|
Frederik V Schenck Van Toutenburg
Frederik Schenck van Toutenburg (ca. 1503 – 25 August 1580) was the first Archbishop of Utrecht (1559–1580). Prior to Schenck's ministry as archbishop, Utrecht was a bishopric with a succession of sixty bishops. The last bishop of Utrecht, prior to Schenck was George van Egmond. After Schenck's death in 1580, the see would remain vacant until Sasbold Vosmeer assumed the archbishopric in 1602. Biography The son of Georg Schenck van Toutenburg, he graduated in law at the Reichskammergericht in Speyer. After being made a priest, he became archdeacon of the Pieterskerk in Bishopric of Utrecht and priest at the Sint-Plechelmusbasiliek in Oldenzaal. He spent his time writing tracts on church law until he was promoted to the Dutch episcopate in 1559 by Philip II, who named him as the very first Archbishop of Utrecht (which was then confirmed in 1561 by Pope Pius IV). Until that time, the Bishopric of Utrecht reported to the Archbishop of Cologne. By agreement between Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Utrecht
List of bishops and archbishops of the diocese and archdioceses of Utrecht. Medieval diocese from 695 to 1580 Founders of the Utrecht diocese * * * * * Bishops * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * **'', rival bishop'' **'', rival bishop'' * * * * * * * * Archbishops * * * * Dutch Mission (1592 – 1853) Roman Catholic archdiocese since 1853 Archbishops *Johannes Zwijsen (1853–1868) *Andreas Ignatius Schaepman (1868–1882) *Petrus Matthias Snickers (1883–1895) *Henricus van de Wetering (1895–1929) * Johannes Henricus Gerardus Jansen (1930–1936) *Johannes de Jong (1936–1955) *Bernardus Johannes Alfrink (1955–1975) * Johannes Gerardus Maria Willebrands (1975–1983) *Adrianus Johannes Simonis (1983–2007) *Willem Jacobus Eijk (since 2007) Auxiliary bishops * Goswin Haex van Loenhout, O. Carm. (15 May 1469 - 31 Mar 1475) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oldenzaal
Oldenzaal (; Tweants: ''Oldnzel'') is a municipality and a city in the eastern province of Overijssel in the Netherlands. It is part of the region of Twente and is close to the German border. It received city rights in 1249. Historically, the city was part of the Hanseatic League as a subsidiary city of the fellow Hanseatic city of Deventer. Located on the A1 motorway from Amsterdam to Germany, Oldenzaal also has a rail connection to Hengelo and Bad Bentheim. As of 1 January 2019, 31,885 people lived in Oldenzaal. In the Netherlands, Oldenzaal is well known for its carnival festivities. During the carnival season Oldenzaal is known as "Boeskool-stad" which is a local dialect of the word Cabbage-town. During the main carnival weekend over 100,000 people come for the big parade showing high and mighty carnival trucks. Transportation The town is served by the Oldenzaal railway station. Notable residents * Balderic of Utrecht (897–975) Bishop of Utrecht, 918 to 975 * Henri Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
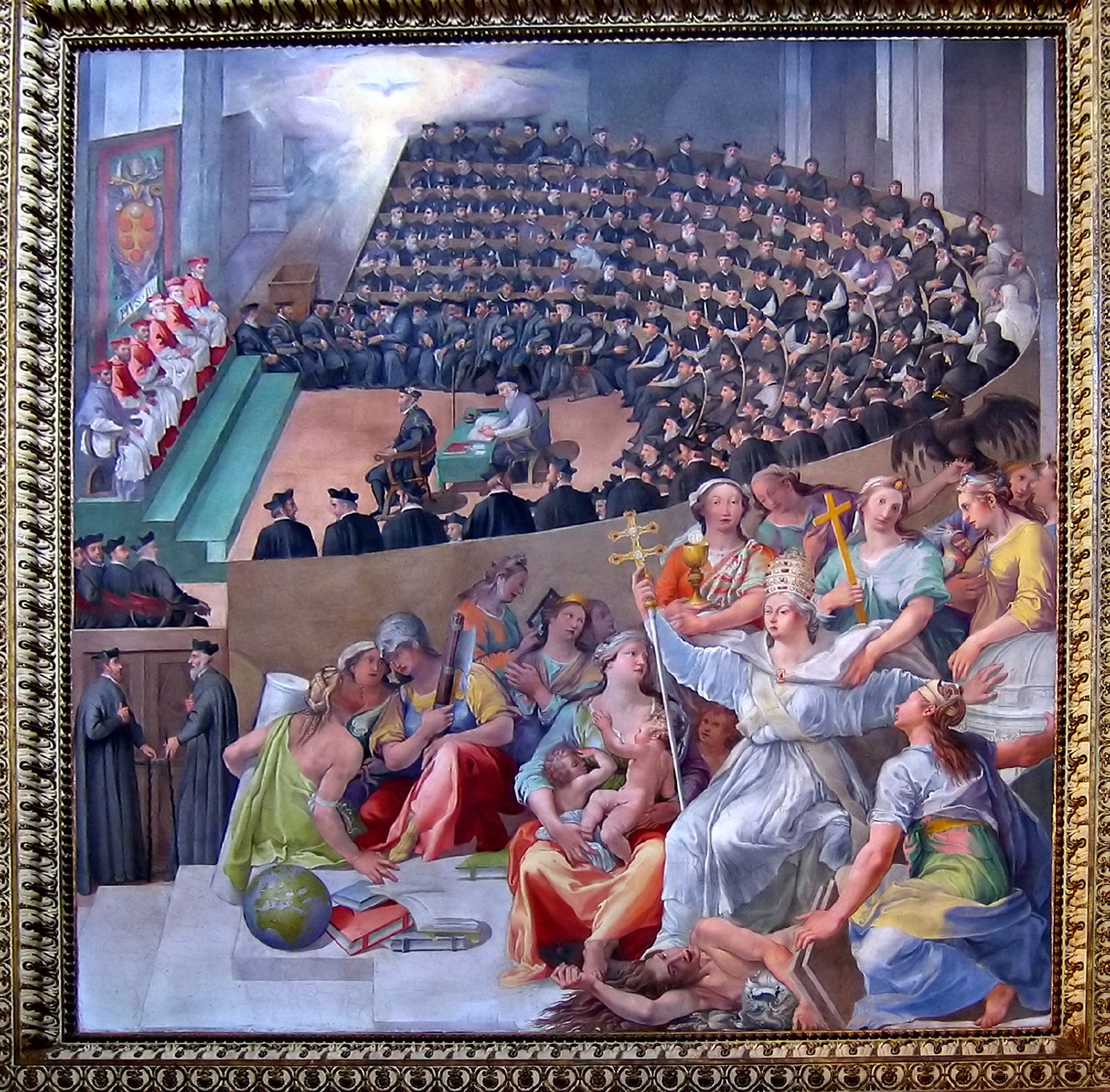
Synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word ''wikt:synod, synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word meaning "council". Originally, synods were meetings of bishops, and the word is still used in that sense in Roman Catholic Church, Catholicism, Oriental Orthodoxy and Eastern Orthodoxy. In modern usage, the word often refers to the governing body of a particular church, whether its members are meeting or not. It is also sometimes used to refer to a church that is governed by a synod. Sometimes the phrase "general synod" or "general council" refers to an ecumenical council. The word ''synod'' also refers to the standing council of high-ranking bishops governing some of the autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches. Similarly, the day-to-day governance of patriarchal and major archbishop, major arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Of Parma
Margaret of Parma (; 5 July 1522 – 18 January 1586) was Governor of the Netherlands from 1559 to 1567 and from 1578 to 1582. She was the illegitimate daughter of the then 22-year-old Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and Johanna Maria van der Gheynst. She was a Duchess of Florence and a Duchess of Parma and Piacenza by her two marriages. Biography Margaret's mother, Johanna Maria van der Gheynst, a servant of Count Charles de Lalaing, Seigneur de Montigny, was a Fleming. Margaret was brought up in Mechelen, under the supervision of two powerful Spanish and Austrian Habsburg Imperial family relatives, her great-aunt, the Archduchess Margaret of Austria, and her aunt Mary of Austria, who were successive governors of the Netherlands from 1507 to 1530 and from 1530 to 1555, respectively. Her early life followed a strict routine set forth by her father, Charles V, who used his daughter as part of his plans to secure his empire. In 1527, the year she turned five, she became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trento, Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italian Peninsula, Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described as the embodiment of the Counter-Reformation."Trent, Council of" in Cross, F. L. (ed.) ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church'', Oxford University Press, 2005 (). The Council issued condemnations of what it defined to be Heresy, heresies committed by proponents of Protestantism, and also issued key statements and clarifications of the Church's doctrine and teachings, including scripture, the biblical canon, sacred tradition, original sin, Justification (theology), justification, salvation, the Sacraments of the Catholic Church, sacraments, the Mass (liturgy), Mass, and the Veneration, veneration of saints.Wetterau, Bruce. ''World History''. New York: Henry Holt and Company, 1994. The Council met for twenty- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the '' Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X until January 1521. The Diet of Worms of May 1521 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
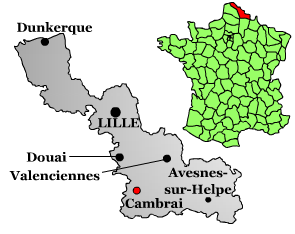
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department and in the Hauts-de-France Regions of France, region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area (France), functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechelen
Mechelen (; french: Malines ; traditional English name: MechlinMechelen has been known in English as ''Mechlin'', from where the adjective ''Mechlinian'' is derived. This name may still be used, especially in a traditional or historical context. The city's French name ' had also been used in English in the past (in the 19th and 20th century) however this has largely been abandoned. Meanwhile, the Dutch derived ' began to be used in English increasingly from late 20th century onwards, even while ''Mechlin'' remained still in use (for example a ''Mechlinian'' is an inhabitant of this city or someone seen as born-and-raised there; the term is also the name of the city dialect; as an adjective ''Mechlinian'' may refer to the city or to its dialect.) is a city and municipality in the province of Antwerp in the Flemish Region of Belgium. The municipality comprises the city of Mechelen proper, some quarters at its outskirts, the hamlets of (adjacent) and (a few kilometers away), as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
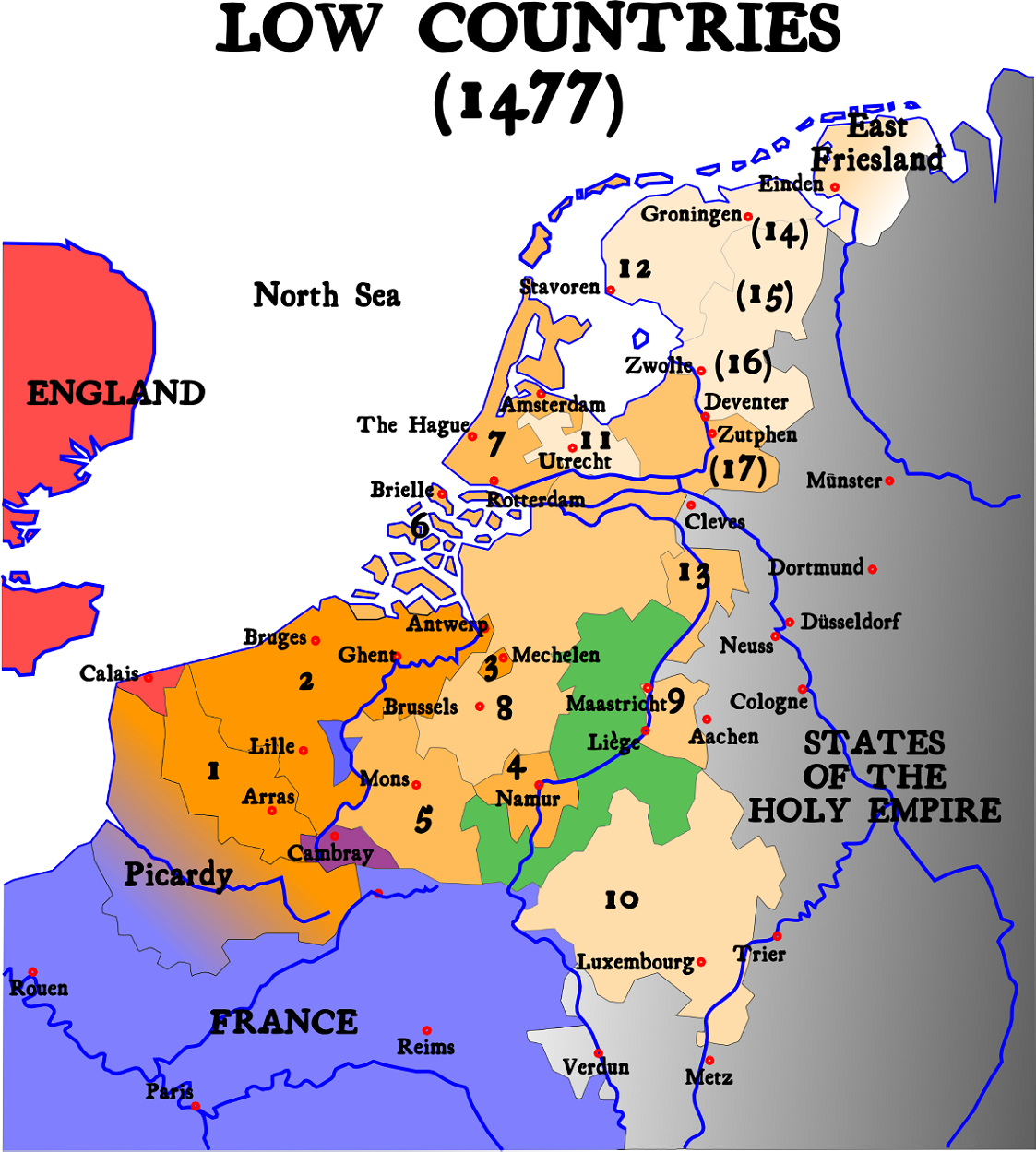
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprised: #th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) and largely ended with the conclusion of the European wars of religion in 1648. Initiated to address the effects of the Protestant Reformation, the Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort composed of apologetic and polemical documents and ecclesiastical configuration as decreed by the Council of Trent. The last of these included the efforts of Imperial Diets of the Holy Roman Empire, heresy trials and the Inquisition, anti-corruption efforts, spiritual movements, and the founding of new religious orders. Such policies had long-lasting effects in European history with exiles of Protestants continuing until the 1781 Patent of Toleration, although smaller expulsions took place in the 19th century. Such reforms included the foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Cologne
The Archbishop of Cologne is an archbishop governing the Archdiocese of Cologne of the Catholic Church in western North Rhine-Westphalia and is also a historical state in the Rhine holding the birthplace of Beethoven and northern Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany and was ''ex officio'' one of the Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire, the Elector of Cologne, from 1356 to 1801. Since the early days of the Catholic Church, there have been ninety-four bishops and archbishops of Cologne. Seven of these ninety-four retired by resignation, including four resignations which were in response to impeachment. Eight of the bishops and archbishops were coadjutor bishops before they took office. Seven individuals were appointed as coadjutors freely by the Pope. One of the ninety-four moved to the Curia, where he became a cardinal. Additionally, six of the archbishops of Cologne were chairmen of the German Bishops' Conference. Cardinal Rainer Woelki has been the Archbishop of Cologne since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)