use as a racial slur. For versions (some of which are cognates) of the word in many other languages (e.g., , , it, zingaro, , and ) this perception is either very small or non-existent. At the first World Romani Congress in 1971, its attendees unanimously voted to reject the use of all exonyms for the Romani people, including ''Gypsy'', due to their aforementioned negative and stereotypical connotations. Linguistic and genetic evidence suggests that the Roma originated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
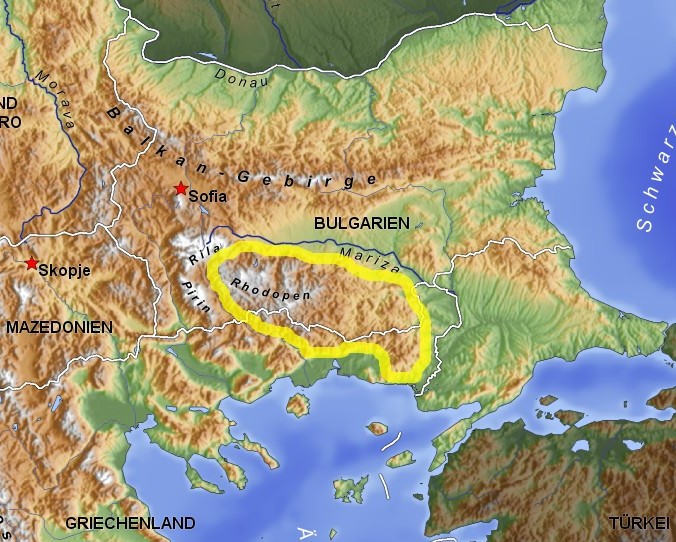
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |