|
François Vernadat
François B. Vernadat (born 1954) is a French and Canadian computer scientist, who has contributed to Enterprise Modelling, Integration and Networking over the last 25 years specialising in enterprise architectures, business process modelling, information systems design and analysis, systems integration and interoperability and systems analysis using Petri nets. Biography F. Vernadat studied from 1973 until 1981 at the University of Clermont, France, where received a master's degree in Electronics and Automatic Control and a PhD in 1981.Arturo Molina et al. (1998). ''Handbook of Life Cycle Engineering: Concepts, Models, and Technologies''. p.225. He has been a research officer first at the National Research Council of Canada (NRCC), Ottawa, from 1981 until 1988, and then at Institut National de Recherche en Informatique et Automatique (INRIA), France, until Sept. 1995. From 1995 until 2001 he has been a professor at the University of Metz in automatic control and industrial eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Scientist
A computer scientist is a person who is trained in the academic study of computer science. Computer scientists typically work on the theoretical side of computation, as opposed to the hardware side on which computer engineers mainly focus (although there is overlap). Although computer scientists can also focus their work and research on specific areas (such as algorithm and data structure development and design, software engineering, information theory, database theory, computational complexity theory, numerical analysis, programming language theory, computer graphics, and computer vision), their foundation is the theoretical study of computing from which these other fields derive. A primary goal of computer scientists is to develop or validate models, often mathematical, to describe the properties of computational systems ( processors, programs, computers interacting with people, computers interacting with other computers, etc.) with an overall objective of discoverin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Engineering
Enterprise engineering is the body of knowledge, principles, and practices used to design all or part of an enterprise. R.E. Giachetti (2010). ''Design of Enterprise Systems: Theory, Methods, and Architecture''. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL. An enterprise is a complex socio-technical system that comprises people, information, and technology that interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. One definition is: "an enterprise life-cycle oriented discipline for the identification, design, and implementation of enterprises and their continuous evolution", supported by enterprise modelling. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, material flows, and organizational structure. Jan Dietz (2006). ''Enterprise Ontology - Theory and Methodology''. Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. Enterprise engineering may focus on the design of the enterprise as a whole, or on the design and integration of certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Modelling Experts
Enterprise (or the archaic spelling Enterprize) may refer to: Business and economics Brands and enterprises * Enterprise GP Holdings, an energy holding company * Enterprise plc, a UK civil engineering and maintenance company * Enterprise Products, a natural gas and crude oil pipeline company * Enterprise Records, a record label * Enterprise Rent-A-Car, a car rental Provider **Enterprise Holdings, the parent company General * Business, economic activity done by a businessperson * Big business, larger corporation commonly called "enterprise" in business jargon (excluding small and medium-sized businesses) * Company, a legal entity practicing a business activity * Enterprises in the Soviet Union, the analog of "company" in the former socialist state * Enterprise architecture, a strategic management discipline within an organization * Enterprise Capital Fund, a type of venture capital in the UK * Entrepreneurship, the practice of starting new organizations, particularly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Doumeingts
Guy Doumeingts (born 1938) is a French engineer, Emeritus professor at the University of Bordeaux 1 and former Director of "Laboratoire d’Automatique, Productique Signal et Image" control theory, known for the development of the GRAI method and his contributions to the field of Enterprise modelling. Biography Doumeingts received his MS at the University of Bordeaux 1, where in 1984 he also received his PhD in Control Theory with the thesis, entitled ''La Méthode GRAI''. Doumeingts spend his academic career at the University Bordeaux I, where he was appointed professor and initiated and directed the GRAI/LAP (Laboratory of Automation and Productics). He chaired the Technical Committee on Computer Application in Technology at the IFIP (International Federation for Information Processing), and was member of the Editorial Board of several journals. In 2012 Doumeingts was elected General Manager of INTEROP-VLab (International Virtual Laboratory for Enterprise Interoperability), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Kosanke
Kurt Kosanke (born ca. 1945) is a German engineer, retired IBM manager, director of the AMICE Consortium and consultant, known for his work in the field of enterprise engineering, Enterprise integration and CIMOSA.Arturo Molina, José M. Sánchez, Andrew Kusiak (1998) ''Handbook of Life Cycle Engineering: Concepts, Models and Technologies''. p. 234 Life and work Kosanke obtained his Engineering degree from the Physikalisch Technische Lehranstalt in Lübeck, Germany, nowadays the Private Berufsfachschule PTL Wedel. He started his career in research and development at IBM Deutschland in Böblingen working on the instrument development of optical printers and large-scale displays. In the 4 years at IBM USA he worked on production control, material logistics, and back in Germany focussed on manufacturing research and simulation. In 1984 Kosanke started participating in the ESPRIT AMICE project as IBM Deutschland representative, focussing on enterprise modelling and CIM Open Systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Engineering
Industrial engineering is an engineering profession that is concerned with the optimization of complex processes, systems, or organizations by developing, improving and implementing integrated systems of people, money, knowledge, information and equipment. Industrial engineering is central to manufacturing operations. Industrial engineers use specialized knowledge and skills in the mathematical, physical and social sciences, together with the principles and methods of engineering analysis and design, to specify, predict, and evaluate the results obtained from systems and processes.Salvendy, Gabriel. Handbook of Industrial Engineering. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 3rd edition p. 5 There are several industrial engineering principles followed in the manufacturing industry to ensure the effective flow of the systems, processes and operations. This includes Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, Information Systems, Process Capability and Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control (DMAIC). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Integrated Manufacturing
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each part. Manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone by the integration of computers. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as ''flexible design and manufacturing''. Overview # Computer-integrated manufacturing is used in automotive, aviation, space, and ship building industries. # The term "computer-integrated manufacturing" is both a method of manufacturing and the name of a computer-automated system in which individual engineering, production, marketing, and support functions of a manufacturing enterprise are organized. # In a CIM system functional areas such as design, analysis, planning, purchasing, cost accounting, inventory control, and distribution are linked through the computer with fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Systems Design
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random, and any observable pattern in any medium can be said to convey some amount of information. Whereas digital signals and other data use discrete signs to convey information, other phenomena and artifacts such as analog signals, poems, pictures, music or other sounds, and currents convey information in a more continuous form. Information is not knowledge itself, but the meaning that may be derived from a representation through interpretation. Information is often processed iteratively: Data available at one step are processed into information to be interpreted and processed at the next step. For example, in written text each symbol or letter conveys information relevant to the word it is part of, each word conveys information relevant to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
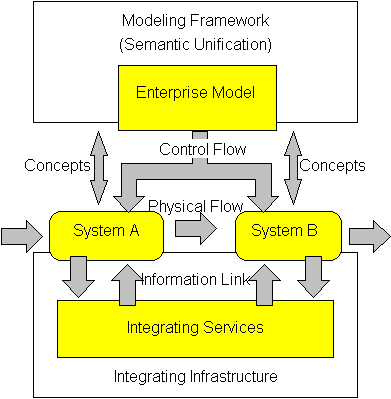
Enterprise Integration
Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments. It is a concept in enterprise engineering to provide the relevant information and thereby enable communication between people, machines and computers and their efficient co-operation and co-ordination. The Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) framework defined by the IFAC/IFIP Task Force provides the necessary guidance of the modelling process, see figure, and enables semantic unification of the model contents as well. The framework identifies the set of components necessary and helpful for enterprise modelling. The general concepts identified and defined in the reference architecture consist of life cycle, life history, model views among others. These concept help the user to create and maintain the process model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Modelling
Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization. It deals with the process of understanding an organization and improving its performance through creation and analysis of enterprise models. This includes the modelling of the relevant business domain (usually relatively stable), business processes (usually more volatile), and uses of information technology within the business domain and its processes. Overview Enterprise modelling is the process of building models of whole or part of an enterprise with process models, data models, resource models and/or new ontologies etc. It is based on knowledge about the enterprise, previous models and/or reference models as well as domain ontologies using model representation languages. F.B. Vernadat (1997)Enterprise Modelling Languages ICEIMT'97 Enterprise Integration - Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |