|
Fraumünster Abbey
The Fraumünster (; lit. in ) is a church in Zürich which was built on the remains of a former abbey for aristocratic women which was founded in 853 by Louis the German for his daughter Hildegard. He endowed the Benedictine convent with the lands of Zürich, Uri, and the Albis forest, and granted the convent immunity, placing it under his direct authority. Today, it belongs to the Evangelical Reformed Church of the canton of Zürich and is one of the four main churches of Zürich, the others being the Grossmünster, Prediger and St. Peter's churches. History In 1045, King Henry III granted the convent the right to hold markets, collect tolls, and mint coins, and thus effectively made the abbess the ruler of the city. Emperor Frederick II granted the abbey '' Reichsunmittelbarkeit'' in 1218, thus making it territorially independent of all authority save that of the Emperor himself, and increasing the political power of the abbess. The abbess assigned the mayor, and she f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
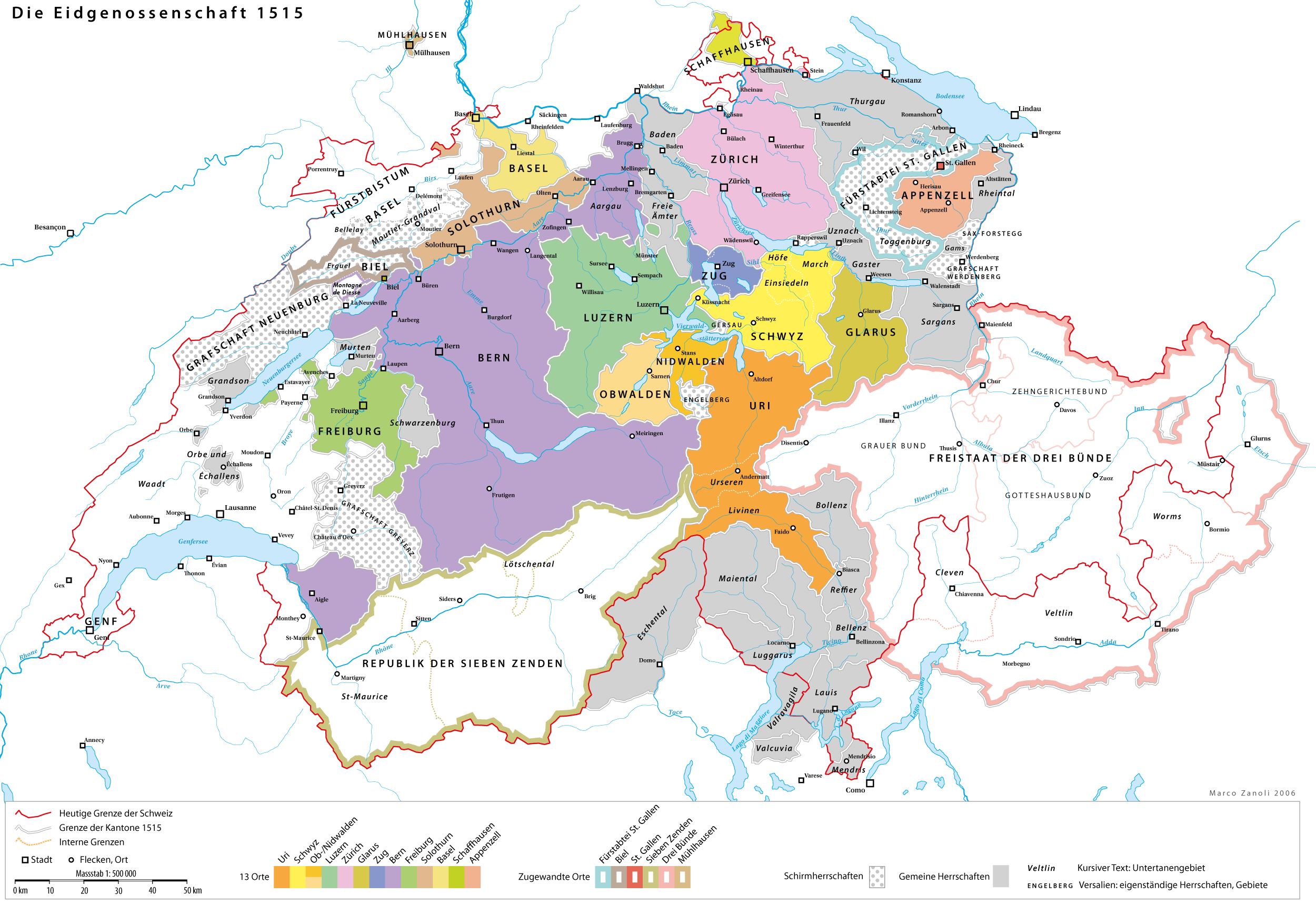
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is geographically divided among the Swiss Plateau, the Swiss Alps, Alps and the Jura Mountains, Jura; the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, whereas most of the country's Demographics of Switzerland, 9 million people are concentrated on the plateau, which hosts List of cities in Switzerland, its largest cities and economic centres, including Zurich, Geneva, and Lausanne. Switzerland is a federal republic composed of Cantons of Switzerland, 26 cantons, with federal authorities based in Bern. It has four main linguistic and cultural regions: German, French, Italian and Romansh language, Romansh. Although most Swiss are German-speaking, national identity is fairly cohesive, being rooted in a common historical background, shared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedictine
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, they are the oldest of all the religious orders in the Latin Church. The male religious are also sometimes called the Black Monks, especially in English speaking countries, after the colour of their habits, although some, like the Olivetans, wear white. They were founded by Benedict of Nursia, a 6th-century Italian monk who laid the foundations of Benedictine monasticism through the formulation of his Rule. Benedict's sister, Scholastica, possibly his twin, also became a religious from an early age, but chose to live as a hermit. They retained a close relationship until her death. Despite being called an order, the Benedictines do not operate under a single hierarchy. They are instead organized as a collection of autonomous monasteries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Reformed Church
The Protestant Church in Switzerland (PCS), formerly named Federation of Swiss Protestant Churches until 31 December 2019, is a federation of 25 member churches – 24 cantonal churches and the Evangelical-Methodist Church of Switzerland. The PCS is not a church in a theological understanding, because every member is independent with its own theological and formal organisation. It serves as a legal umbrella before the federal government and represents the church in international relations. Except for the Evangelical-Methodist Church, which covers all of Switzerland, the member churches are restricted to a certain territory. The president of the PCS is Rita Famos. History The Reformation spread primarily into the cities of Switzerland, which was then composed of loosely connected cantons. Breakthroughs began in the 1520s in Zurich under Huldrych Zwingli, in Bern in 1528 under Berchtold Haller, and in Basel in 1529 under Johannes Oecolampadius. After the death of Zwingli in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadthaus Zürich
Stadthaus is a nine-storey residential building in Hackney, London, completed in 2009. With nine stories (30 meters/98 feet), it was considered the second tallest timber residential building made of wood in the world at the time of its construction, after the Forte apartment complex in Melbourne, Australia. It was designed in collaboration between architects Waugh Thistleton, structural engineers Techniker, and timber panel manufacturer KLH. Stadthaus is the first high-density housing building to be built from pre-fabricated cross-laminated timber panels. It is the first building in the world of this height to construct not only load-bearing walls and floor slabs but also stair and lift cores entirely from timber. The record was later broken by Mjøstårnet in 2019 and the Ascent MKE high-rise apartment-building in 2022. Ecological aspects Timber stores 0.8t of carbon dioxide within 1 cubic metre and is a replenishable material. In comparison, the production of both concret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katharina Von Zimmern
Katharina von Zimmern (1478 – 17 August 1547), also known as the imperial abbess of Zürich and Katharina von Reischach, was the last abbess of the Fraumünster Abbey in Zürich. Early life Katharina von Zimmern was born in 1478 in Messkirch into the rich southern German noble family of baron Hans Werner von Zimmern and countess Margarethe von Oettingen. Katharina was the fourth girl and had four further brothers and two sisters. Her father loved hunting, played several musical instruments, and was in the service of the Duke Sigmund of Tyrol. In 1488 he fell from the favour of Emperor Frederick III due to intrigues and was forced to flee with his family. Katharina survived an adventurous escape with her mother and some siblings to Weesen on Walensee lakeshore. Probably there she met in 1490 the 6-year-old Ulrich Zwingli, who had been given to his uncle, the parish priest in charge. Kathrina's father tried to accommodate her and her older sister in the Fraumünster A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a Swiss Christian theologian, musician, and leader of the Reformation in Switzerland. Born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenaries, Swiss mercenary system, he attended the University of Vienna and the University of Basel, a scholarly center of Renaissance humanism. He continued his studies while he served as a pastor in Glarus and later in Einsiedeln, where he was influenced by the writings of Erasmus. During his tenures at Basel and Einsiedeln, Zwingli began to familiarize himself with many criticisms Christian institutions were facing regarding their reform guidance and garnered scripture which aimed to address such criticisms. IIn 1519, Zwingli became the (people's priest) of the Grossmünster in Zurich where he began to preach ideas on reform of the Catholic Church. In his first public controversy in 1522, he attacked the Fasting and abstinence in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformation In Zürich
The Reformation in Zürich was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrates of the city of Zürich and the princess abbess Katharina von Zimmern of the Fraumünster Abbey, and the population of the city of History of Zürich, Zürich and agriculture-oriented population of the present Canton of Zürich in the early 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matters in Zürich and spread to several other Cantons of Switzerland, cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy, and thus initiated the Reformation in Switzerland. Prologue At the time of the reformation, the city of Zürich was mainly dominated by the ancient families of Zürich and the guild representatives in the ''Kleiner Rat'' and ''Grosser Rat.'' The ''Kleiner Rat'' was equivalent to the executive branch of government. After about the 1490s, the ''Grosser Rat'' was mainly an equivalent of present-day ''committees'' to assist. Those dominating Zürich supported, in the lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisabeth Of Wetzikon
Elisabeth of Wetzikon (1235 – 1298 in Zürich) was imperial abbess of the Fraumünster abbey in Zürich from 1270 until 1298, when the abbey was at the height of its power, having extensive properties reaching well into Central Switzerland (governing for example the canton of Uri) and political authority over the city of Zurich: Elisabeth appointed the mayor of Zurich and his deputy, she was the supreme judge of the city, and she collected the trade taxes (tariffs). There are 170 surviving documents containing her name, some of them with her seal. In a document dated 25 January 1274, Rudolph of Habsburg granted her the right to mint coins. Elisabeth was a daughter of the Freiherr Ulrich von Wetzikon. She is first mentioned in 1265 as a nun of the Fraumünster abbey. Mentions in famous works of literature Elisabeth of Wetzikon is mentioned in several famous works of literature: * Johannes Hadlaub in the «Codex Manesse»: ''… von Zürich diu vürstin …'' (''of Zurich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a Municipal corporation, municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well as the means by which a mayor is elected or otherwise mandated. Depending on the system chosen, a mayor may be the chief executive officer of the municipal government, may simply chair a multi-member governing body with little or no independent power, or may play a solely ceremonial role. A mayor's duties and responsibilities may be to appoint and oversee municipal managers and employees, provide basic governmental services to constituents, and execute the laws and ordinances passed by a municipal governing body (or mandated by a state, territorial or national governing body). Options for selection of a mayor include direct election by the public, or selection by an elected governing council or board. The term ''mayor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsunmittelbarkeit
In the Holy Roman Empire, imperial immediacy ( or ) was the status of an individual or a territory which was defined as 'immediate' () to Emperor and Empire () and not to any other intermediate authorities, while one that did not possess that status was defined as 'mediate' (). The possession of this imperial immediacy granted a constitutionally unique form of territorial authority known as "territorial superiority" () which had nearly all the attributes of sovereignty, but fell short of true sovereignty since the rulers of the Empire remained answerable to the Empire's institutions and basic laws. In the early modern period, the Empire consisted of over 1,800 immediate territories, ranging in size from quite large such as Austria, Bavaria, Saxony, and Brandenburg, down to the several hundred tiny immediate estates of the Imperial knights of only a few square kilometers or less, which were by far the most numerous. Acquisition The criteria of immediacy varied and classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predigerkirche Zürich
Predigerkirche is one of the four main churches of the old town of Zürich, Switzerland, besides Fraumünster, Grossmünster and St. Peter. First built in 1231 AD as a Romanesque church of the then Dominican ''Predigerkloster'', the Basilica was converted in the first half of the 14th century, the choir between 1308 and 1350 rebuilt, and a for that time unusual high bell tower was built, regarded as the highest Gothic edifice in Zürich. History Located nearby the medieval ''Neumarkt'' quarter, the church that commonly is named ''Predigerkirche'' was mentioned for the first time in 1234 AD as the Predigerkloster monastery of the Dominican Order. The first Dominican friars settled, according to the chronicler Heinrich Brennwald, outside of the city walls of medieval Zürich at Stadelhofen in 1230, and the construction of a new convent in Zürich was first mentioned in 1231. Initially, against the resistance of the Grossmünster canons, the Dominican's inclusion in Zürich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grossmünster
The Grossmünster (; "great minster") is a Romanesque-style Protestant church in Zürich, Switzerland. It is one of the four major churches in the city (the others being the Fraumünster, Predigerkirche, and St. Peterskirche). Its congregation forms part of the Evangelical Reformed Church of the Canton of Zürich. The core of the present building near the banks of the Limmat was constructed on the site of a Carolingian church, which was, according to legend, originally commissioned by Charlemagne. Construction of the present structure commenced around 1100 and it was inaugurated around 1220. The Grossmünster was a monastery church, vying for precedence with the Fraumünster across the Limmat throughout the Middle Ages. According to legend, the Grossmünster was founded by Charlemagne, whose horse fell to its knees over the tombs of Felix, Regula and Exuperantius, Zürich's patron saints. The legend helps support a claim of seniority over the Fraumünster, which was founded b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |