|
Free Dacian
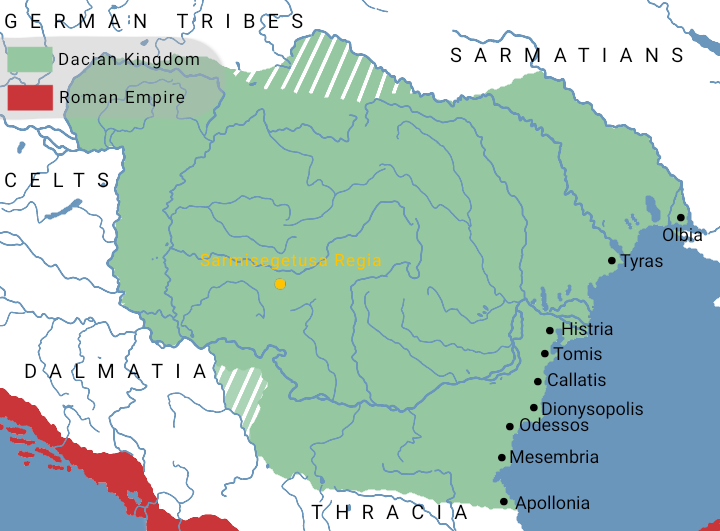
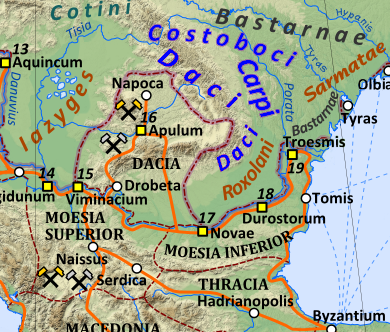
The Free Dacians () is the name given by some modern historians to those Dacians who remained outside, or emigrated from, the Roman Empire after the emperor Trajan's Dacian Wars (AD 101-6). Dio Cassius named them ''Dakoi prosoroi'' (Latin language, Latin: ''Daci limitanei'') meaning "neighbouring Dacians". A population of Dacians existed on the fringes of the Balkan Roman provinces, especially in the eastern Carpathian Mountains, at least until about AD 340. They were responsible for a series of incursions into Roman Dacia in the period AD 120-272, and into the Roman Empire south of the Danube after the province of Dacia was abandoned by the Romans around AD 275. Traditional paradigm According to many scholars, amongst the Free Dacians were refugees from the Roman conquest, who had left the Roman-occupied zone, and some Dacian-speaking tribes resident outside that zone, notably the Costoboci and the Carpi (people), Carpi in SW Ukraine, Moldavia and Bessarabia. The refugees may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decebalus
Decebalus (; ), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invasion in the reign of Domitian, securing a period of independence during which Decebalus consolidated his rule. When Trajan came to power, his armies invaded Dacia to weaken its threat to the Roman border territories of Moesia. Decebalus was defeated in 102 AD, and his own sister was abducted within this timeframe and forcibly wed into Roman nobility, causing some historians to infer that she was the ancestress of the usurper, Regalianus, who claimed to be a kinsman of Decebalus. He remained in power as a client king, but continued to assert his independence, leading to a final and overwhelming Roman invasion north of the Danube in 105 AD. Trajan reduced the Dacian capital Sarmizegetusa Regia, Sarmizegetusa to ruins in 106 AD, abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province Of Dacia (106 - 271 AD)
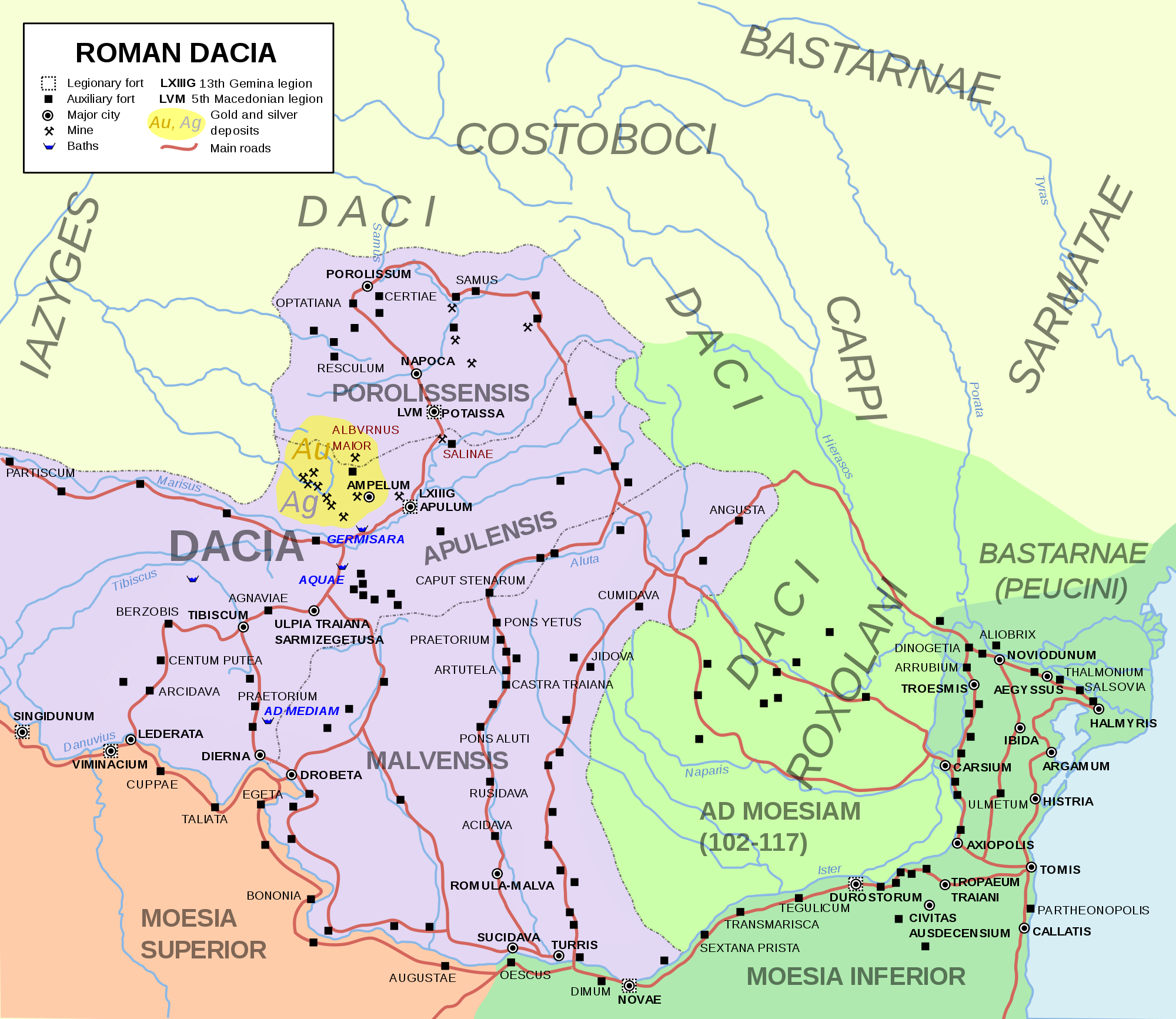
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Superi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
056 Conrad Cichorius, Die Reliefs Der Traianssäule, Tafel LVI
56 may refer to: * 56 (number) * One of the years 56 BC, AD 56, 1956, 2056 * 56.com, a Chinese online video platform * Fiftysix, Arkansas, an unincorporated community in the United States * Fifty-Six, Arkansas, a city in the United States * "Fifty Six", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Arch Stanton'', 2014 * 56 Melete, a main-belt asteroid * Isaiah 56, the fifty-sixth chapter of the Old Testament of the Christian Bible * Cityrider 56, a bus route in Tyne and Wear, UK {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muntenia
Muntenia (, also known in English as Greater Wallachia) is a historical region of Romania, part of Wallachia (also, sometimes considered Wallachia proper, as ''Muntenia'', ''Țara Românească'', and the rarely used ''Valahia'' are synonyms in Romanian). It is situated between the Danube (south and east), the Carpathian Mountains (the Transylvanian Alps branch) and Moldavia (both north), and the Olt River to the west. The latter river is the border between Muntenia and Oltenia (or ''Lesser Wallachia''). Part of the traditional border between Wallachia/Muntenia and Moldavia was formed by the rivers Milcov and Siret. Geography Muntenia includes București - Ilfov, Sud - Muntenia, and part of the Sud-Est development regions. It consists of nine counties entirely: * Brăila * Buzău * Călărași * Argeș * Dâmbovița * Giurgiu * Ialomița * Ilfov * Prahova And parts of four others: * Teleorman (the entire county with the exception of Islaz) * Vrancea (southern p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4th century CE. The earliest known reference to the Sarmatians occurs in the Avesta, where they appear as ''Sairima-'', which in later Iranian sources becomes ''*Sarm'' and Salm (Shahnameh), ''Salm''. Originating in the central parts of the Eurasian Steppe, the Sarmatians formed part of the wider Scythian cultures. They started migrating westward around the fourth and third centuries BCE, coming to dominate the closely related Scythians by 200 BCE. At their greatest reported extent, around 100 BCE, these tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black Sea, Black and Caspian Sea, Caspian seas and the Caucasus to the south. In the first century CE, the Sarmatians beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bastarnae
The Bastarnae, Bastarni or Basternae, also known as the Peuci or Peucini, were an ancient people who are known from Greek and Roman records to have inhabited areas north and east of the Carpathian Mountains between about 300 BC and about 300 AD, stretching in an ark from the sources of the Vistula in present-day Poland and Slovakia, to the Lower Danube, and including all or most of present-day Moldava. The Peucini were sometimes described as a subtribe, who settled the Peuke Island in the Danube Delta, but apparently due to their importance their name was sometimes used for the Bastarnae as a whole. Near the sources of the Vistula another part of the Bastarnae were the Sidones, while the Atmoni, another tribe of the Bastarnae are only mentioned in one listing by Strabo. The earliest Graeco-Roman historians to refer to the Bastarnae imply that they were culturally La Tène culture, Celtic. Also consistent with connections to the cultures to their west, later Roman-era sources stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurisci
The Taurisci were a federation of Celtic tribes who dwelt in today's Carinthia and northern Slovenia (Carniola) before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC). According to Pliny the Elder, they are the same as the people known as the Norici. Etymology The etymology of the name is disputed. ''Taurisci'' may stem from a root meaning 'mountain' or 'high rock', although it has been demonstrated that it is not related to the neighbouring '' Tauern'' mountain. Another proposed etymology is the Celtic root ''*'' 'bull' (see Gaulish ''taruos''). History Affiliated with the Celto-Ligurian Taurini, the Taurisci settled on the upper Sava river after their defeat at the Battle of Telamon in 225 BC. Following in the wake of the Boii, they migrated to northern Italia and the Adriatic coast. The Greek chronicler Polybius (ca. 203–120 BC) mentioned Tauriscian gold mining in the area of Aquileia. Along with the troops of the Roman Republic, they were defeated by invading Germanic Cimbr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anartes
The Anartes (or Anarti, Anartii or Anartoi)Jan Czarnecki (1975) 120 were Celtic tribes, or, in the case of those sub-groups of Anartes which penetrated the ancient region of Dacia (roughly modern Romania), Celts culturally assimilated by the Dacians.Oltean Ioana A (2007) 47 Ptolemy's ''Geographia'' locates the ''Anartoi'' in the north of Dacia.Jan Czarnecki (1975) 119 Some groups of Anartes occupied parts of modern Slovakia and southeastern Poland. The Dacian town of '' Docidava'' was situated in the territory of the Anartes, according to Pârvan. The ''Anartophracti'' (or ''Anartofraktoi'') are mentioned by Ptolemy. This tribe's name appears to be compound Latin-Greek name and may be related to the ''Anartoi'' resident in Dacia, Czarnecki argues.Jan Czarnecki (1975) 119 The ''Anartofraktoi'' were a northern Dacian tribe, according to Braune or mixed Dacian-Celtic, according to Pârvan. In ancient sources, the earliest mention of the Anartes is in the Elogium of Tusculum (10 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bukovina
Bukovina or ; ; ; ; , ; see also other languages. is a historical region at the crossroads of Central and Eastern Europe. It is located on the northern slopes of the central Eastern Carpathians and the adjoining plains, today divided between Romania and Ukraine. Inhabited by many cultures and peoples, settled by both Ukrainians ( Ruthenians) and Romanians (Moldavians), it became part of the Kievan Rus' and Pechenegs' territory early on during the 10th century and an integral part of the Principality of Moldavia in the 14th century where the capital of Moldavia, Suceava, was founded, eventually expanding its territory all the way to the Black Sea. Consequently, the culture of the Kievan Rus' spread in the region during the early Middle Ages. During the time of the Golden Horde, namely in the 14th century (or in the High Middle Ages), Bukovina became part of Moldavia under Hungarian suzerainty (i.e. under the medieval Kingdom of Hungary). According to the Moldo-Russian Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olt River
The Olt ( Romanian and Hungarian; ; or ', , ''Alytos'') is a river in Romania. It is long, and its basin area is . It is the longest river flowing exclusively through Romania. Its average discharge at the mouth is . It originates in the Hășmaș Mountains of the eastern Carpathian Mountains, near Bălan, rising close to the headwaters of the river Mureș. The Olt flows through the Romanian counties of Harghita, Covasna, Brașov, Sibiu, Vâlcea, and Olt. The river was known as ''Alutus'' or ''Aluta'' in Roman antiquity. Olt County and the historical province of Oltenia are named after the river. Sfântu Gheorghe, Râmnicu Vâlcea and Slatina are the main cities on the river Olt. The Olt flows into the Danube river near Turnu Măgurele. Settlements The main cities along the river Olt are Miercurea Ciuc, Sfântu Gheorghe, Făgăraș, Râmnicu Vâlcea and Slatina. The Olt passes through the following communes, from source to mouth: Bălan, Sândominic, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes Transalutanus
Limes Transalutanus is the modern name given to a fortified frontier system of the Roman Empire, built on the western edge of Teleorman County, Teleorman's forests as part of the Dacian Limes in the Roman province of Roman Dacia, Dacia, modern-day Romania. The Limes Transalutanus, of 235 km length, was needed to shorten the line of communication to the strategic fort at Angustia (castra), Angustia by almost 30 per cent compared to the earlier route via the Limes Alutanus. In first half of the 3rd century AD Septimius Severus advanced the province's eastern frontier by some east of the existing Limes Alutanus although the road and many of the forts on the Limes date from the end of Trajan's Dacian Wars (c.106 AD).C. C. Petolescu, Auxilia dacica. Contribuție la istoria militară a Daciei Roma- ne (Bucharest 2002) p55 Between 244–247, after the Carpi (people), Carpian and Getae (or Goths) attacks, Philip the Arab abandoned the limes for some time. The Romans returned to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timiș River
The Timiș or Tamiš (, , , ) is a river that flows through the Banat region of Romania and Serbia and joins the Danube near Pančevo, in northern Serbia. Due to its position in the region, it has been labeled as the "spine of the Banat". Name In antiquity, the river was known as ''Tibiscus'' (in Latin) and ''Tibisis'' (Θίβισις in ancient Greek), and as ''Timisis'' in De Administrando Imperio; in addition, Edward Gibbon referred to it as the ''Teyss''. ''The Romans, who traversed the plains of Hungary, suppose that they passed several navigable rivers, either in canoes or portable boats; but there is reason to suspect that the winding stream of the Teyss, or Tibiscus, might present itself in different places under different names.'' Geography The drainage area covers , of which in Romania. With the Danube, the Timis belongs to the Black Sea drainage basin. The river flows through Romania for , and through Serbia. Its average discharge at the mouth is . The sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |