|
Frankish Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperator Germanorum, german: Römisch-deutscher Kaiser, lit, Roman-German emperor), was the ruler and head of state of the Holy Roman Empire. The title was held in conjunction with the title of king of Italy (''Rex Italiae'') from the 8th to the 16th century, and, almost without interruption, with the title of king of Germany (''Rex Teutonicorum'', lit. "King of the Teutons") throughout the 12th to 18th centuries. The Holy Roman Emperor title provided the highest prestige among medieval Roman Catholic monarchs, because the empire was considered by the Roman Catholic Church to be the only successor of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. Thus, in theory and diplomacy, the emperors were considered ''primus inter par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-headed Eagle
In heraldry and vexillology, the double-headed eagle (or double-eagle) is a charge (heraldry), charge associated with the concept of Empire. Most modern uses of the symbol are directly or indirectly associated with its use by the late Byzantine Empire, originally a dynastic emblem of the Palaiologos dynasty, Palaiologoi. It was adopted during the Late Medieval to Early Modern period in the Holy Roman Empire on the one hand, and in Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox principalities (Kingdom of Serbia (medieval), Serbia and Tsardom of Russia, Russia) on the other, representing an heraldic augmentation, augmentation of the (single-headed) eagle (heraldry), eagle or ''Aquila (Roman), Aquila'' associated with the Roman Empire. In a few places, among them the Holy Roman Empire and Russia, the motif was further augmented to create the less prominent triple-headed eagle. The motif has predecessors in Bronze Age art, found in Illyria, Mycenaean Greece, and in the Ancient Near East, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz in the Austrian Empire (modern-day Slavkov u Brna in the Czech Republic). The decisive victory of Napoleon's Grande Armée at Austerlitz brought the War of the Third Coalition to a rapid end, with the Treaty of Pressburg signed by the Austrians later in the month. The battle is often cited as a tactical masterpiece, in the same league as other historic engagements like Cannae or Gaugamela.Farwell p. 64. "Austerlitz is generally regarded as one of Napoleon's tactical masterpieces and has been ranked as the equal of Arbela, Cannae, and Leuthen."Dupuy p. 102 After eliminating an Austrian army during the Ulm Campaign, French forces seized Vienna in November 1805. The Austrians avoided further conflict until the arrival of the Russians bolster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Habsburg-Lorraine
The House of Habsburg-Lorraine (german: Haus Habsburg-Lothringen) originated from the marriage in 1736 of Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis III, Duke of Lorraine and Bar, and Maria Theresa, Maria Theresa of Austria, later successively List of Bohemian monarchs, Queen of Bohemia, Queen of Hungary, List of rulers of Croatia, Queen of Croatia and Archduchess of Austria. Its members are the legitimate surviving line of both the House of Habsburg and the House of Lorraine, inheriting their patrimonial possessions and Vocation#Senses, vocation to the Empire from their Matrilineality, female ancestress of the House of Habsburg and from the Patrilineality, male line of the House of Lorraine. The branch of Count of Vaudémont, Vaudemont and House of Guise, Guise from the House of Lorraine become the major branch after a brief interlude in 1453–1473, when the duchy passed in right of Charles I, Duke of Bourbon, Charles de Bourbon's daughter to her husband John II, Duke o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
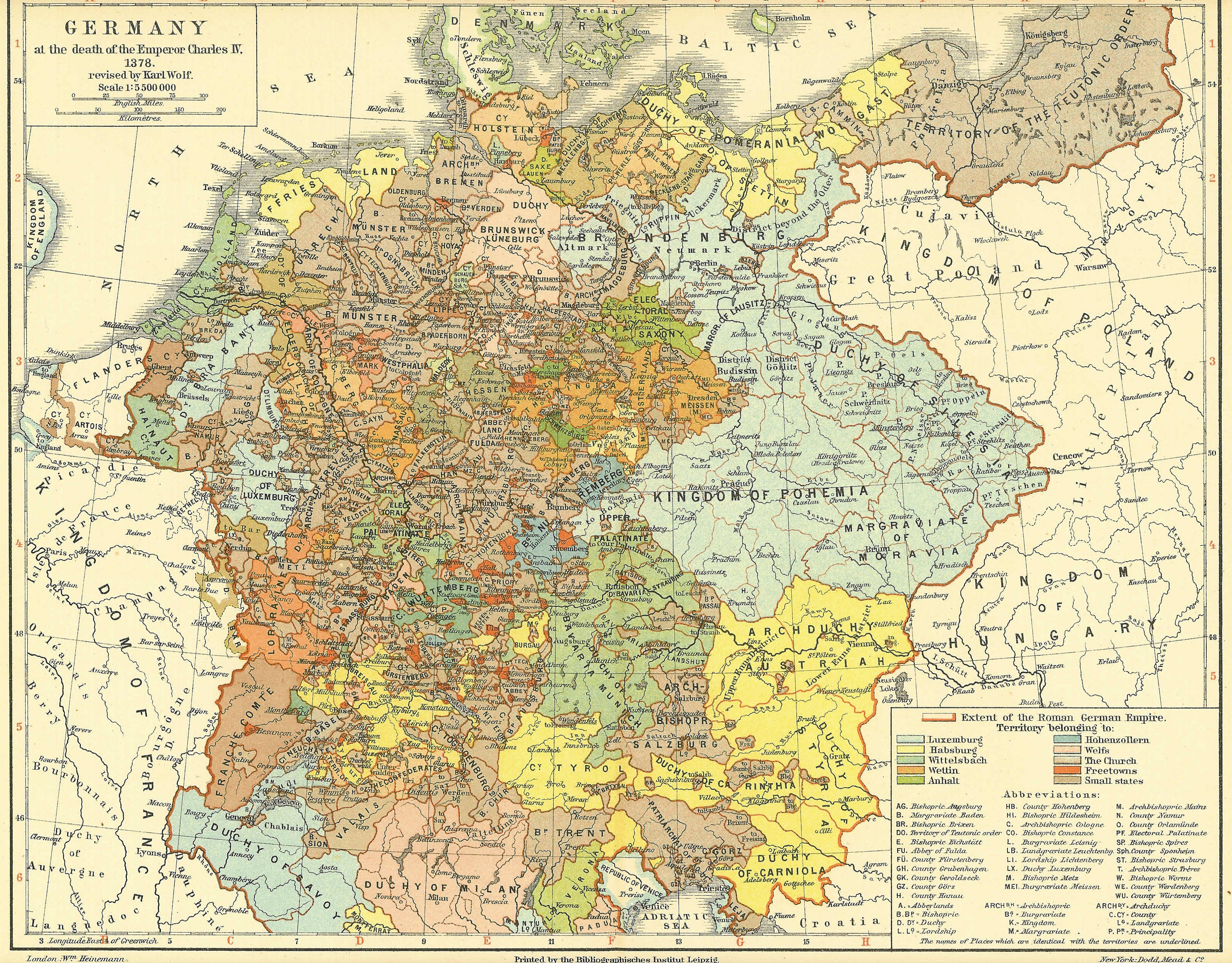
Interregnum (Holy Roman Empire)
In the Holy Roman Empire, the Great Interregnum (so-called to distinguish it from the shorter period between 924 and 962) was a period of time following the death of Frederick II where the succession of the Holy Roman Empire was contested and fought over between pro- and anti-Hohenstaufen factions. Starting around 1250 with the death of Frederick II, conflict over who was the rightful emperor and King of the Romans would continue into the 1300s until Charles IV of Luxembourg was elected emperor and secured succession for his son Wenceslaus. This period saw a multitude of emperors and kings be elected or propped up by rival factions and princes, with many kings and emperors having short reigns or reigns that became heavily contested by rival claimants. The long-lasting effects of the Interregnum were primarily the end of centralization of the imperial monarchy and the fragmentation of power towards the princes and prince-electors. The efforts of the Houses of Welf and Hohenstaufen t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salian Dynasty
The Salian dynasty or Salic dynasty (german: Salier) was a dynasty in the High Middle Ages. The dynasty provided four kings of Germany (1024–1125), all of whom went on to be crowned Holy Roman emperors (1027–1125). After the death of the last Ottonian emperor in 1024, the Kingdom of Germany and later the entire Holy Roman Empire passed to Conrad II, a Salian. He was followed by three more Salian rulers: Henry III, Henry IV, and Henry V. They established their monarchy as a major European power. The Salian dynasty developed a permanent administrative system based on a class of public officials answerable to the crown. Origins and name Modern historians suppose that the Salians descended from the Widonids, a prominent noble kindred emerging in the 7th century. Their estates were located at the confluence of rivers Moselle and Saar and they supported the Carolingians. The Widonids' eastward expansion towards the river Rhine started after they founded Hornbach Abbey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottonian Dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty (german: Ottonen) was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman Emperors named Otto, especially its first Emperor Otto I. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German stem duchy of Saxony. The family itself is also sometimes known as the Liudolfings (), after its earliest known member Count Liudolf (d. 866) and one of its most common given names. The Ottonian rulers were successors of the Germanic king Conrad I, who was the only Germanic king to rule in East Francia after the Carolingian dynasty and before this dynasty. The Ottonians are associated with the notable military success that transformed the political situation in contemporary Western Europe: "It was the success of the Ottonians in molding the raw materials bequeathed to them into a formidable military machine that made possible the establishment of Germany as the preeminent kingdom in Europe from the tenth th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire. From the 13th century onwards, the prince-electors had the privilege of electing the monarch who would be crowned by the pope. After 1508, there were no imperial coronations and the election was sufficient. Charles V (elected in 1519) was the last emperor to be crowned (1530); his successors were elected emperors by the electoral college, each being titled "Elected Emperor of the Romans" (german: erwählter Römischer Kaiser; la, electus Romanorum imperator). The dignity of elector carried great prestige and was considered to be second only to that of king or emperor. The electors held exclusive privileges that were not shared with other princes of the Empire, and they continued to hold their original titles alongside that of elector. The heir apparent to a secular prince-ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elective Monarchy
An elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by an elected monarch, in contrast to a hereditary monarchy in which the office is automatically passed down as a family inheritance. The manner of election, the nature of candidate qualifications, and the electors vary from case to case. Historically, it was common for elective monarchies to transform into hereditary ones over time or for hereditary ones to acquire at least occasional elective aspects. Evolution Many, if not most, kingdoms were officially elective historically, though the candidates were typically only from the family of the deceased monarch. Eventually, however, most elected monarchies introduced hereditary succession, guaranteeing that the title and office stayed within the royal family and specifying, more or less precisely, the order of succession. Today, almost all monarchies are hereditary monarchies in which the monarchs come from one royal family with the office of sovereign being passed from one family member to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The dynasty consolidated its power in the 8th century, eventually making the offices of mayor of the palace and '' dux et princeps Francorum'' hereditary, and becoming the ''de facto'' rulers of the Franks as the real powers behind the Merovingian throne. In 751 the Merovingian dynasty which had ruled the Germanic Franks was overthrown with the consent of the Papacy and the aristocracy, and Pepin the Short, son of Martel, was crowned King of the Franks. The Carolingian dynasty reached its peak in 800 with the crowning of Charlemagne as the first Emperor of the Romans in the West in over three centuries. His death in 814 began an extended period of fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire and decline that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocracy
Autocracy is a system of government in which absolute power over a state is concentrated in the hands of one person, whose decisions are subject neither to external legal restraints nor to regularized mechanisms of popular control (except perhaps for the implicit threat of a coup d'état or other forms of rebellion). In earlier times, the term ''autocrat'' was coined as a favorable description of a ruler, having some connection to the concept of "lack of conflicts of interests" as well as an indication of grandeur and power. This use of the term continued into modern times, as the Russian Emperor was styled "Autocrat of all the Russias" as late as the early 20th century. In the 19th century, Eastern and Central Europe were under autocratic monarchies within the territories of which lived diverse peoples. Autocracy is the most common and durable regime type since the emergence of the state. History and etymology Autocracy comes from the Ancient Greek ''autos'' (Greek: αὐ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |