|
Frederic Shoberl
Frederic Shoberl (1775–1853), also known as Frederick Schoberl, was an English journalist, editor, translator, writer and illustrator. Shoberl edited ''Forget-Me-Not'', the first literary annual, issued at Christmas "for 1823" and translated ''The Hunchback of Notre Dame''. Biography Shoberl was born in London in 1775, and educated at the Moravian school at the Fulneck Moravian Settlement in West Yorkshire.G. C. Boase, "Shoberl , Frederic (1775–1853)", rev. Nilanjana Banerji, ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 200retrieved 1 June 2010/ref> From 1809 he began editing Rudolph Ackermann's ''Repository of Arts'' which had just started and was only at its third edition. Ackermann was seen as the populariser of aquatint engraving and his ''Repository of Arts'' was intended to cover "arts, literature, commerce, manufactures, fashions, and politics". At the beginning of February 1814, Shoberl and Henry Colburn founded and became co-proprietors of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
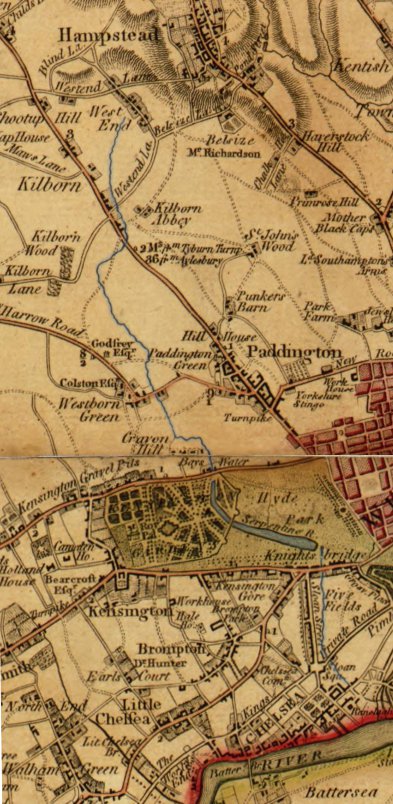
Brompton, London
Brompton, sometimes called Old Brompton, survives in name as a ward in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in London. Until the latter half of the 19th century it was a scattered village made up mostly of market gardens in the county of Middlesex. It lay south-east of the village of Kensington, abutting the parish of St Margaret's, Westminster at the hamlet of Knightsbridge to the north-east, with Little Chelsea to the south. It was bisected by the Fulham Turnpike, the main road westward out of London to the ancient parish of Fulham and on to Putney and Surrey. It saw its first parish church, Holy Trinity Brompton, only in 1829. Today the village has been comprehensively eclipsed by segmentation due principally to railway development culminating in London Underground lines, and its imposition of station names, including Knightsbridge, South Kensington and Gloucester Road as the names of stops during accelerated urbanisation, but lacking any cogent reference to local hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Adolf Krummacher
Friedrich Adolf Krummacher (July 13, 1767 – April 14, 1845) was a German Reformed theologian and a writer of devotional poetry and prose. Biography He was born in Tecklenburg, Westphalia. Having studied theology at Lingen and Halle, he became successively rector of the grammar school at Moers (1793), a professor of theology at the University of Duisburg (1800), a preacher in Kettwig (1807), ''Consistorialrath'' and superintendent in Bernburg (1812), and, after declining an invitation to the University of Bonn, pastor of the Ansgariuskirche in Bremen (1824). He died in Bremen. Literary works He was the author of many religious works, but is best known by his ''Parabeln'' (1805; 9th edition 1876; English translation 1844). In 1858, they were added to Bohn's "Illustrated Library", with 40 illustrations. *''Hymnus an die Liebe'', 1801 *''Parabeln'', 3 volumes, 1805–1817 *''Über den Geist und die Form der evangelischen Geschichte in historischer und ästhetischer Hinsicht'', 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan. It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the Nagasaki Region have been recognized and included in the UNESCO World Heritage List. Part of Nagasaki was home to a major Imperial Japanese Navy base during the First Sino-Japanese War and Russo-Japanese War. Near the end of World War II, the American atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki made Nagasaki the second and, to date, last city in the world to experience a nuclear attack (at 11:02 am, August 9, 1945 'Japan Standard Time (UTC+9)'). , the city has an estimated population of 407,624 and a population density of 1,004 people per km2. The total area is . History Nagasaki as a Jesuit port of call The first contact with Portuguese explorers occurred in 1543. An early visitor was Fernão Mendes Pinto, who came from Sagres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock company in the world, granting it a 21-year monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia. Shares in the company could be bought by any resident of the United Provinces and then subsequently bought and sold in open-air secondary markets (one of which became the Amsterdam Stock Exchange). It is sometimes considered to have been the first multinational corporation. It was a powerful company, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, strike its own coins, and establish colonies. They are also known for their international slave trade. Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Titsingh
Isaac Titsingh FRS ( January 1745 – 2 February 1812) was a Dutch diplomat, historian, Japanologist, and merchant.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Isaak Titsingh" in . During a long career in East Asia, Titsingh was a senior official of the Dutch East India Company ( nl, Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie (VOC)). He represented the European trading company in exclusive official contact with Tokugawa Japan, traveling to Edo twice for audiences with the shogun and other high bakufu officials. He was the Dutch and VOC governor general in Chinsura, Bengal.Stephen R. Platt, ''Imperial Twilight: the Opium War and the End of China's Last Golden Age'' (NY: Knopf, 2018), 166-73. Titsingh worked with his counterpart, Charles Cornwallis, who was governor general of the British East India Company. In 1795, Titsingh represented Dutch and VOC interests in China, where his reception at the court of the Qing Qianlong Emperor stood in contrast to the rebuff suffered by British diplomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illustrations Of Japan
Illustrations of Japan is a book on Japanese culture by the Dutch merchant and diplomat Isaac Titsingh. The book was first published posthumously in French under the editorship of his friends Jean-Pierre Abel-Rémusat and Heinrich Julius von Klaproth in 1820, followed by an English edition in 1822 and a Dutch edition in 1824. The book surveys Japanese history, customs, and ceremonies during the Tokugawa shogunate and is a notable early account of Japan by a Western observer. About the book The book recounts the observations of Titsingh during his stay in Dejima from 1779 to 1784 in his position as Dutch East India Company (VOC) senior official (opperhoofd). During his stay in Japan, Titsingh had the project of an overall collection on Japanese history, culture and civilization in mind. This project would be his life work and accomplishment. Therefore, he collected and translated data and wrote essays for his collection. In his perception this collection was important in o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Upcott
William Upcott (1779–1845) was an English librarian and antiquary. Life Born in Oxfordshire, he was the illegitimate son of Ozias Humphry by Delly Wickens, daughter of an Oxford shopkeeper, called Upcott from the maiden name of Humphry's mother. His father bequeathed to him his miniatures, pictures, drawings, and engravings, as well as correspondence with many leading figures. Upcott was initially a bookseller, at first an assistant of Robert Harding Evans of Pall Mall, and then of John Wright of Piccadilly. While at Wright's shop he attracted the attention of John Ireland, William Gifford, and the writers of the '' Anti-Jacobin'' who met there, and he witnessed the scuffle there between Gifford and John Wolcot, helping to eject Wolcot. When Richard Porson was made librarian of the London Institution, Upcott was appointed as his assistant (23 April 1806), and he continued in the same position under William Maltby. On 30 May 1834 he resigned his office. Upcott spent the rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Watkins (writer)
John Watkins ('' fl.'' 1792–1831) was an English miscellaneous writer, known as a biographer. He is most famous for being the author of '' An Universal Biographical and Historical Dictionary''. Life Born in Devon, he was educated at Bristol for the nonconformist ministry. Becoming dissatisfied, he conformed to the Church of England around 1786, with his friend Samuel Badcock, and for some years kept an academy in Devon. Watkins moved to London soon after beginning to write, probably about 1794. He became editor of the ''Orthodox Churchman's Magazine''. His latest preface is dated 30 May 1831. Works His first independent publication appeared in 1792, entitled ''An Essay towards the History of Bideford'', 1792. Chapter x. consists of the depositions in a trial for witchcraft held at Exeter on 14 August 1682. The work was reprinted and published at Bideford in 1883. In 1796 appeared ''The Peeper: a collection of Essays, Moral, Biographical, and Literary'' (London, 1796; 2nd edit. L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Academy
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its purpose is to promote the creation, enjoyment and appreciation of the visual arts through exhibitions, education and debate. History The origin of the Royal Academy of Arts lies in an attempt in 1755 by members of the Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce, principally the sculptor Henry Cheere, to found an autonomous academy of arts. Prior to this a number of artists were members of the Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce, including Cheere and William Hogarth, or were involved in small-scale private art academies, such as the St Martin's Lane Academy. Although Cheere's attempt failed, the eventual charter, called an 'Instrument', used to establish the Royal Academy of Arts over a decad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Wollstonecraft
Mary Wollstonecraft (, ; 27 April 1759 – 10 September 1797) was a British writer, philosopher, and advocate of women's rights. Until the late 20th century, Wollstonecraft's life, which encompassed several unconventional personal relationships at the time, received more attention than her writing. Today Wollstonecraft is regarded as one of the founding feminist philosophers, and feminists often cite both her life and her works as important influences. During her brief career, she wrote novels, treatises, a travel narrative, a history of the French Revolution, a conduct book, and a children's book. Wollstonecraft is best known for ''A Vindication of the Rights of Woman'' (1792), in which she argues that women are not naturally inferior to men, but appear to be only because they lack education. She suggests that both men and women should be treated as rational beings and imagines a social order founded on reason. After Wollstonecraft's death, her widower published a ''Memoir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Hoorn.jpg)



